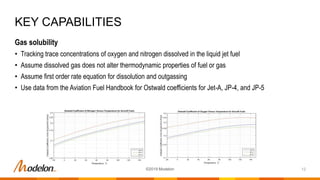
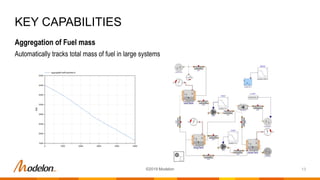
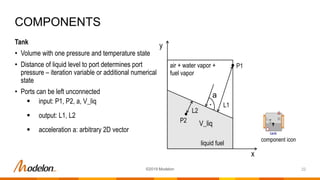
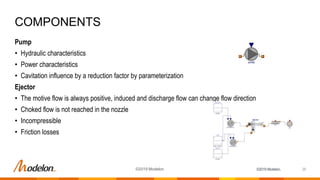
The document provides an overview of Modelon's fuel system library, designed for the simulation and analysis of fuel systems in civil and military aircraft under various operating conditions. Key capabilities include real-time simulation, handling of complex system dynamics, and integration with other Modelon libraries, while key applications encompass fuel transfer, inerting, and flammability assessments. The latest release, version 2019.2, features enhanced model compatibility and new calculation tools for improved accuracy and functionality.






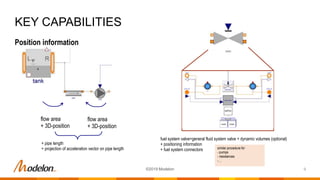
![Position information
Pipes
• Receive position information and cross sectional area from connected components
• Receive acceleration vector via inner/outer
• Optional dynamic momentum balance: pressure drop, static head and resistance losses can be computed
from massflow as state
All other components
• Set position information and cross section for each connection point
• Optional multibody frame connector can be enabled to set position
• Numerical states: p, T, X[1:nS-1]
• Acceleration is only accounted for in pipe and tank models
KEY CAPABILITIES
8©2019 Modelon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fsl-2019-191016191404/85/Fuel-System-Library-Overview-8-320.jpg)