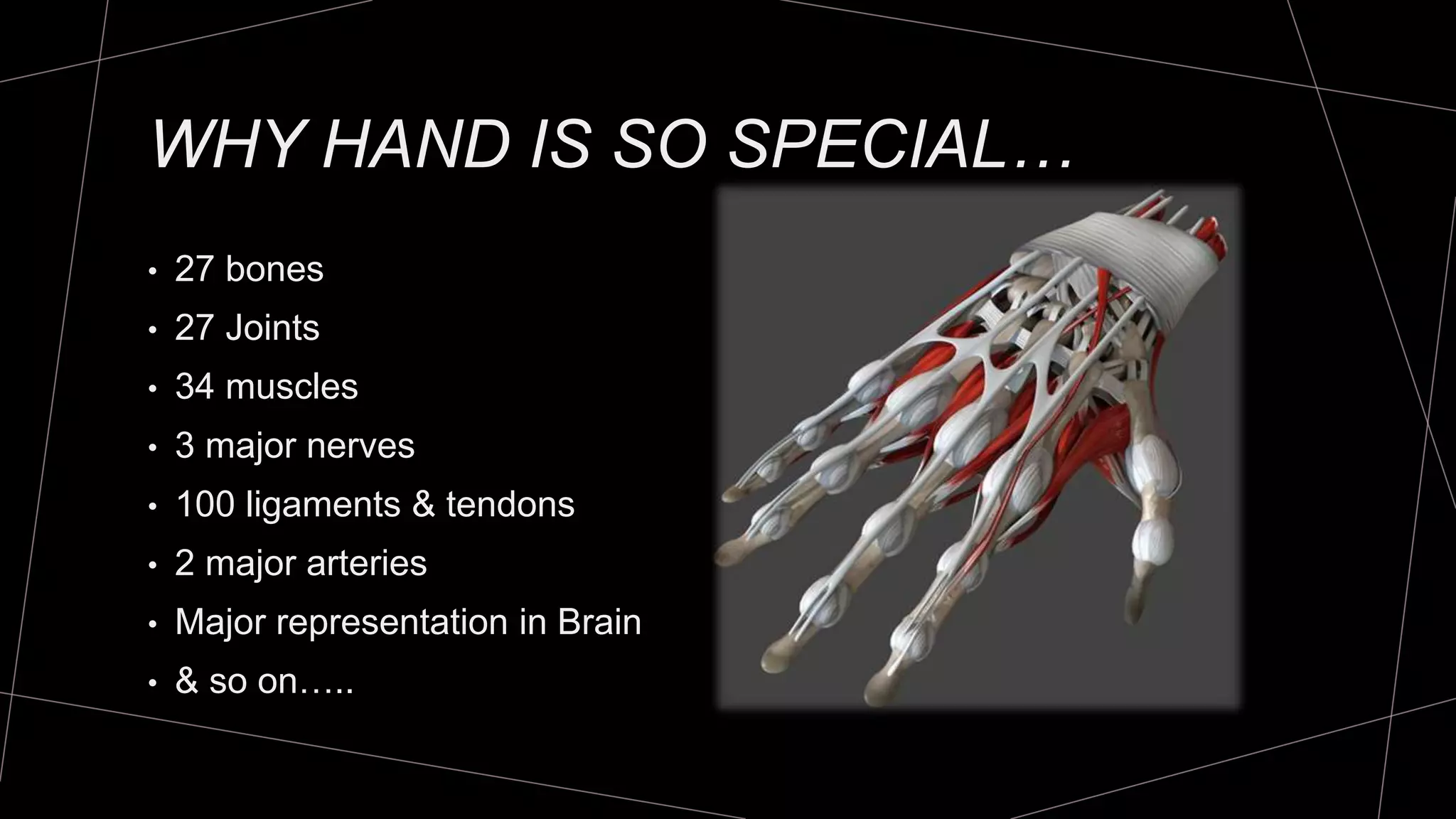
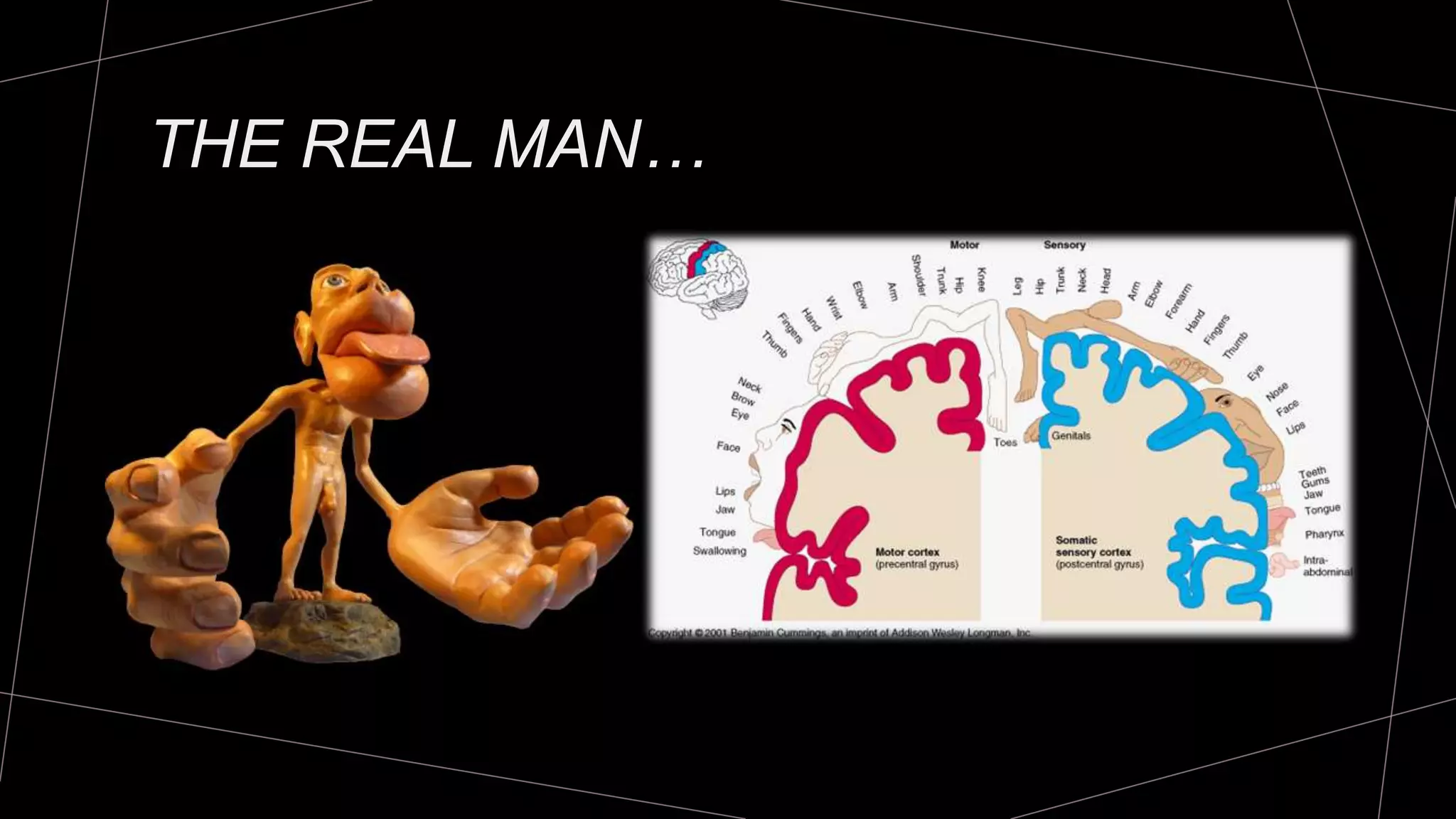
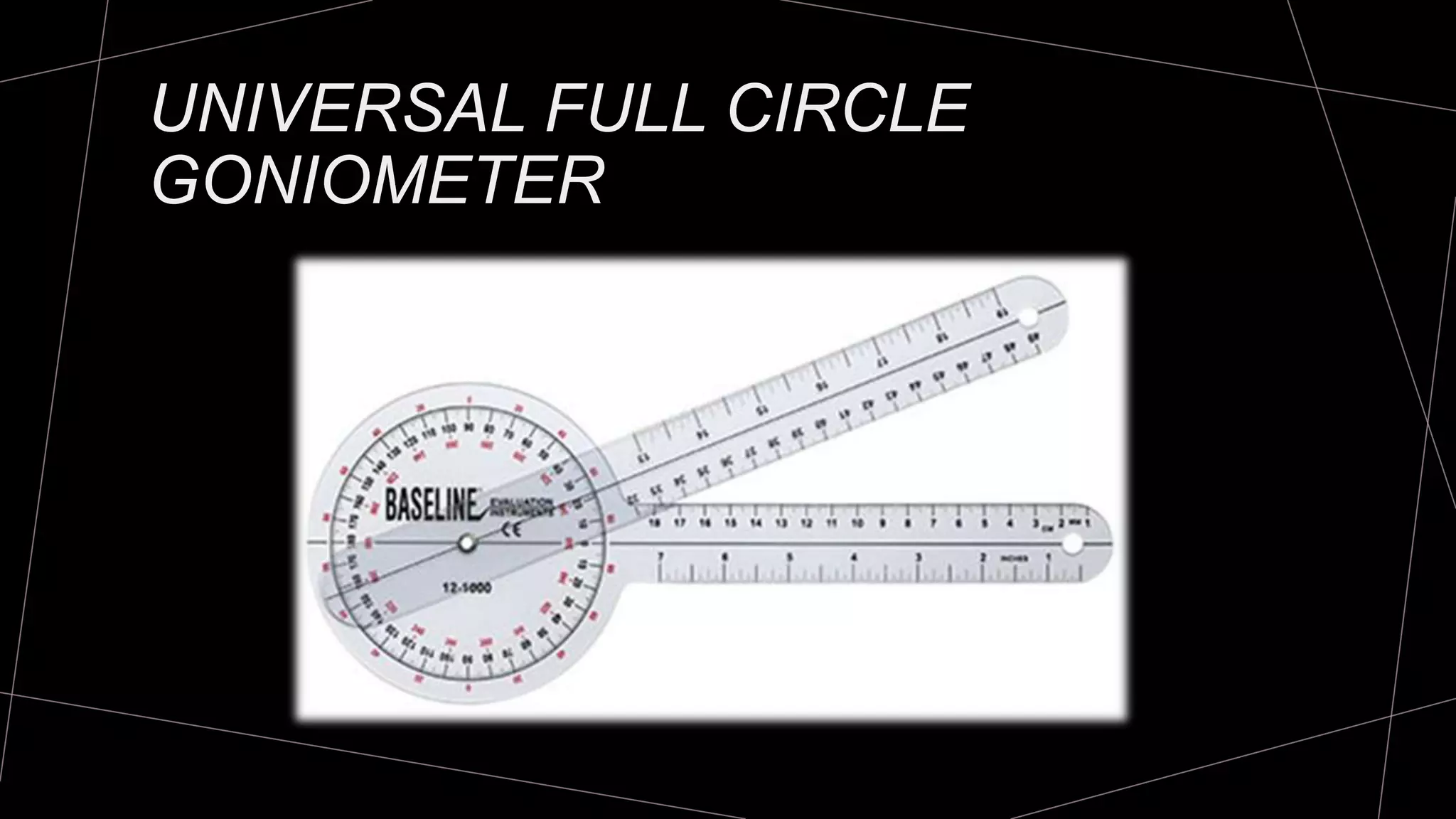
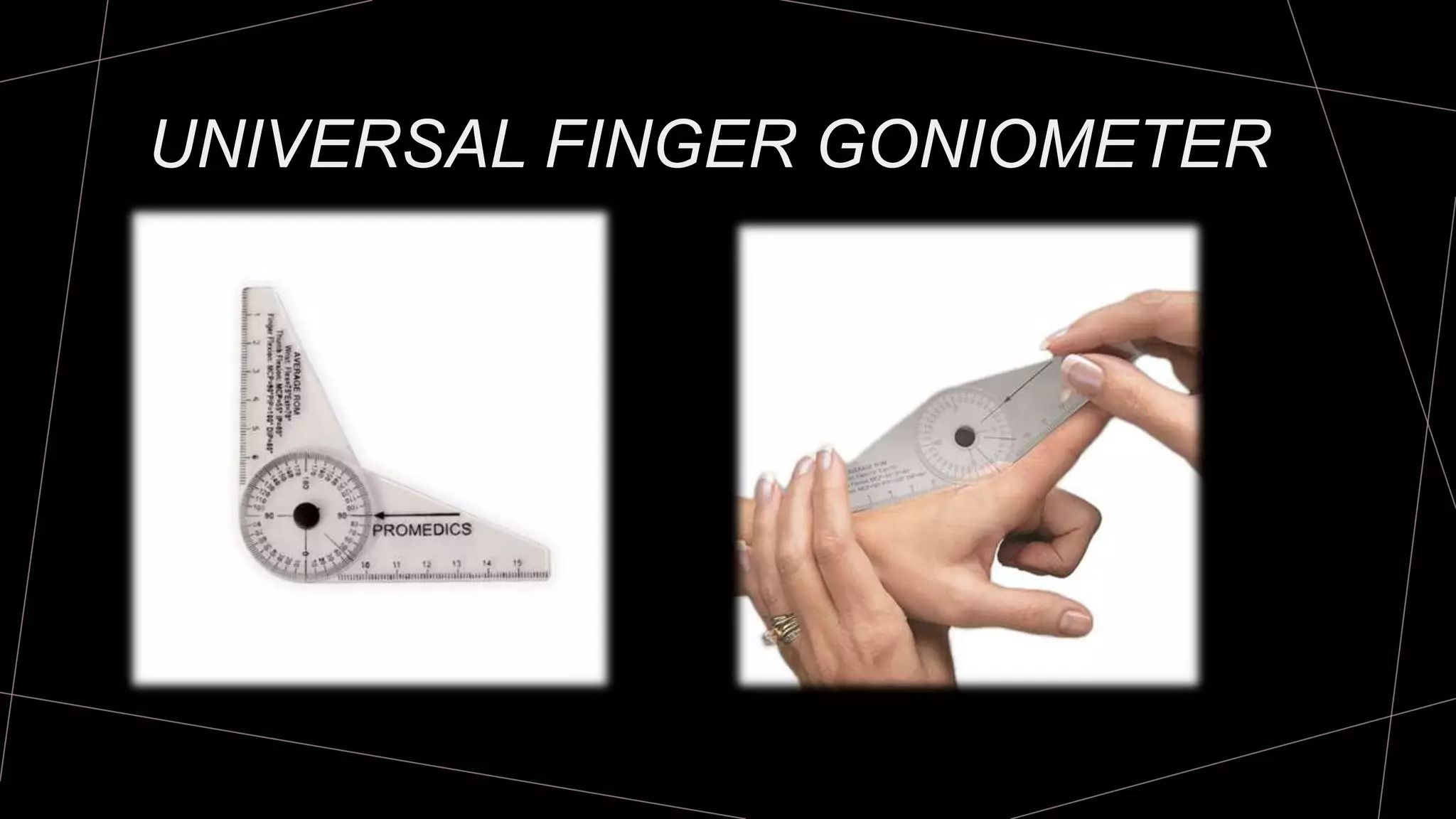
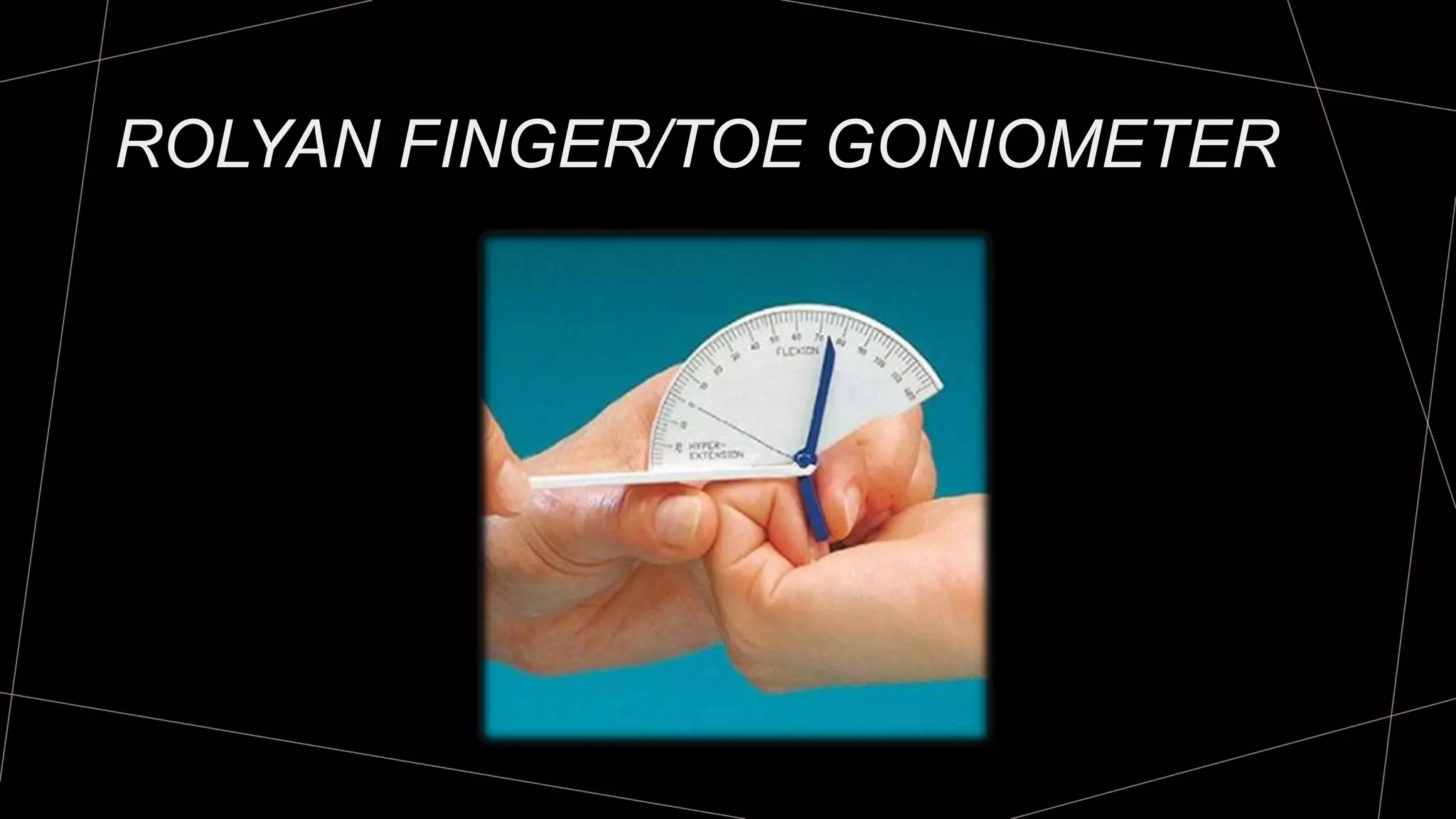
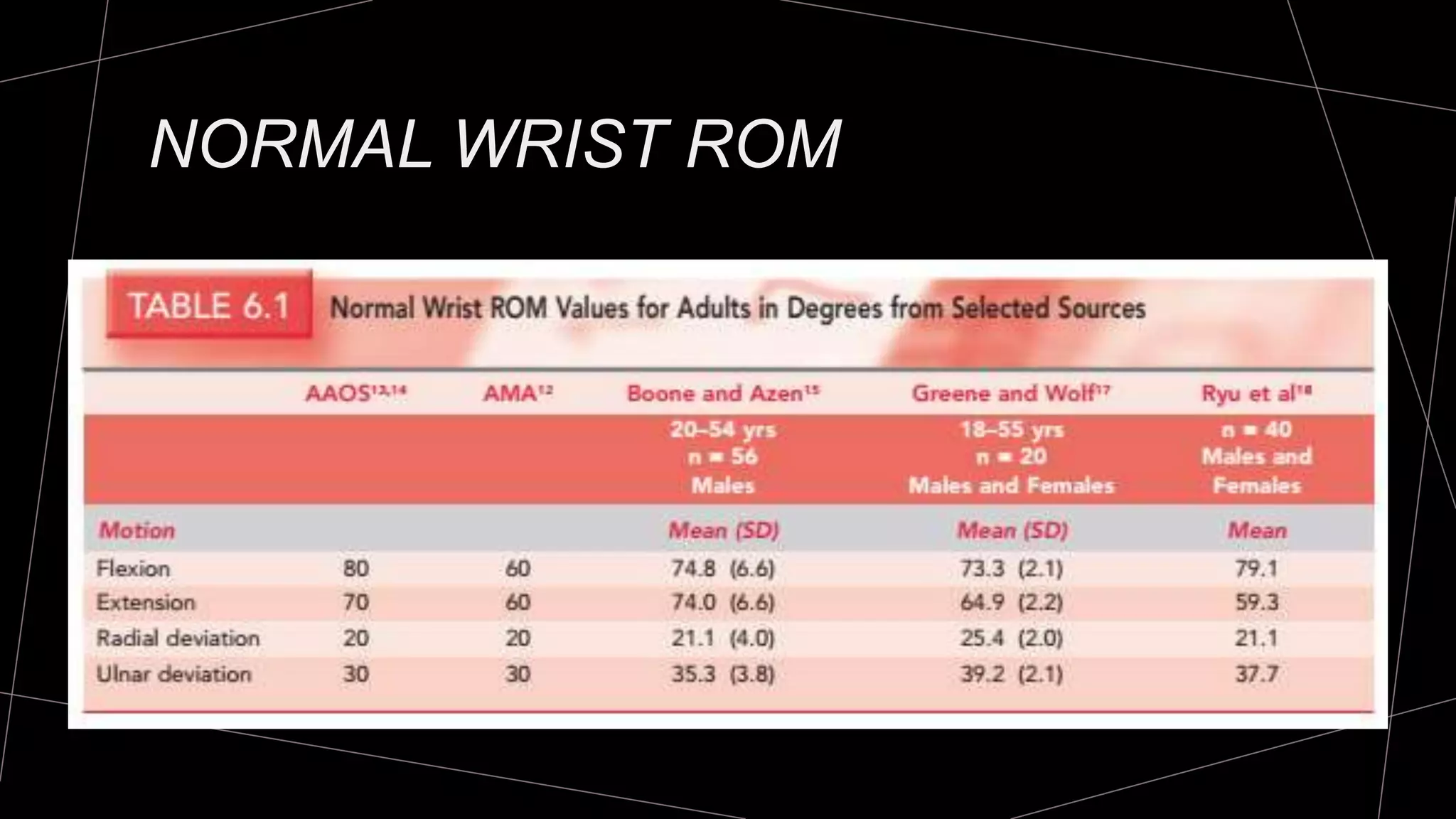
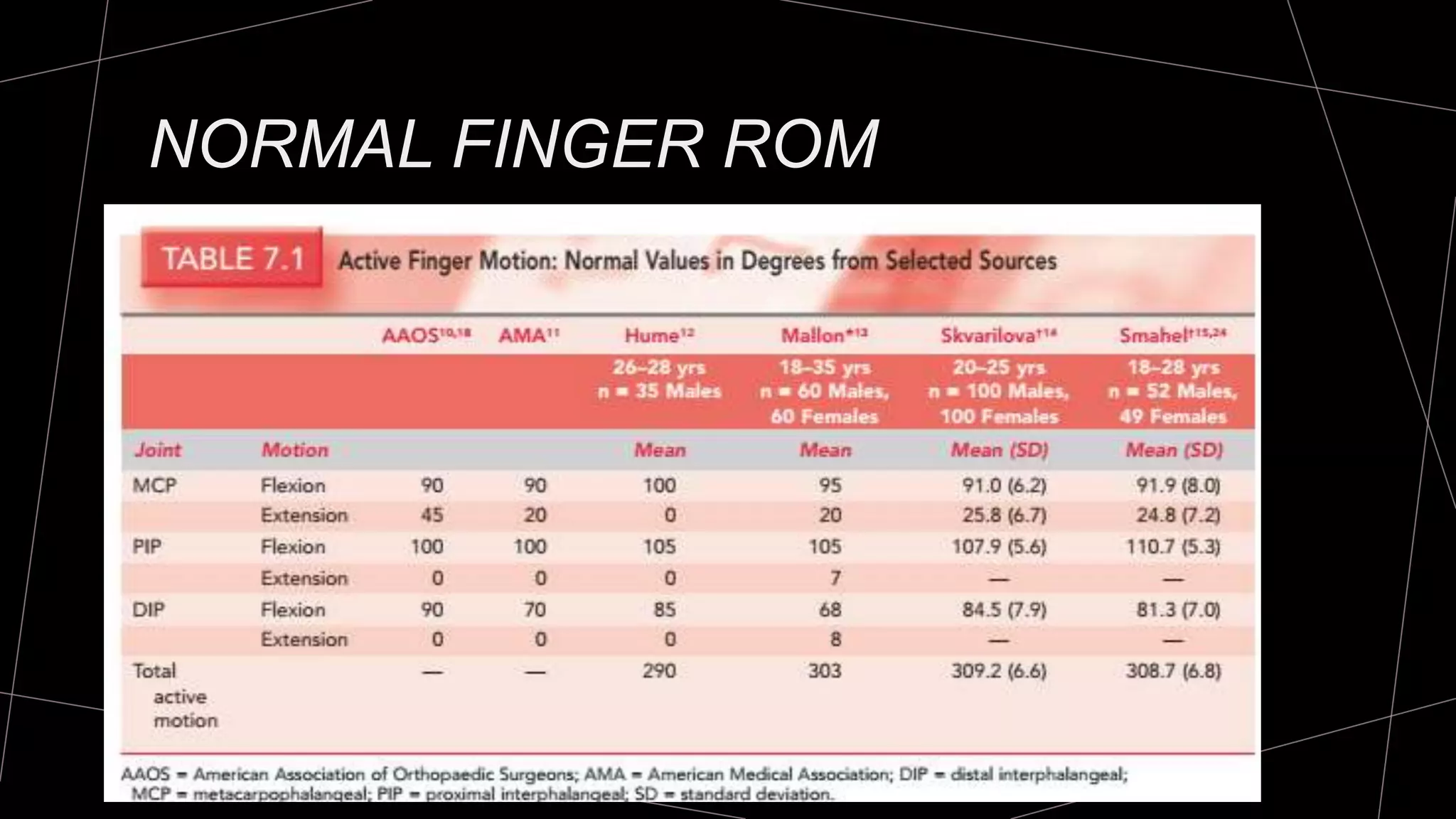
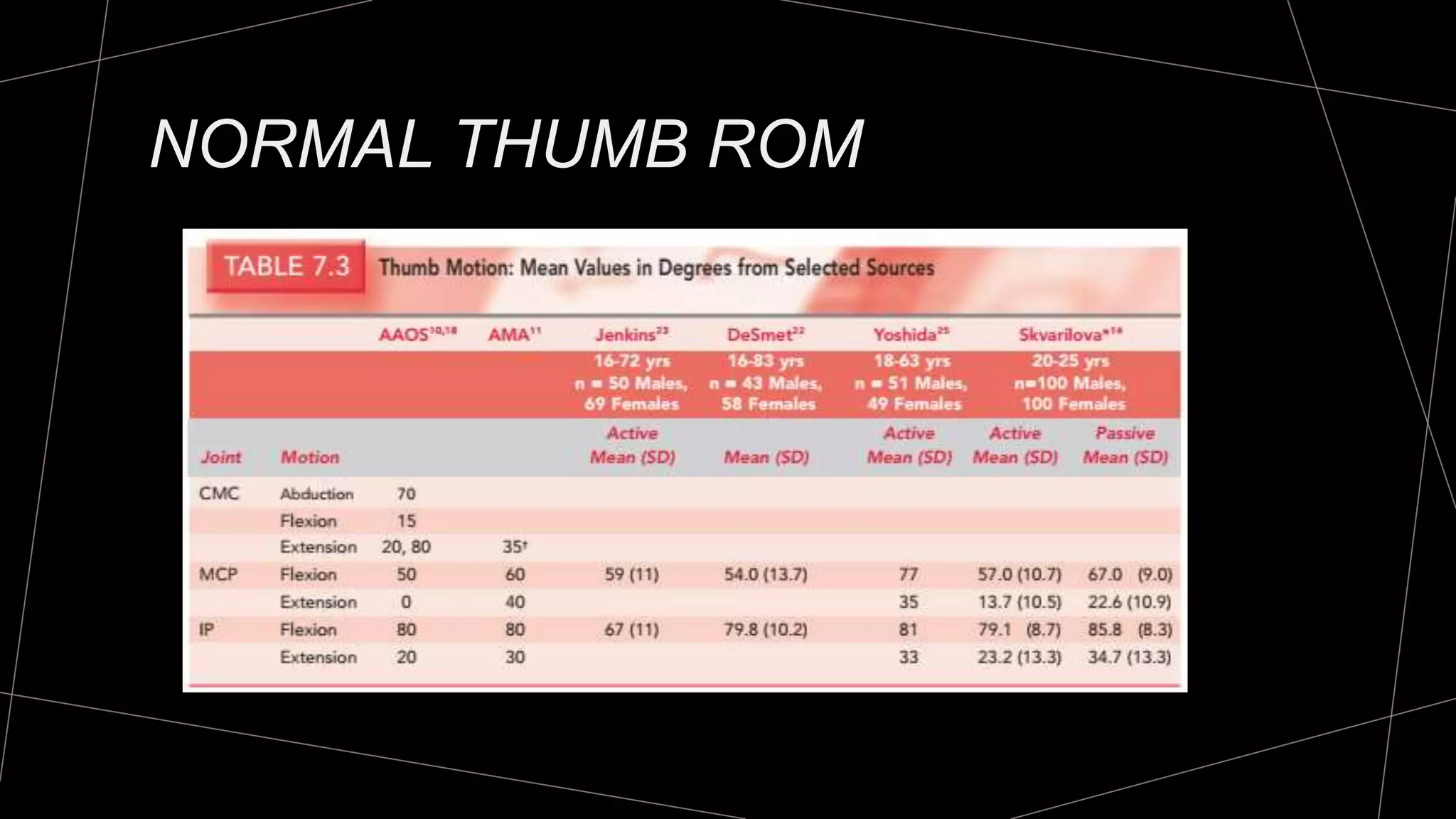
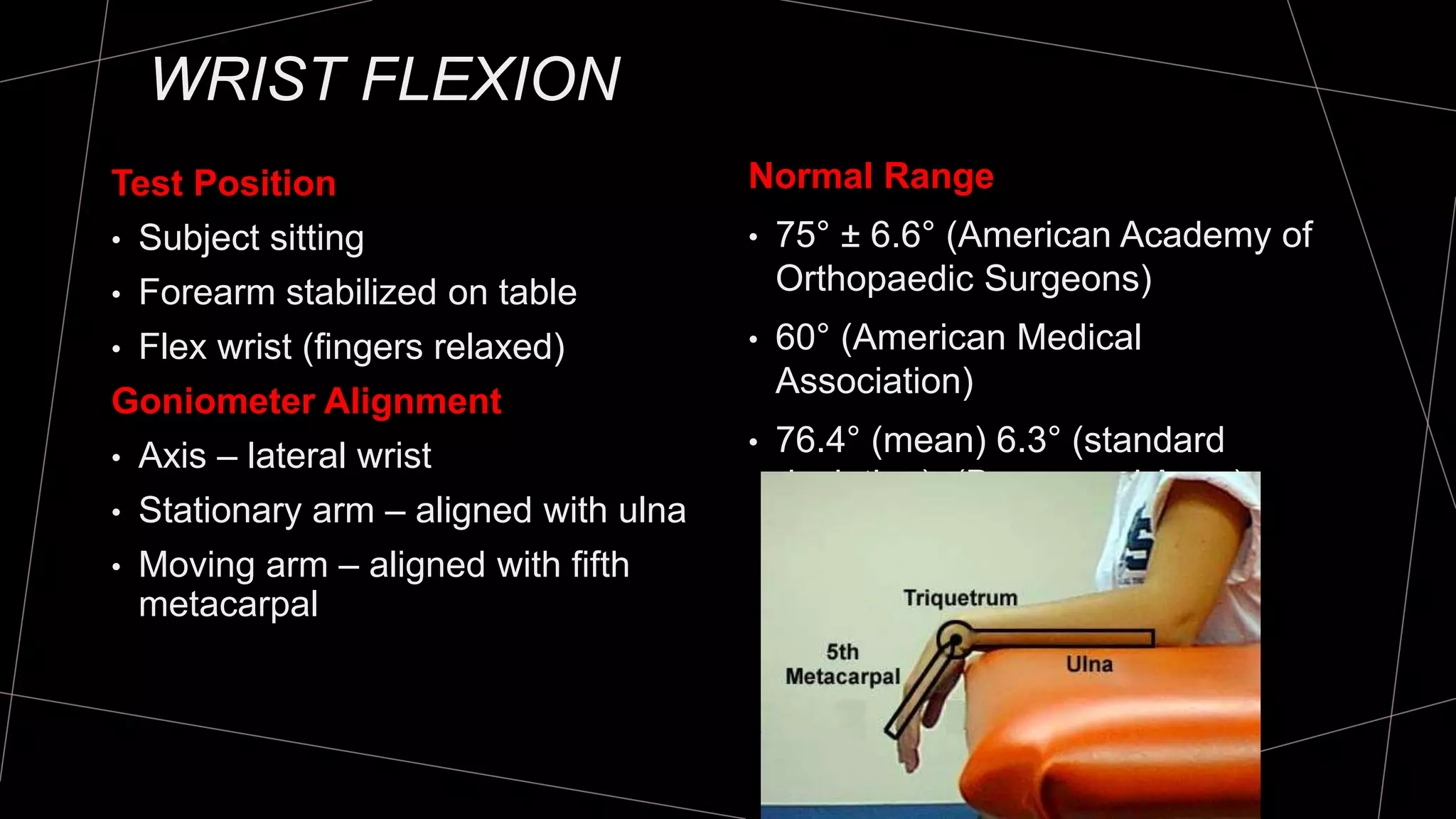
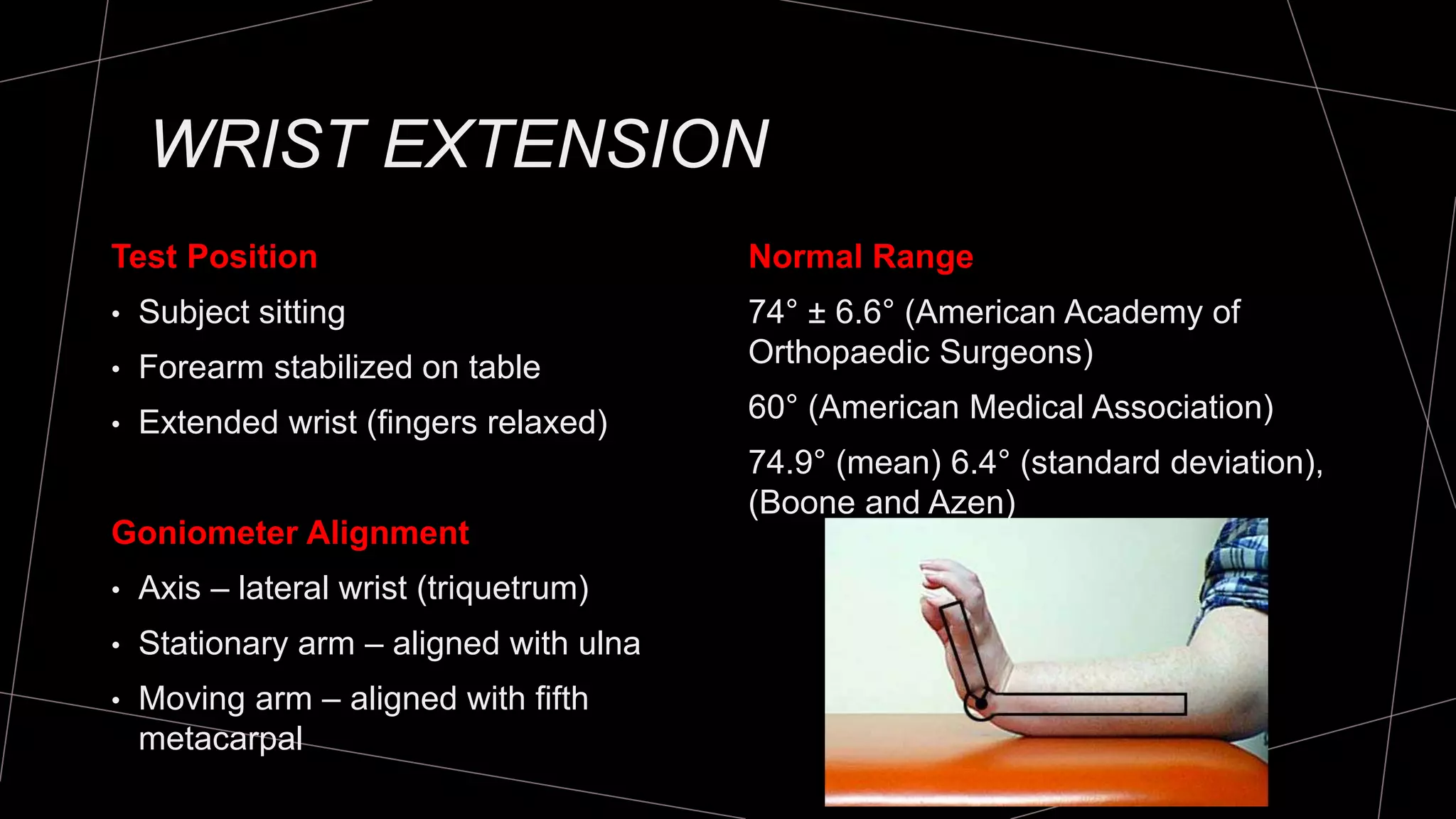
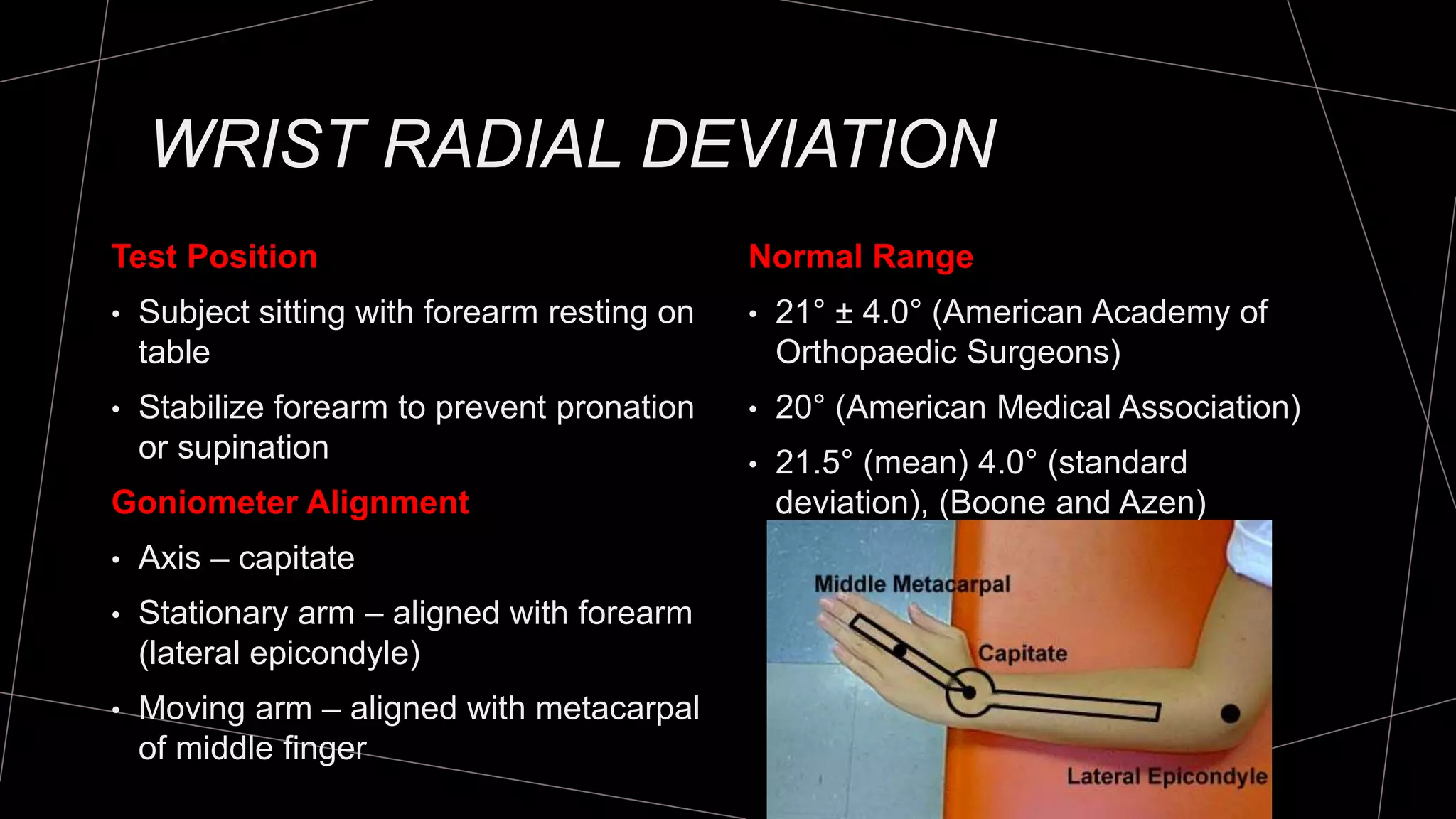
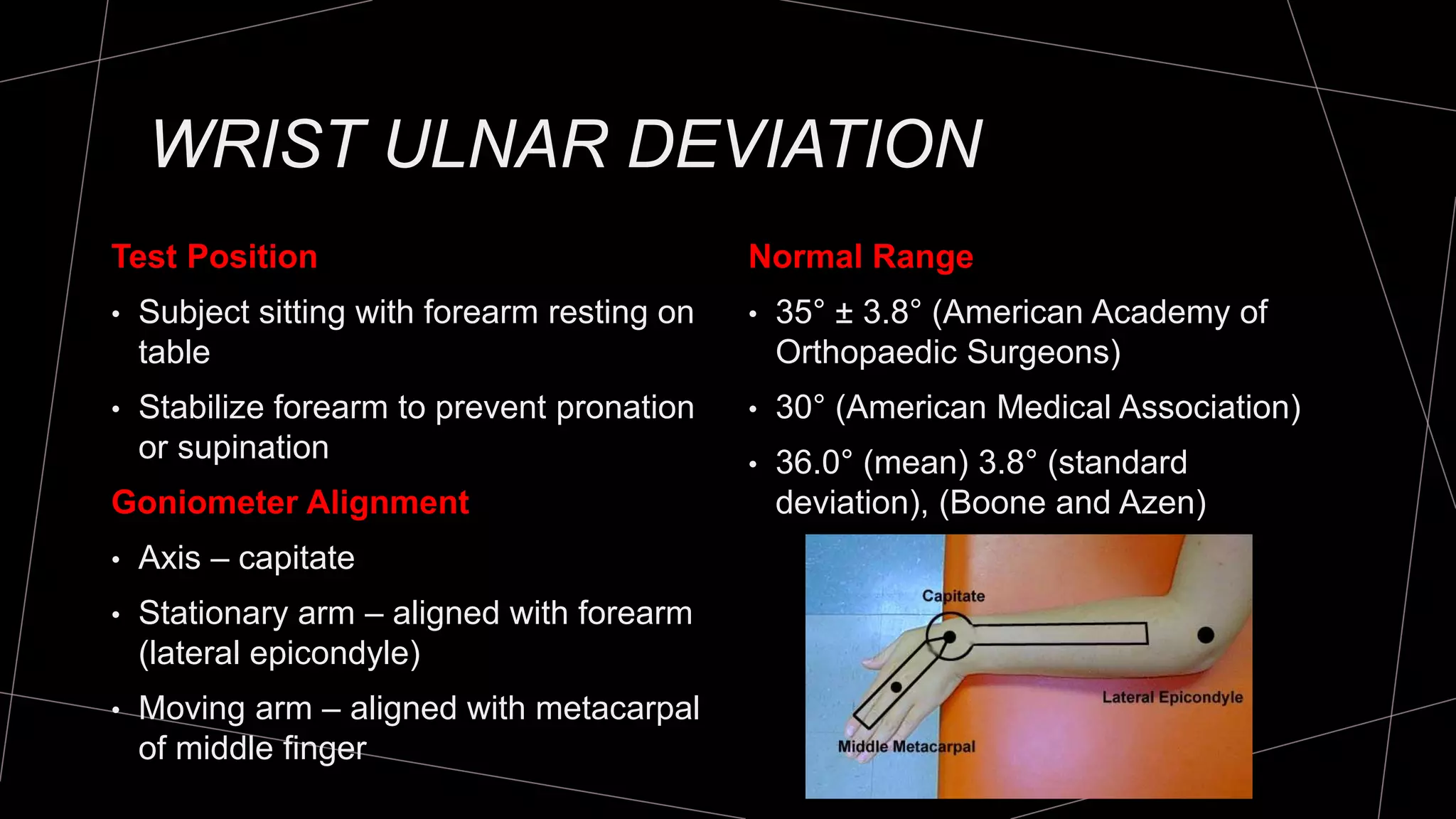
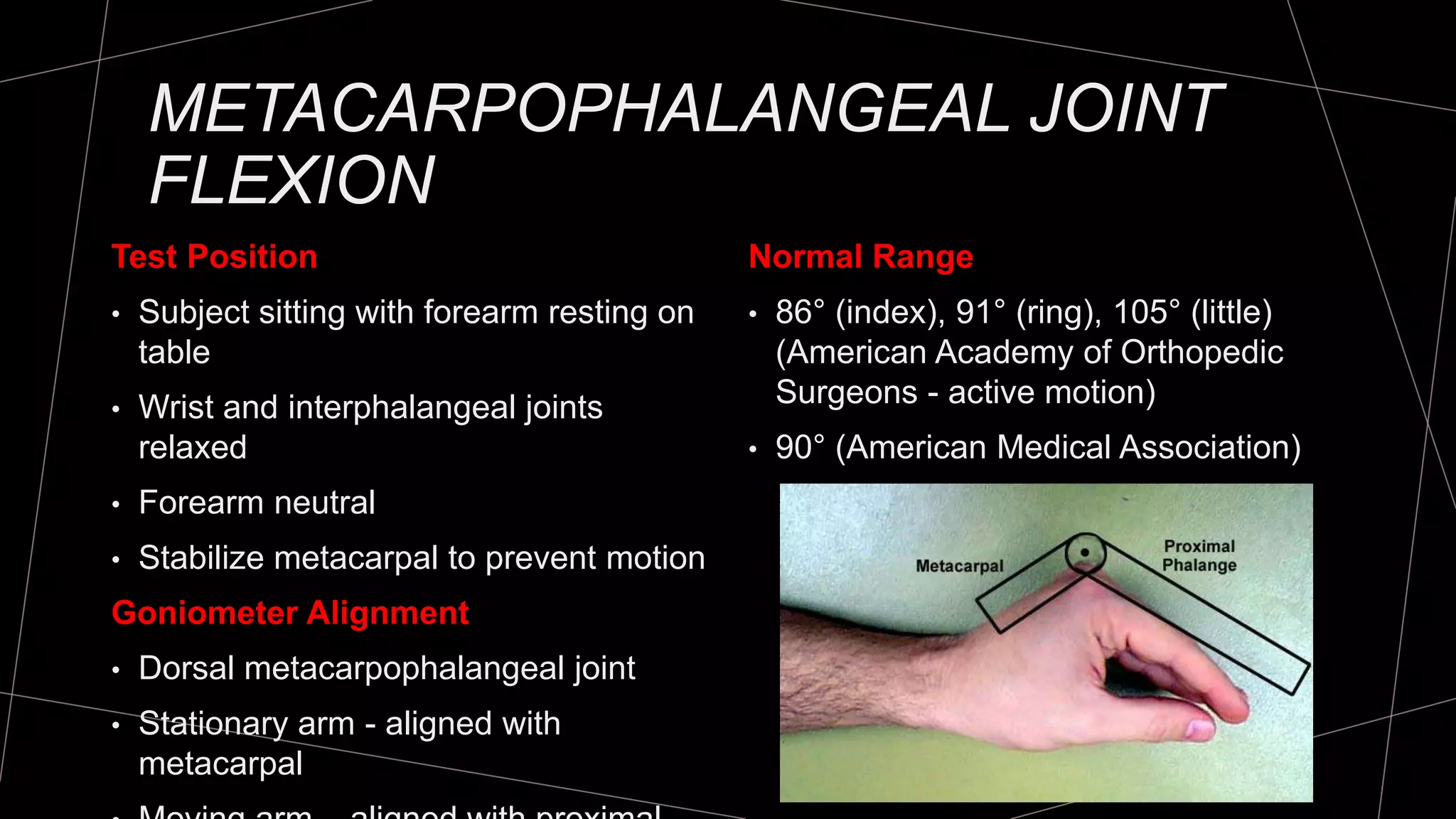
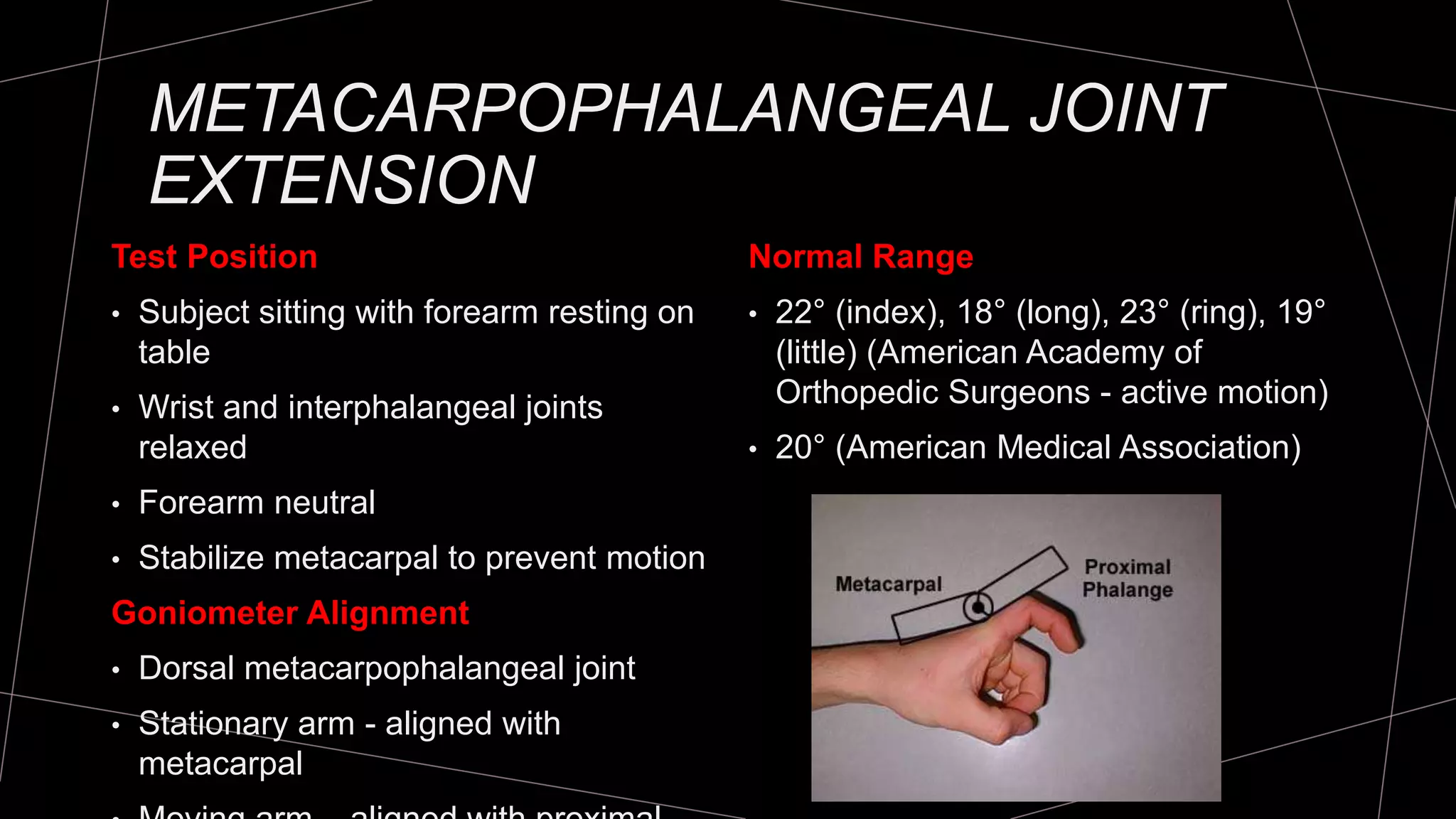
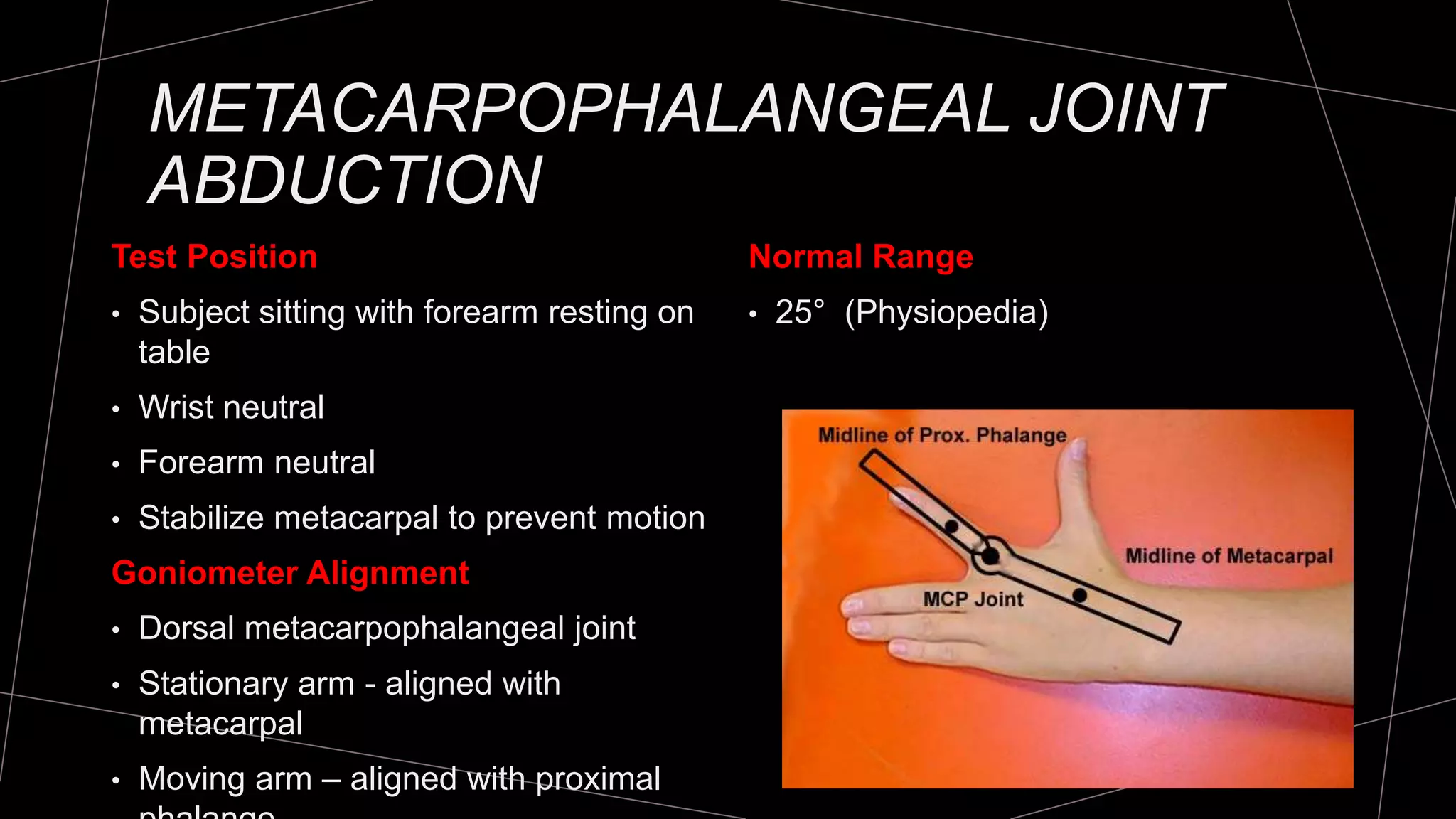
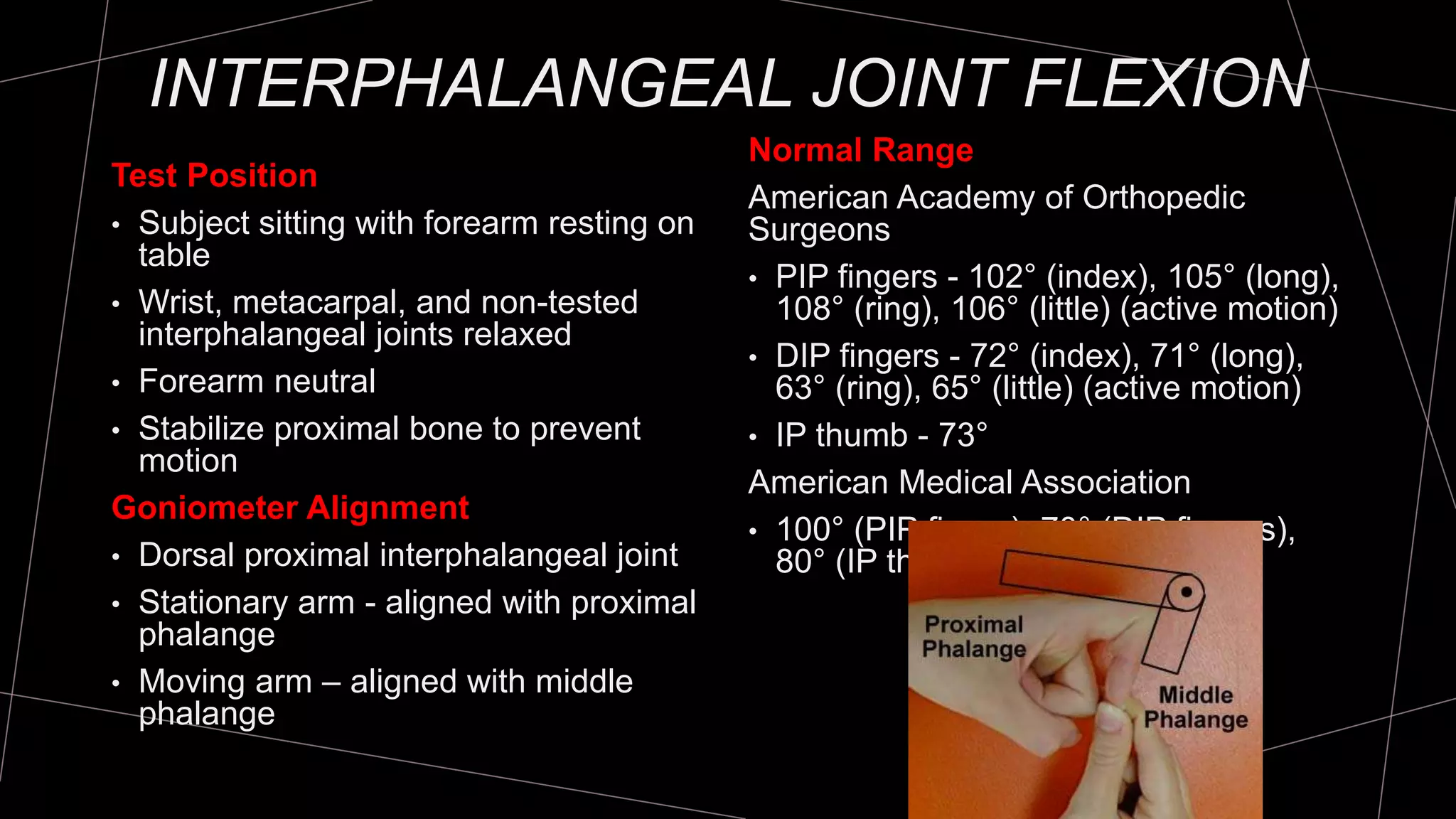
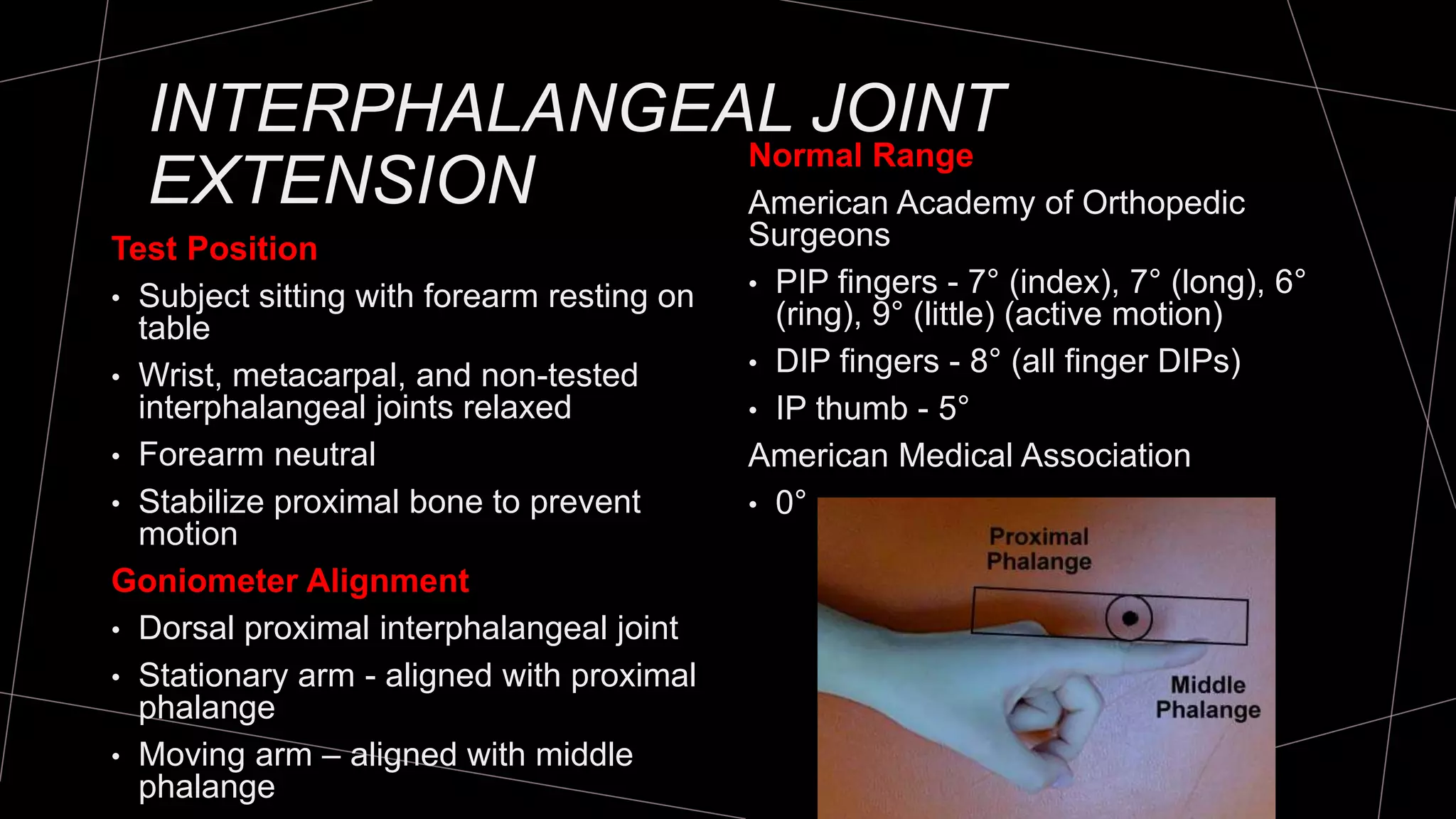
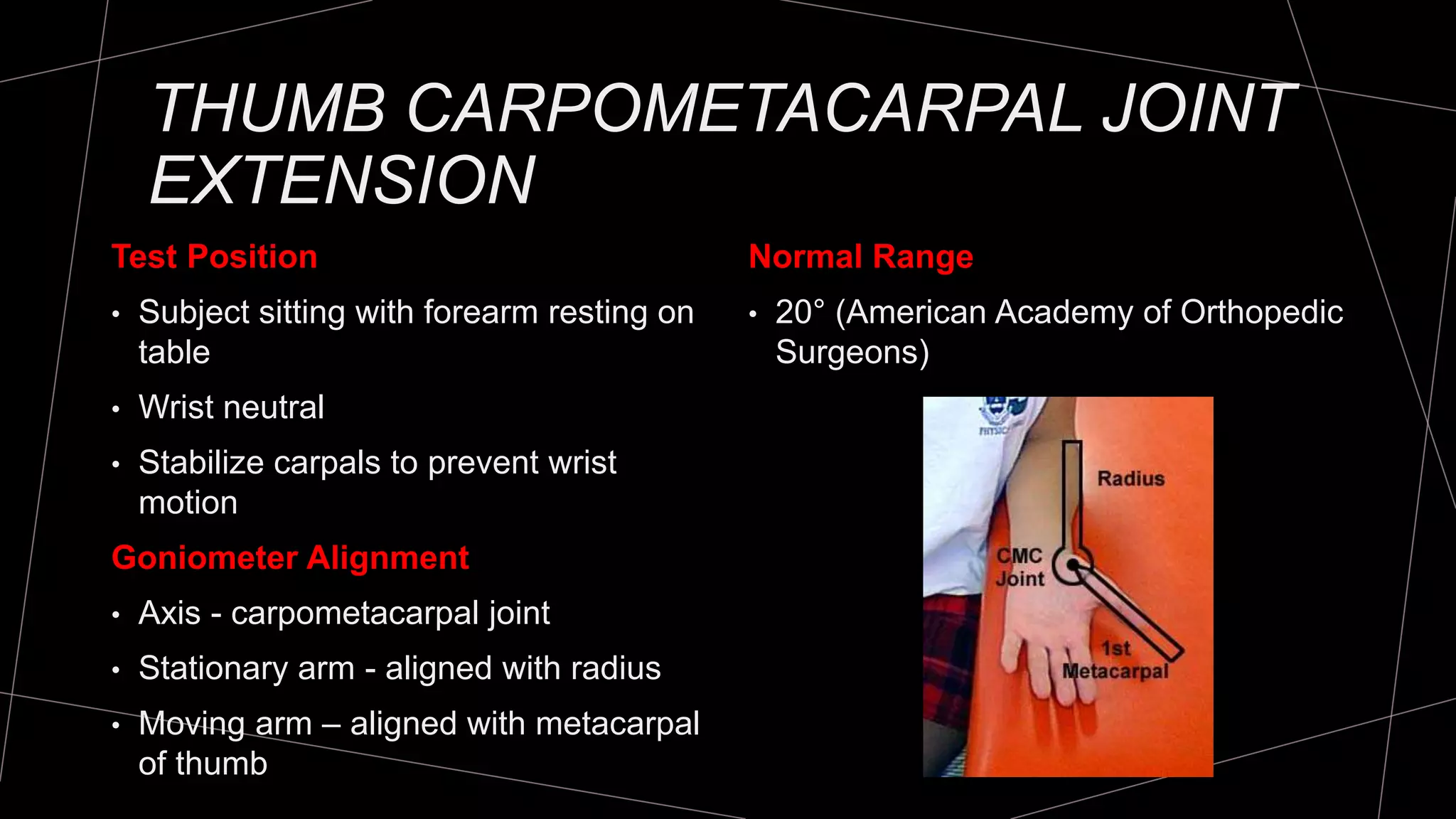
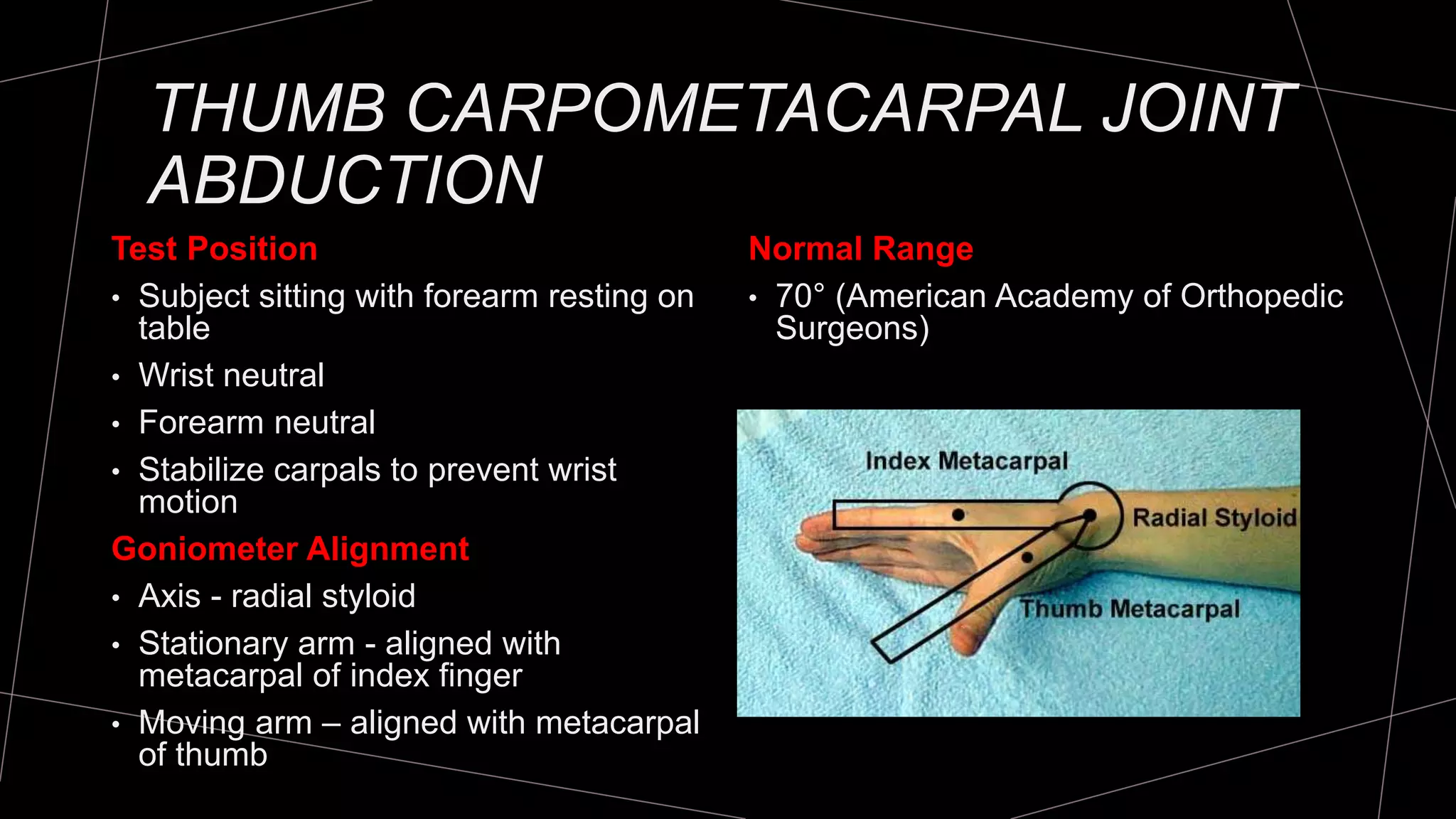
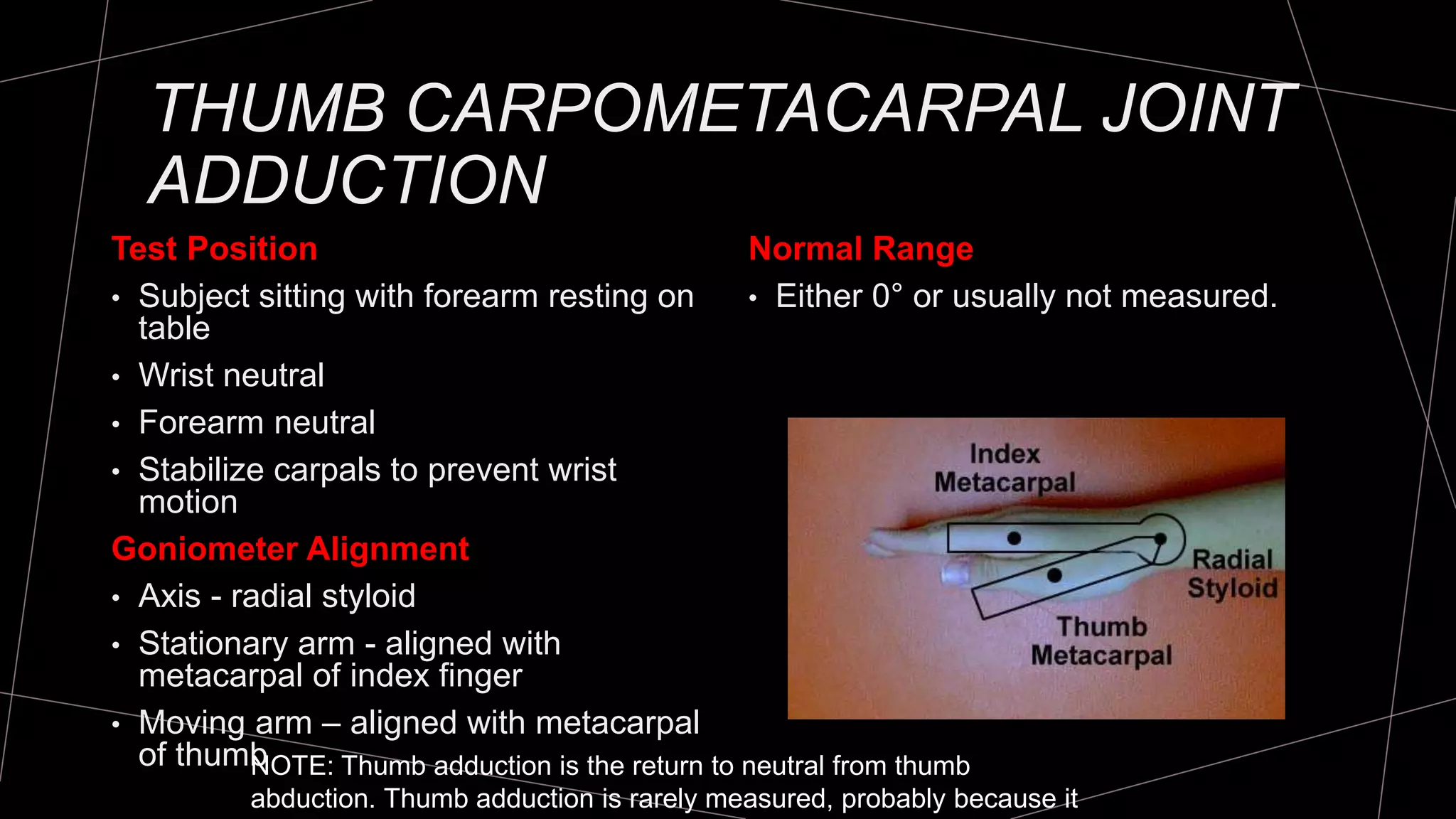
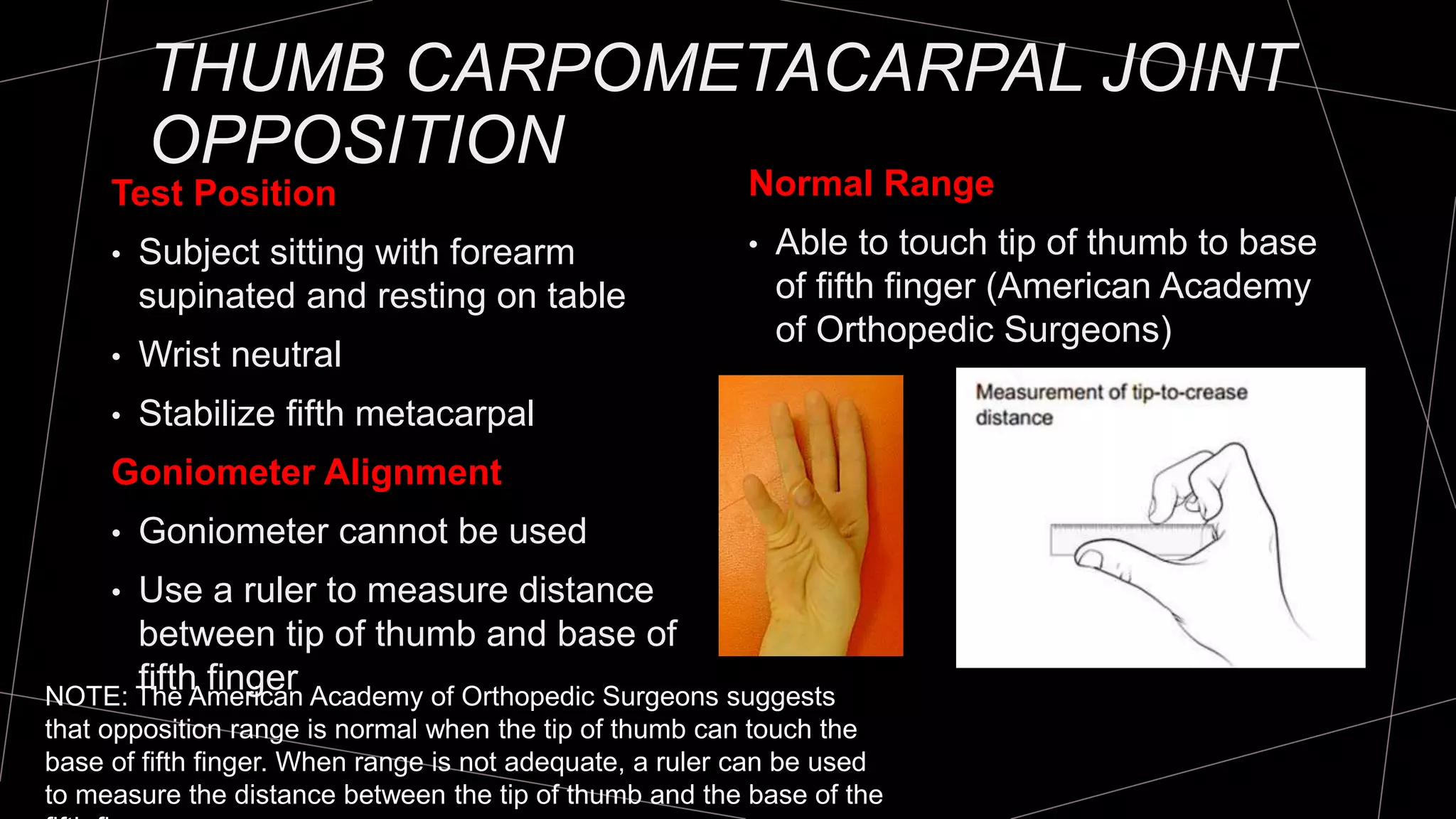
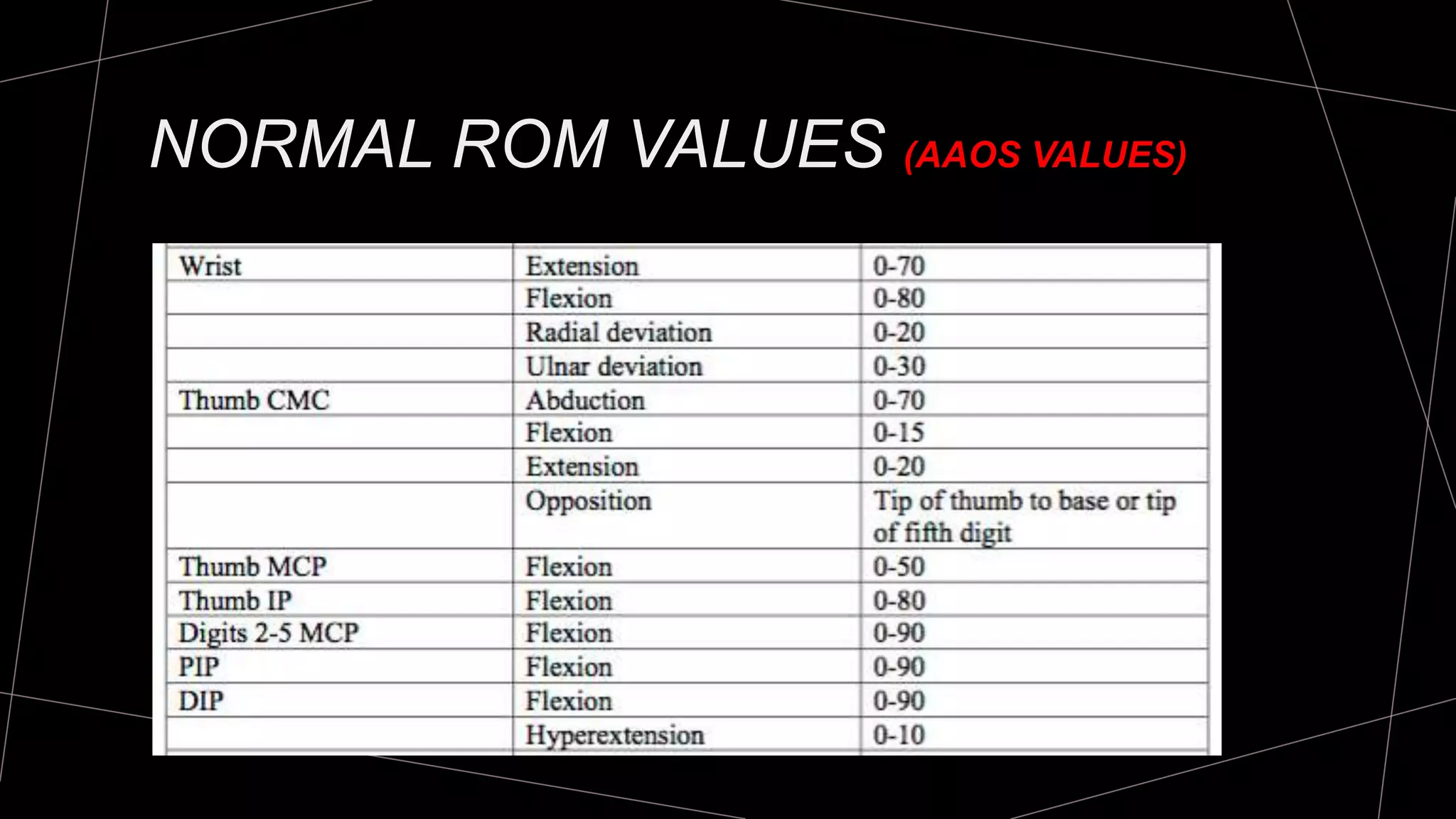
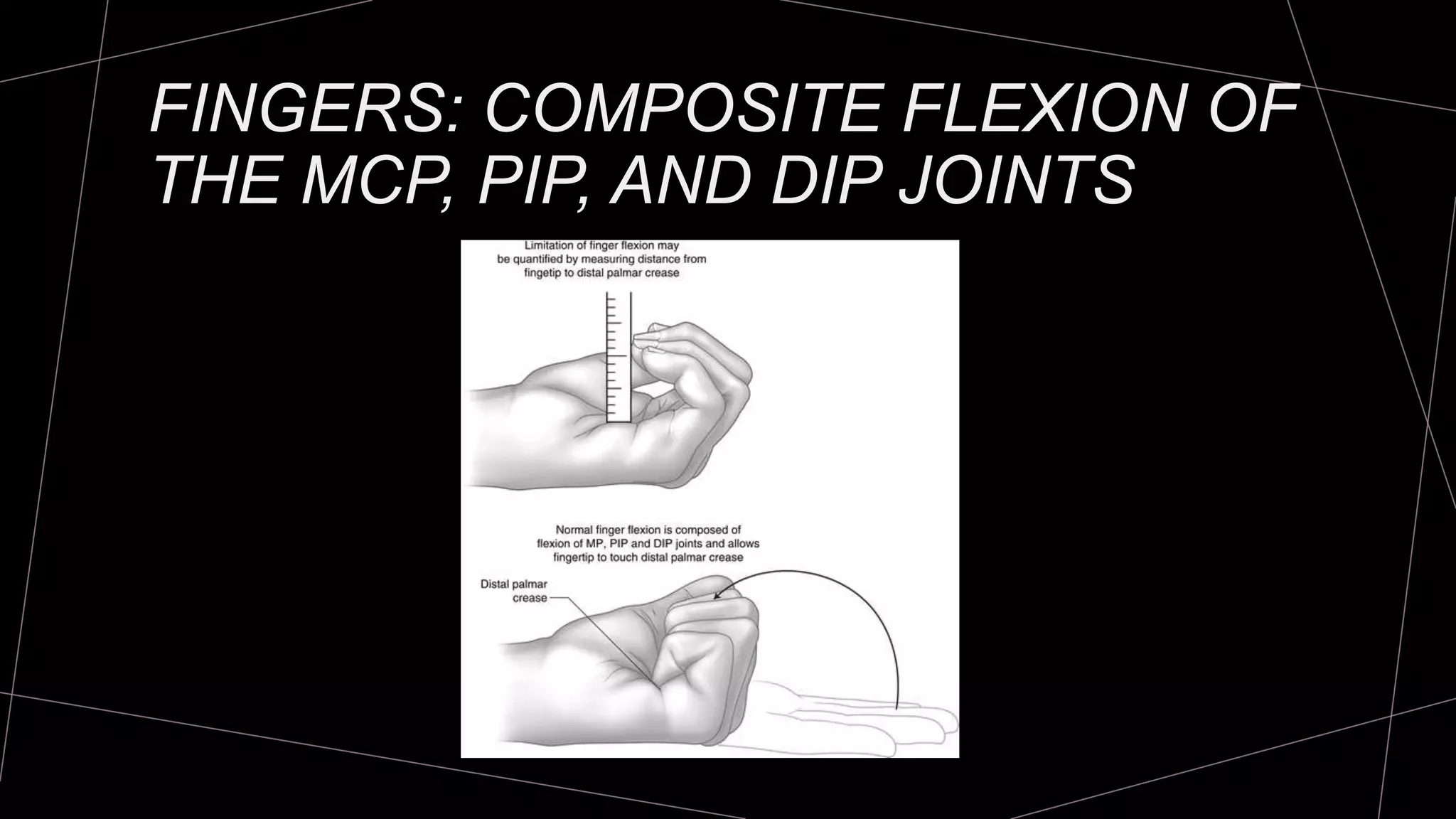
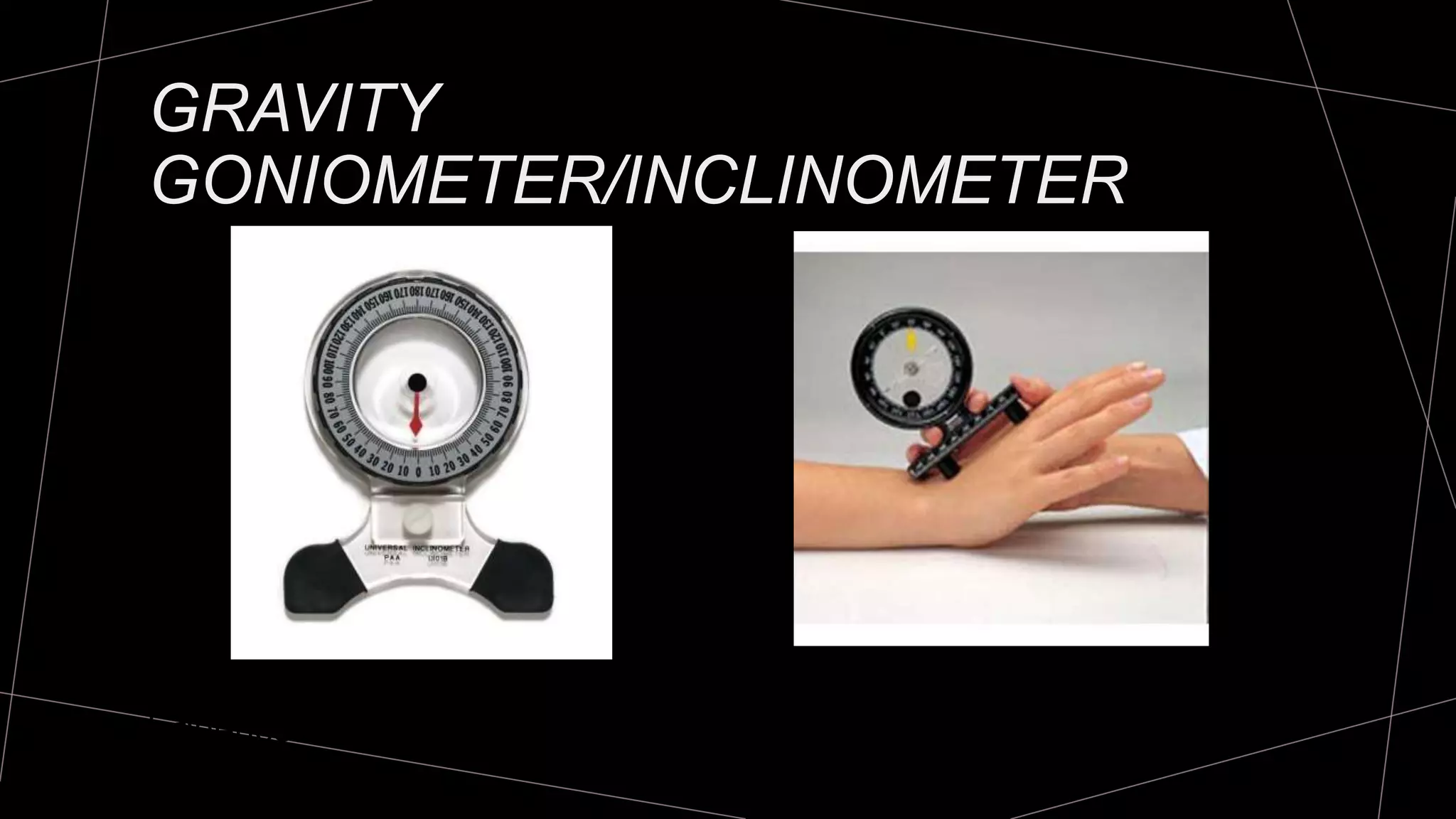
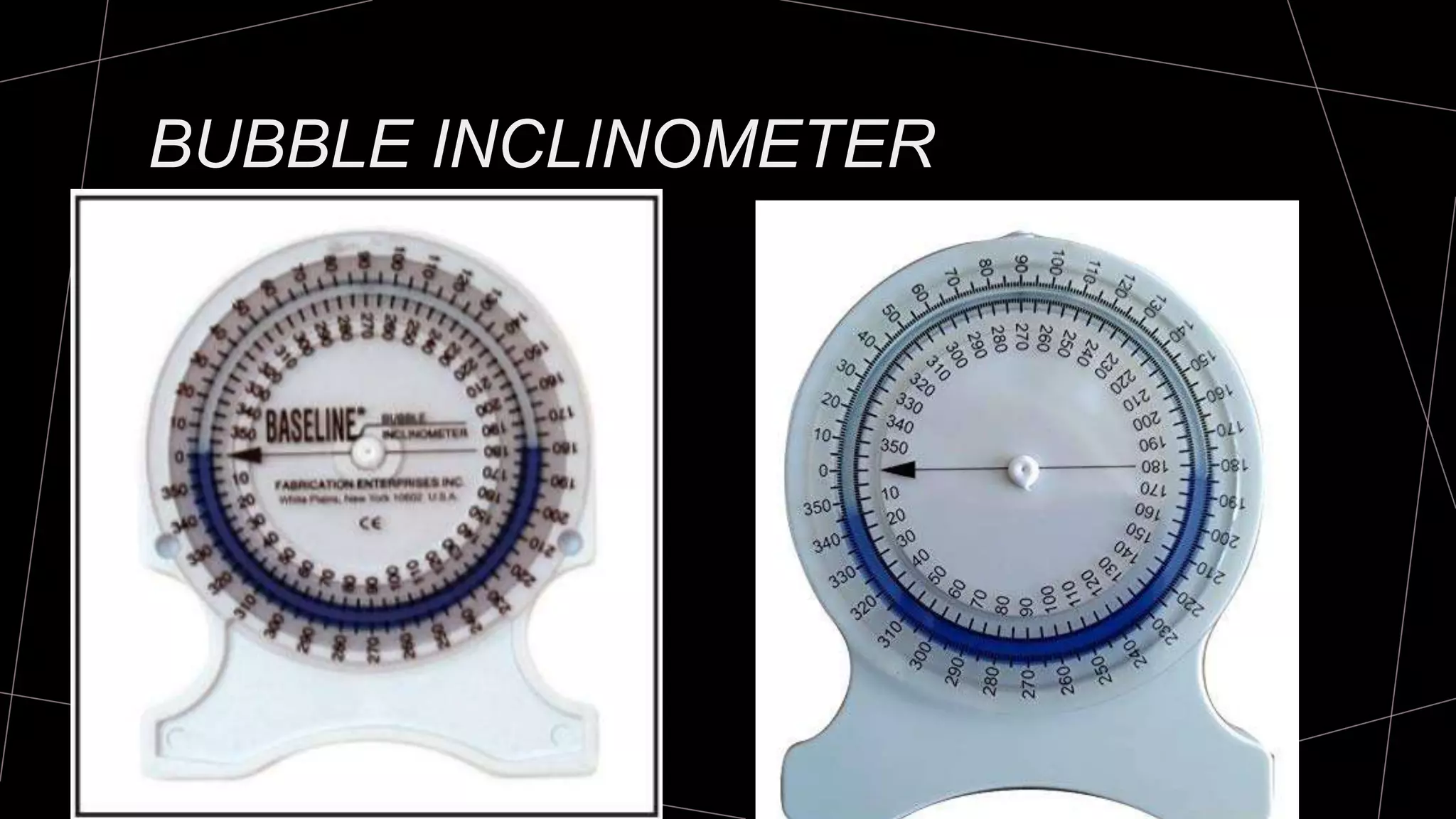
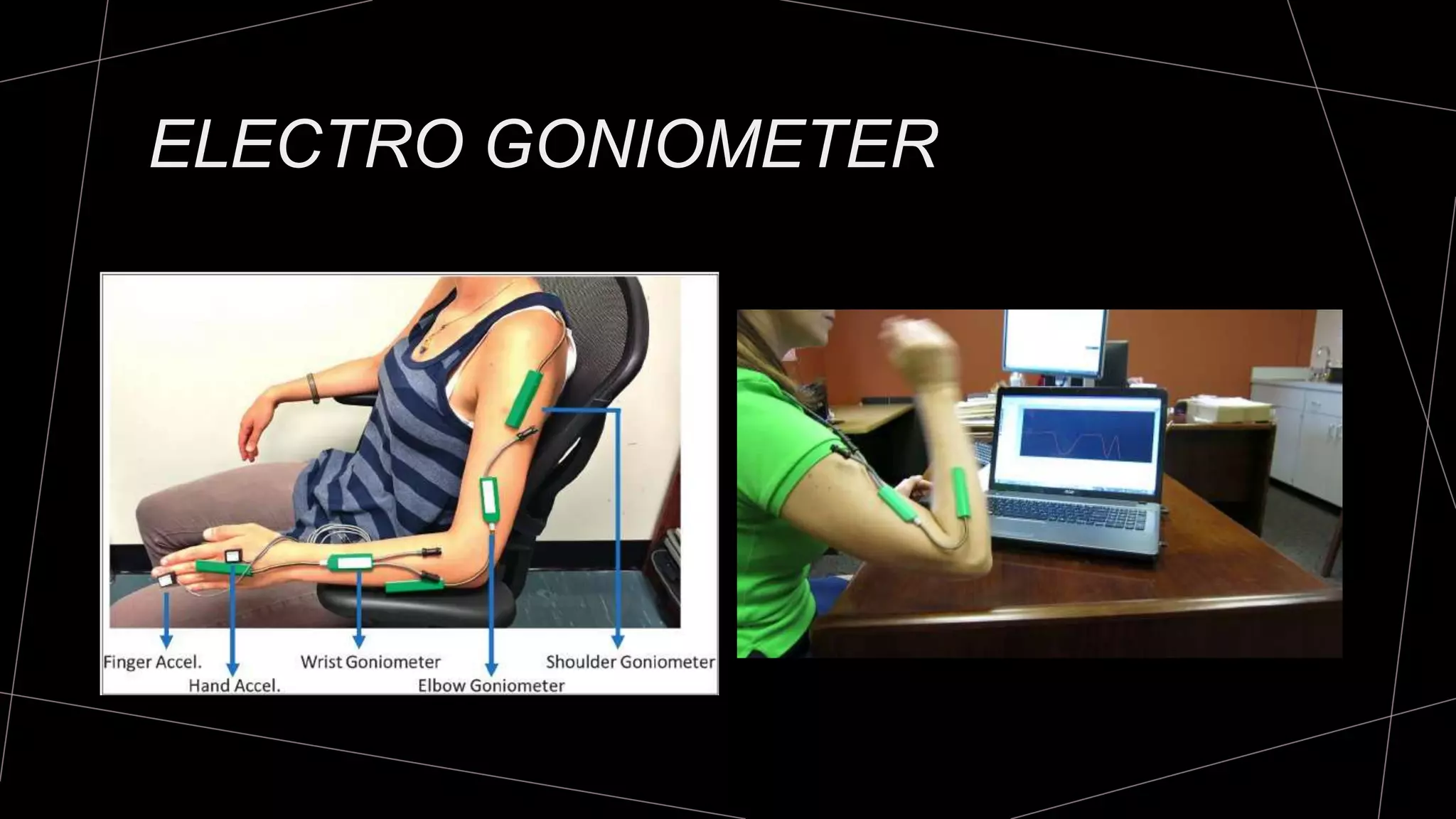
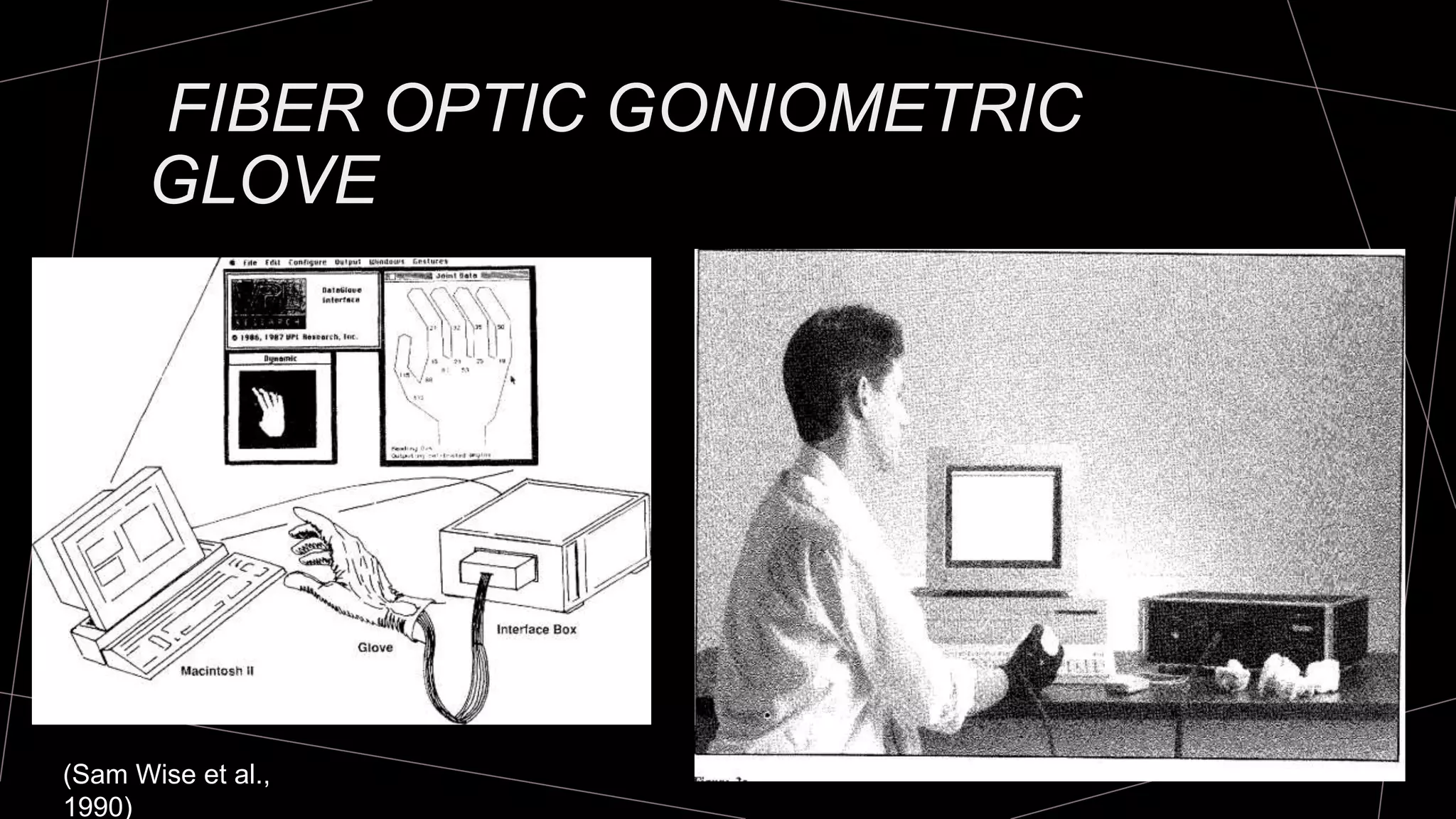
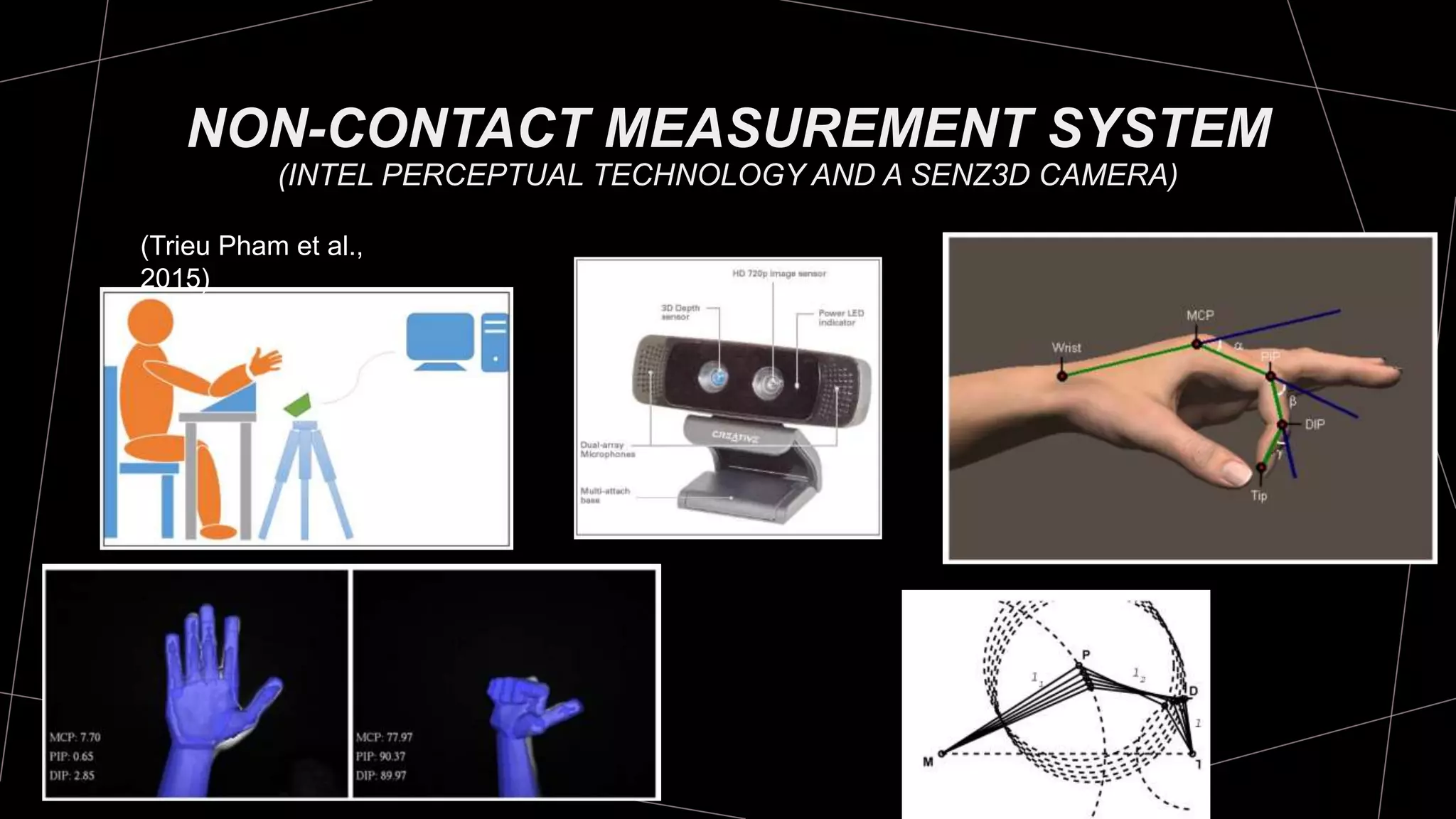
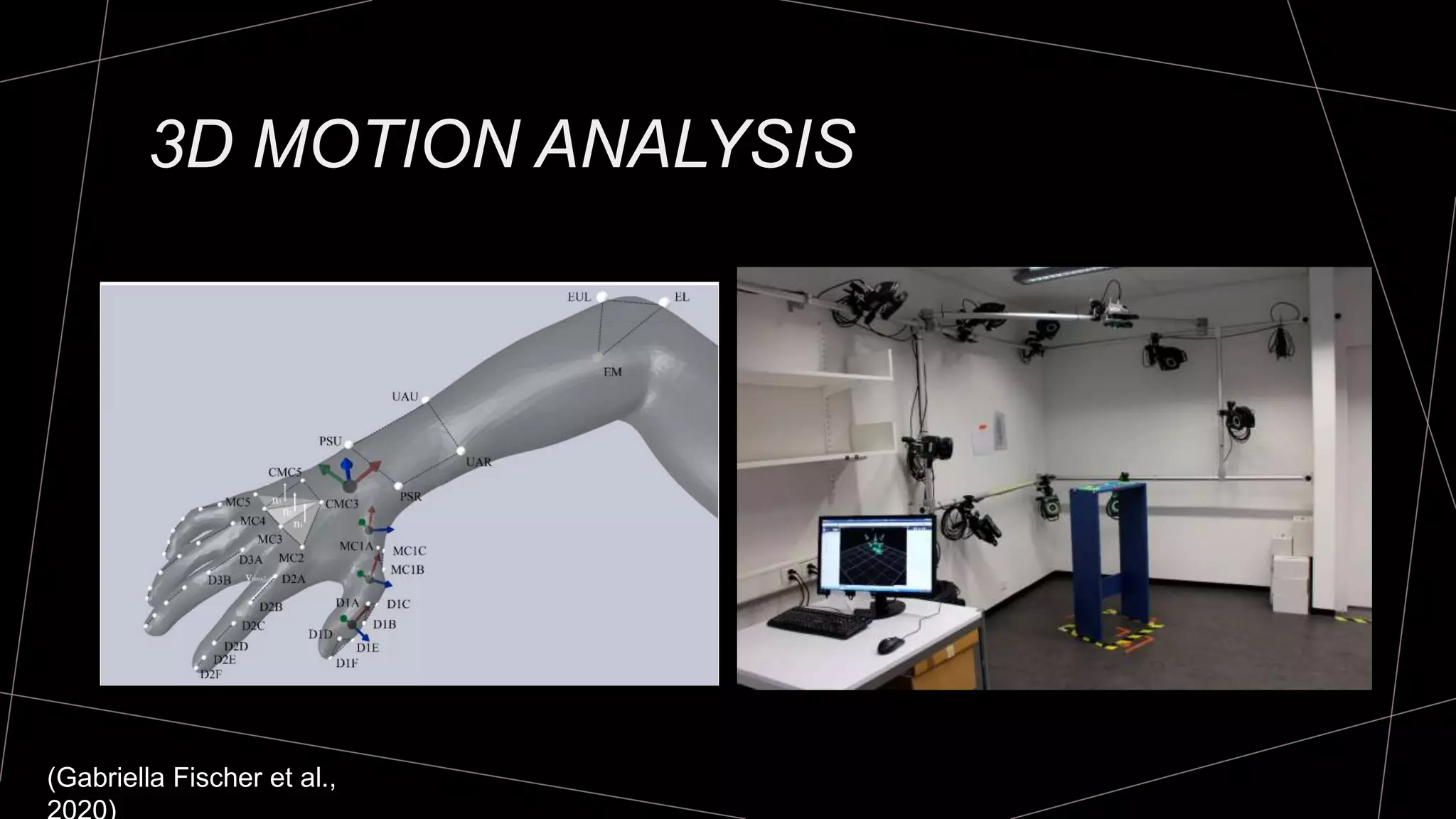
The document discusses goniometry techniques for measuring range of motion of the wrist and fingers. It provides details on positioning, goniometer alignment, and normal range of motion values for various wrist, hand, and finger motions according to sources like the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. A variety of goniometry tools are presented, from universal goniometers to electrogoniometers, digital tools, and 3D motion analysis systems.