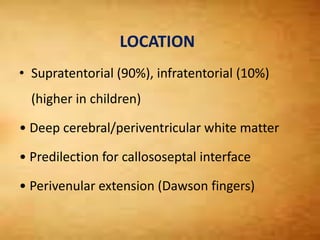
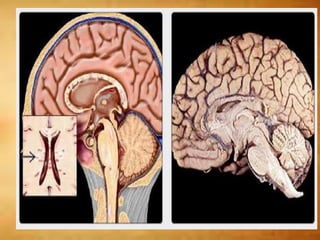
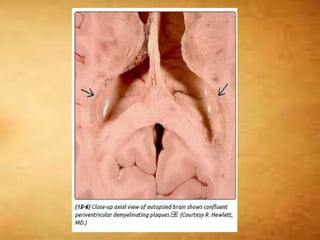
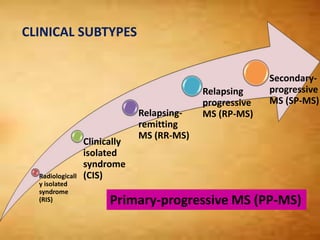
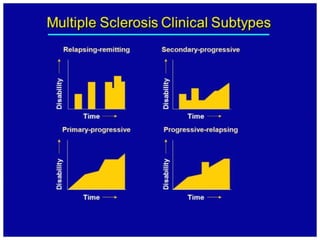
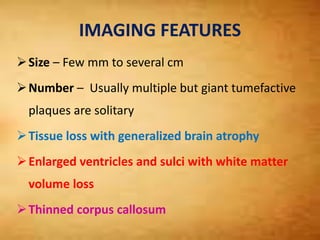
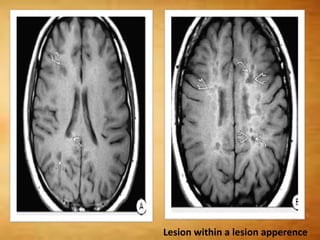
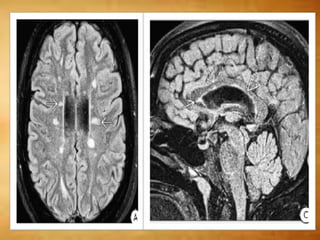
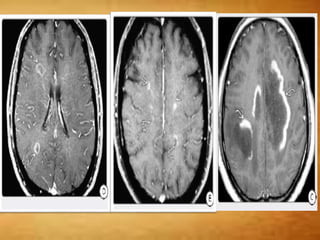
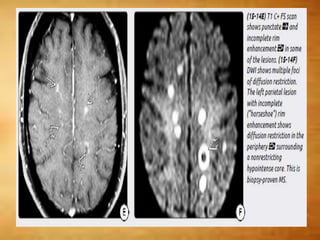
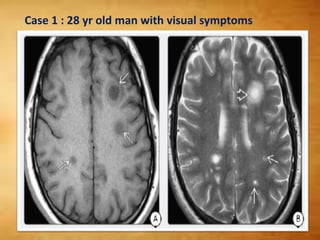
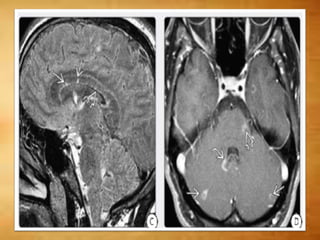
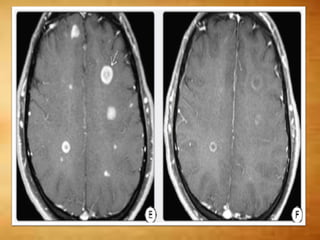
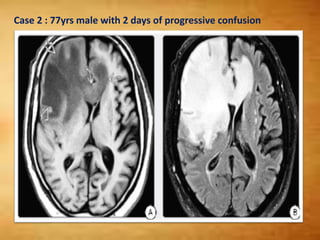
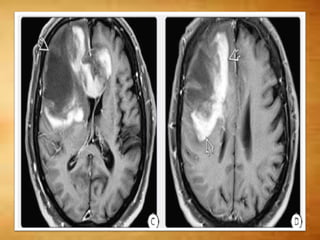
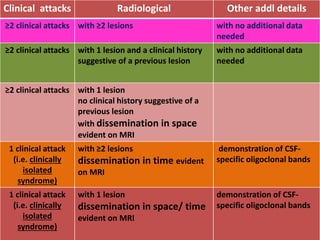
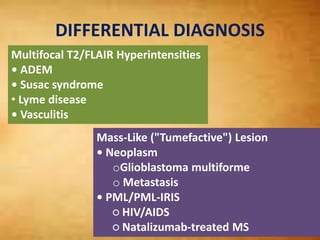
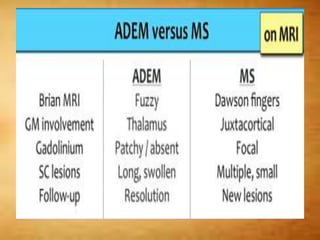
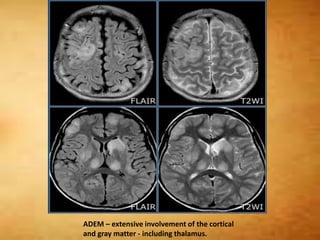
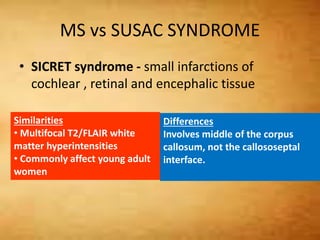
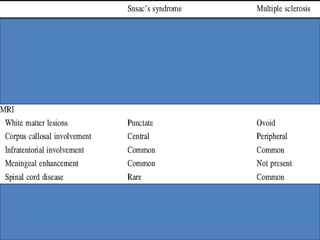
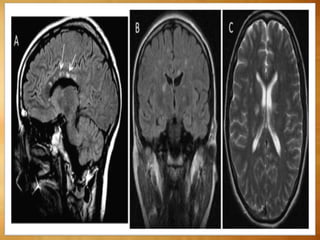
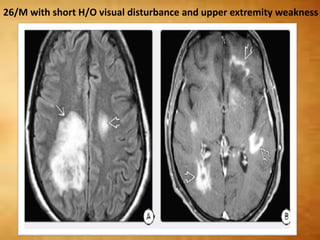
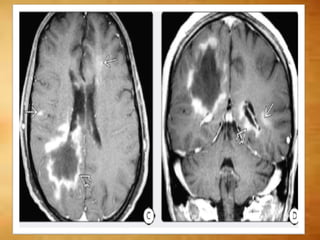
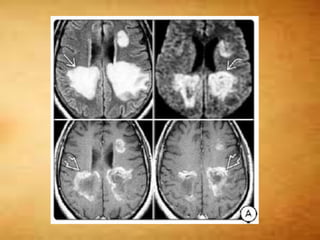
This document summarizes multiple sclerosis (MS), a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. It discusses the etiology, pathology, clinical presentation, imaging features, diagnostic criteria, variants, and differential diagnosis of MS. Key points include: MS is characterized by inflammatory demyelinating lesions ("plaques") in the brain and spinal cord; risk factors include genetic and environmental factors; clinical presentation varies from relapsing-remitting to progressive forms; MRI is important for diagnosis and demonstrates disseminated hyperintense lesions; and differential diagnosis includes ADEM, Susac syndrome, and CNS tumors.