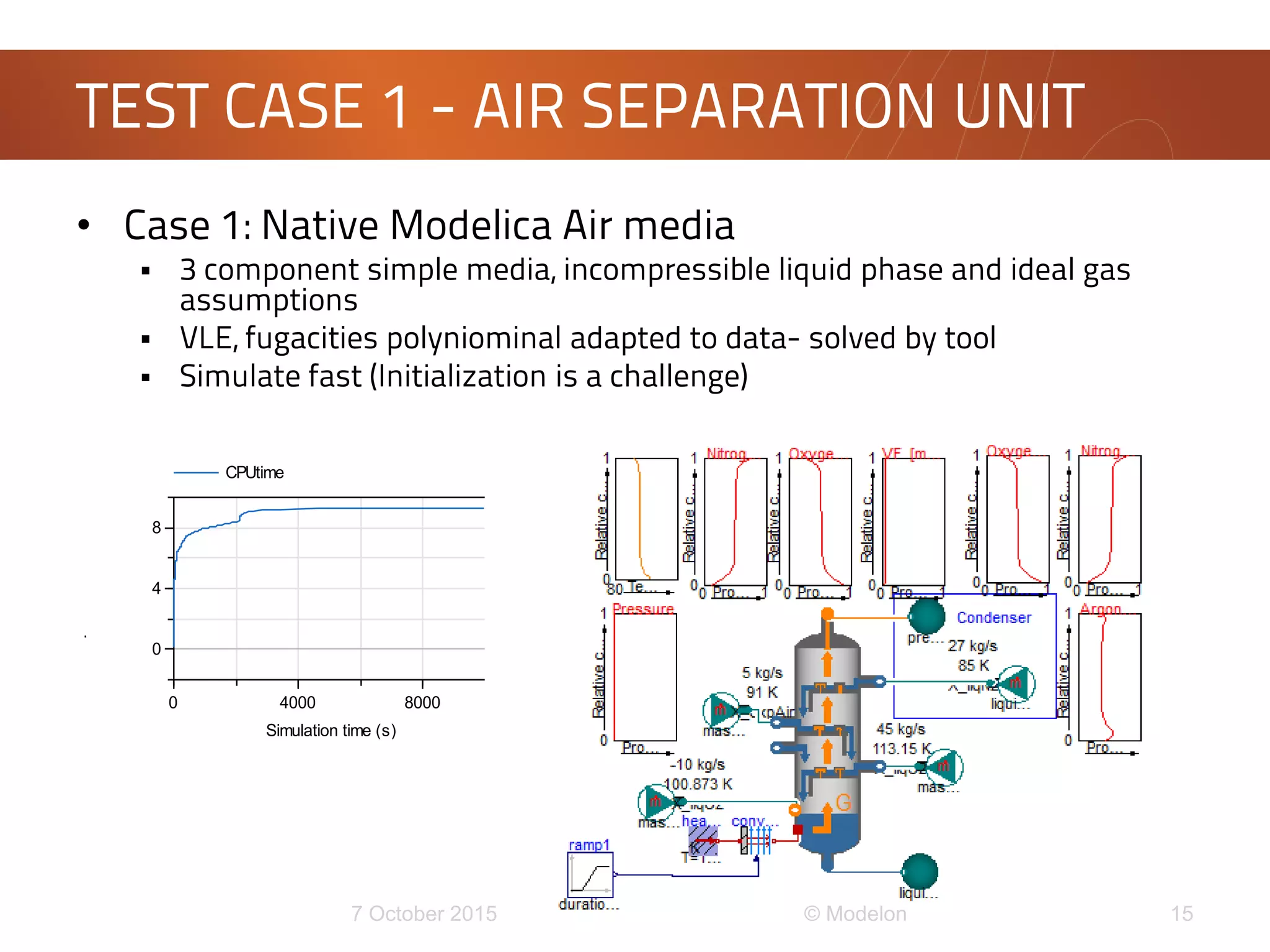
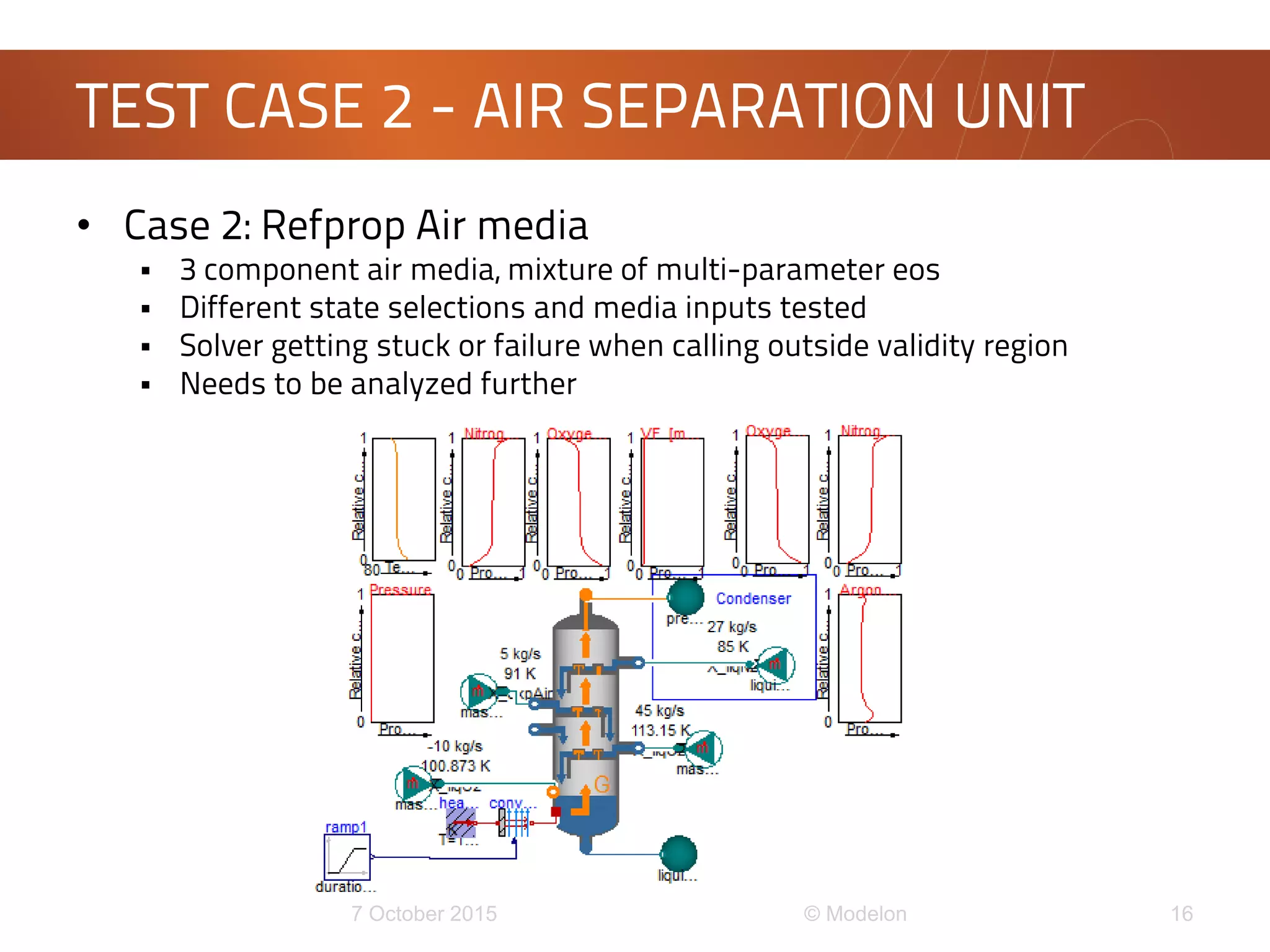
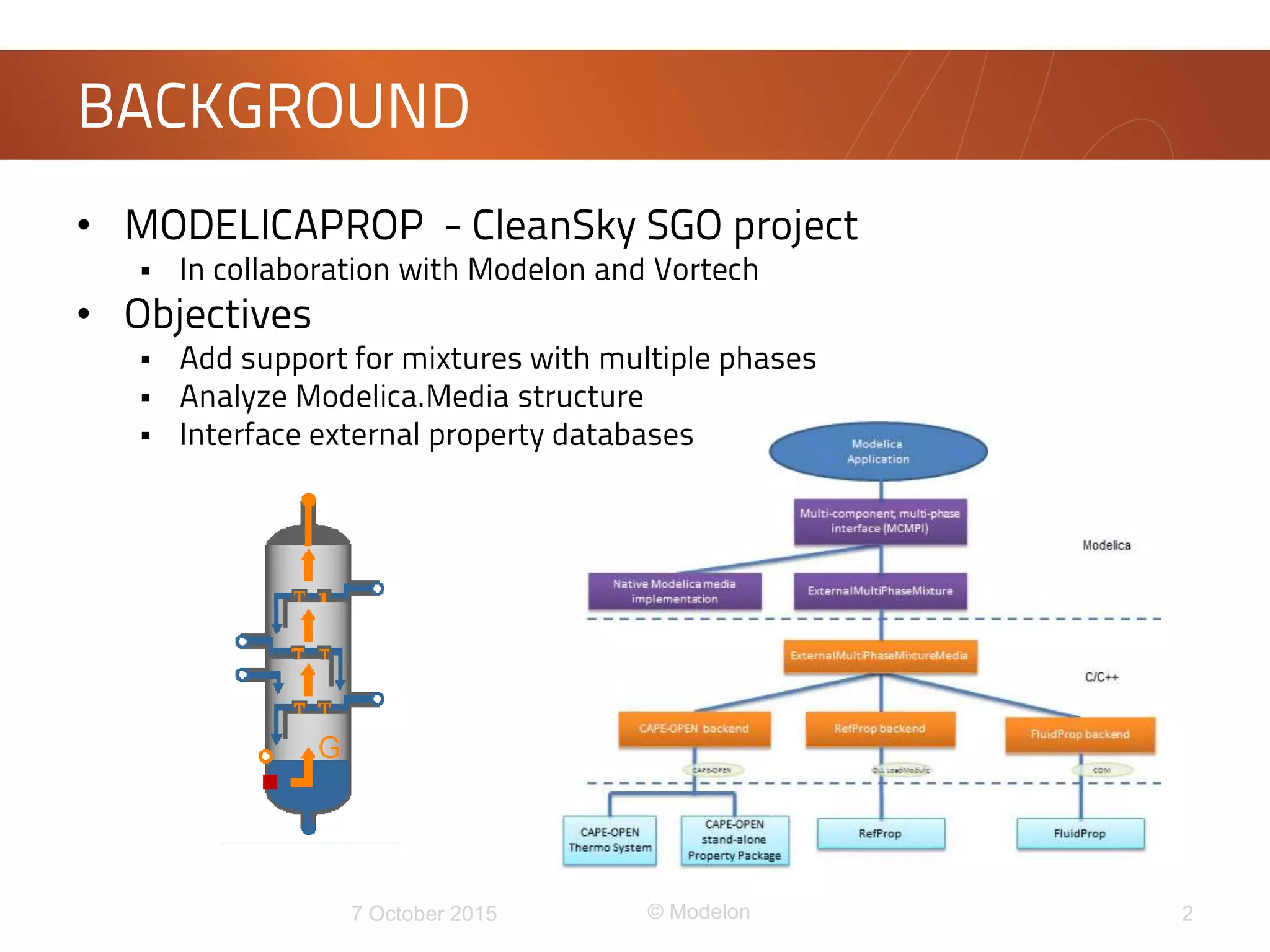
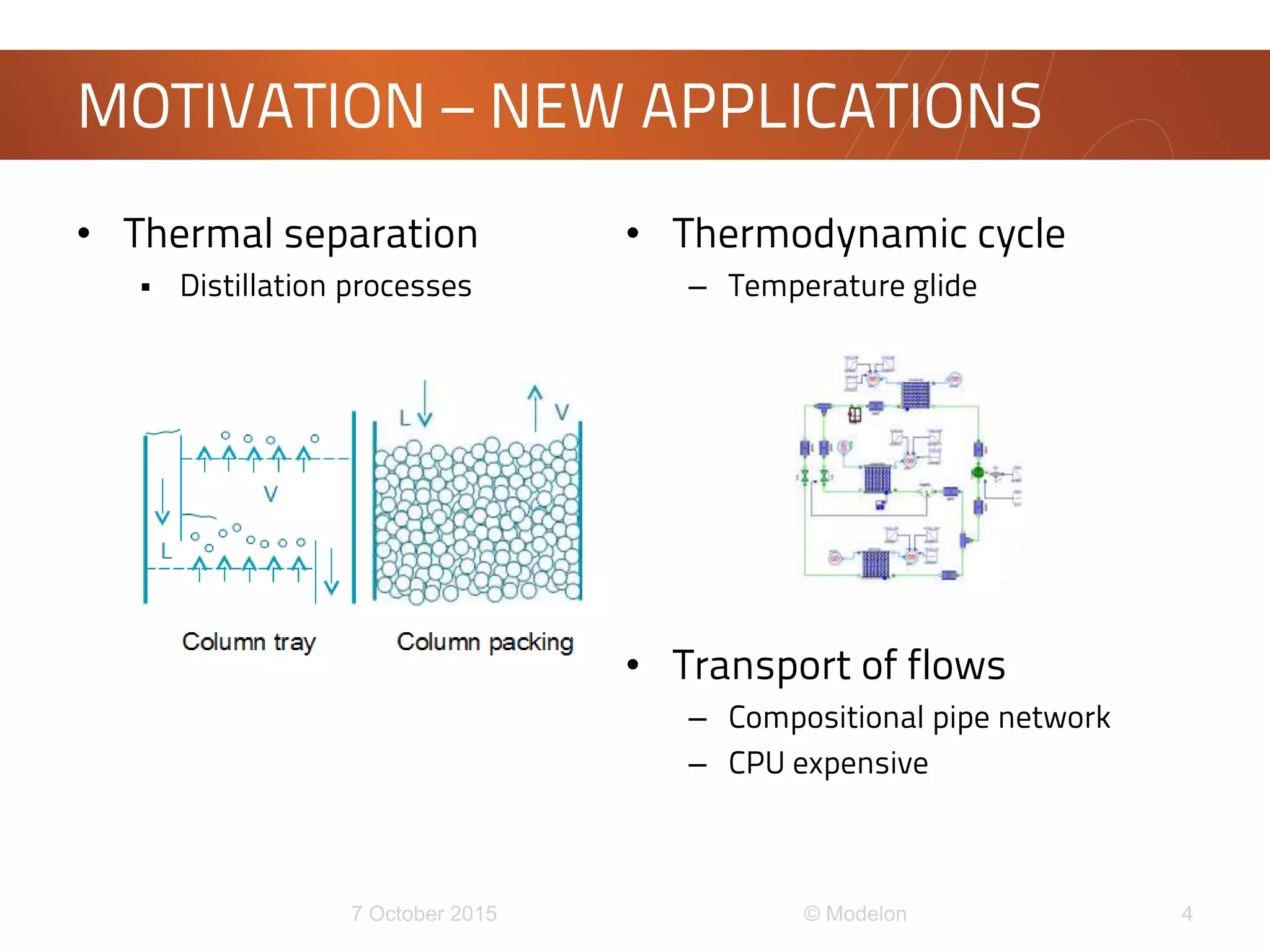
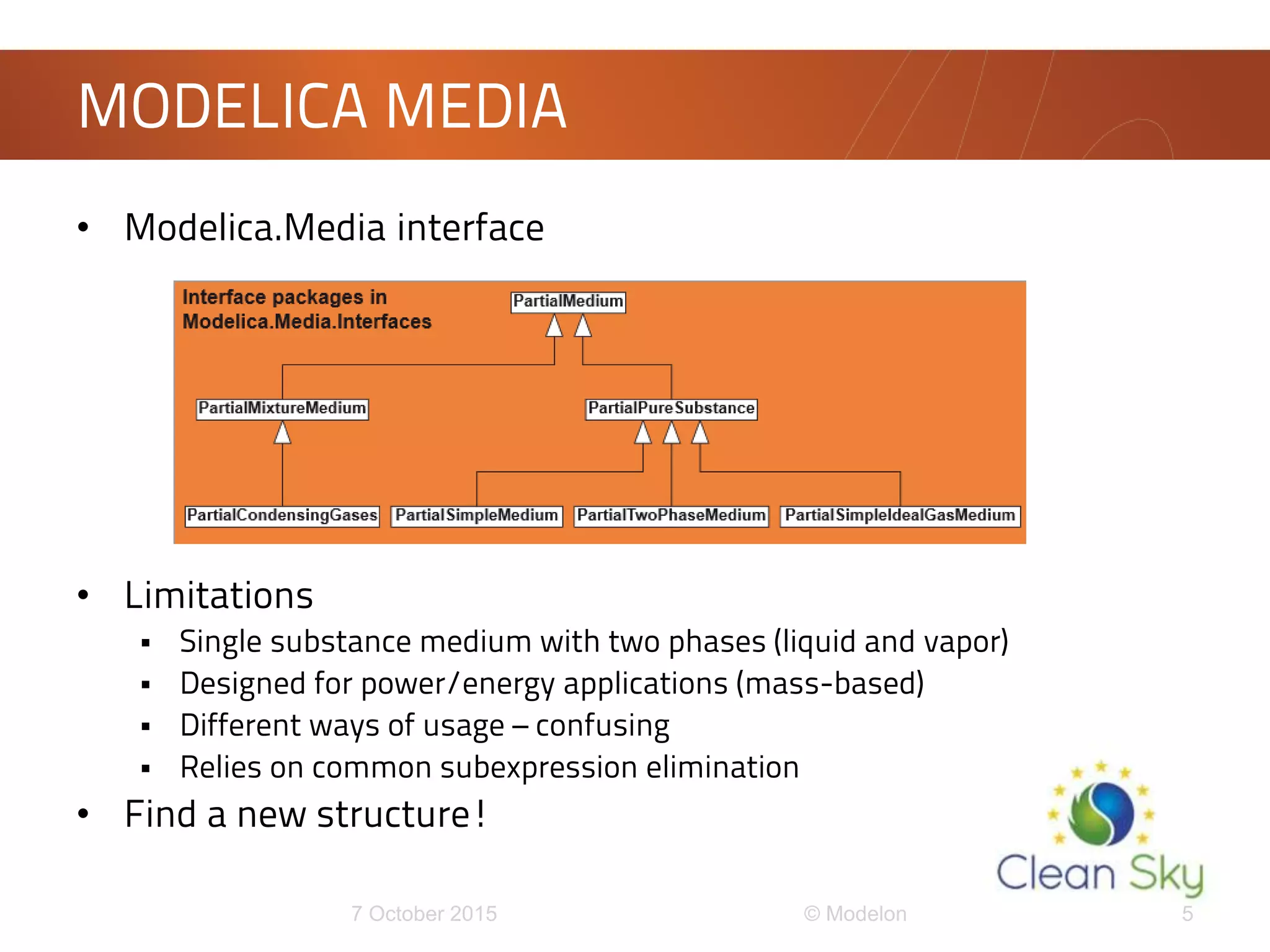
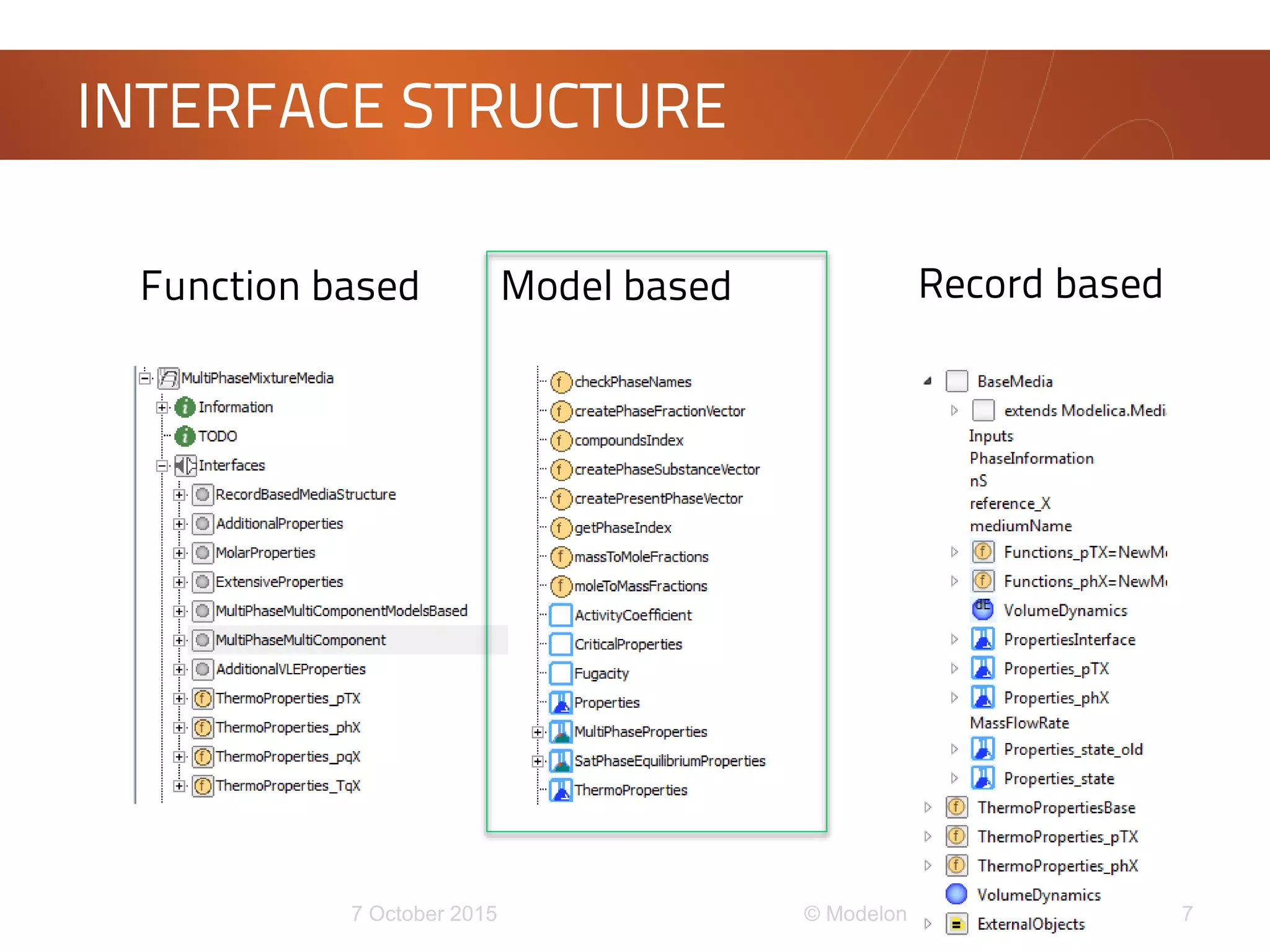
This document discusses the development of a new framework for modeling multi-component multi-phase mixtures in Modelica. The goals are to support both native Modelica media implementations and connections to external thermophysical property databases, address limitations of the existing Modelica.Media interface, and enable new applications involving multi-phase processes. A model-based interface structure is proposed to overcome restrictions of using pure functions. An example demonstrates the approach for simulating air separation processes using both a simple native Modelica air media and a connection to Refprop. Further testing and development is still needed to fully realize the new framework.


![MULTI-PHASE MIXTURE
• Package with models and helper functions
• ThermoProperties - similar to
BaseProperties in MSL
• parameters: inputs.pTX, init, optimization
• variables: p,T, d, … (mass and mole based)
• MultiPhaseProperties
• Overall (_overall) and single phase (_1ph)[nP]
properties
• phaseComposition, phaseFraction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multi-phasemixturemedia-151007144822-lva1-app6892/75/Multi-phase-mixture-media-9-2048.jpg)