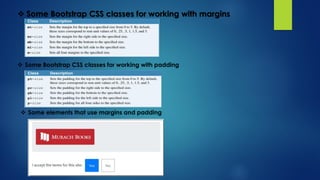
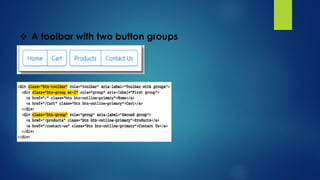
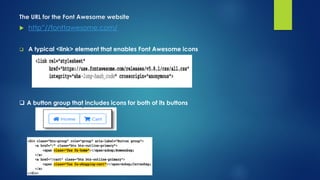
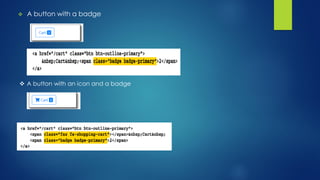
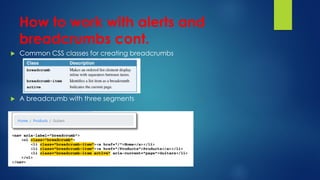
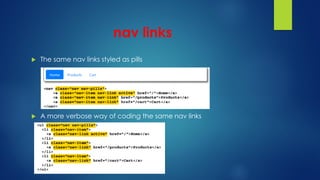
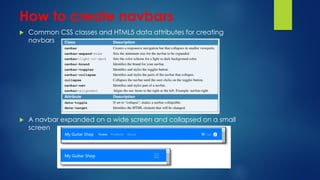
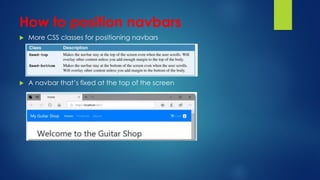
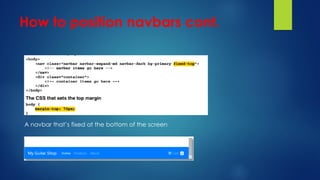
This document explains responsive web design and how to use the Bootstrap framework to develop web applications that adapt to various screen sizes. It covers the essentials of implementing Bootstrap in ASP.NET Core MVC applications, including adding client-side libraries, utilizing the grid system, and creating components like forms, buttons, and navbars. Additionally, it provides insights on CSS classes for styling and managing layout for a mobile-friendly web experience.