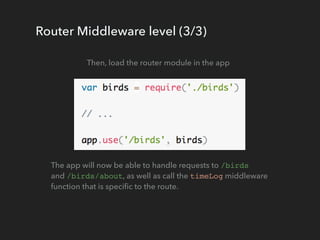
Express.js is a web application framework for Node.js that provides a flexible set of features for building web and mobile apps. Express apps use middleware functions that have access to the request and response objects and allow for intermediate processing in the request-response cycle. Middleware functions can execute code, modify requests/responses, and call the next middleware function. Express supports application-level middleware, router-level middleware, error handling middleware, built-in middleware like static file serving, and third-party middleware.












![Built-in Middleware handlers
The only built-in middleware function in Express is
express.static. This function is based on serve-static, and is
responsible for serving static assets such as HTML files,
images, and so on.
The function signature is: express.static(root, [options])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressjs-180501133642/85/Expressjs-14-320.jpg)


