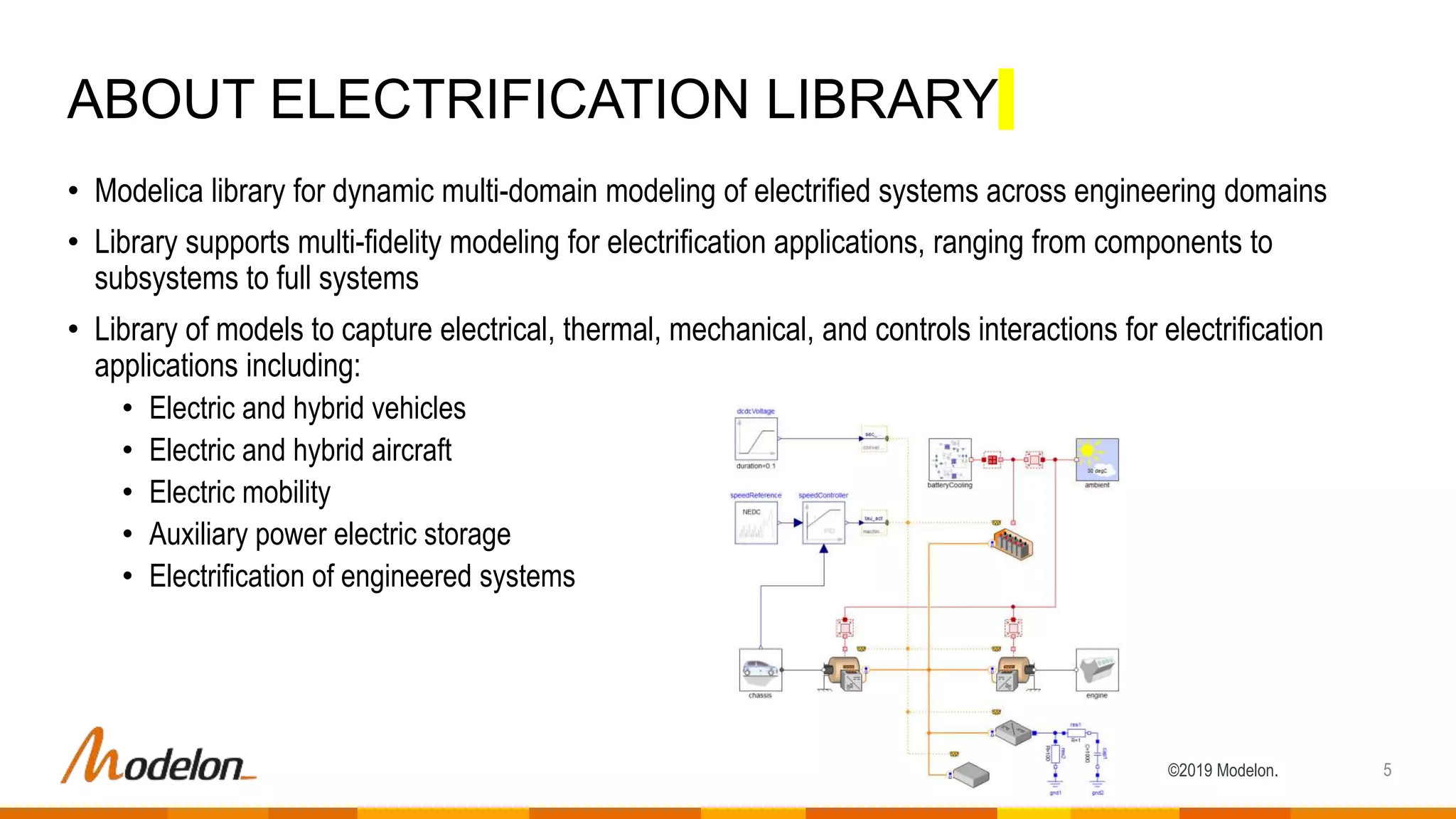
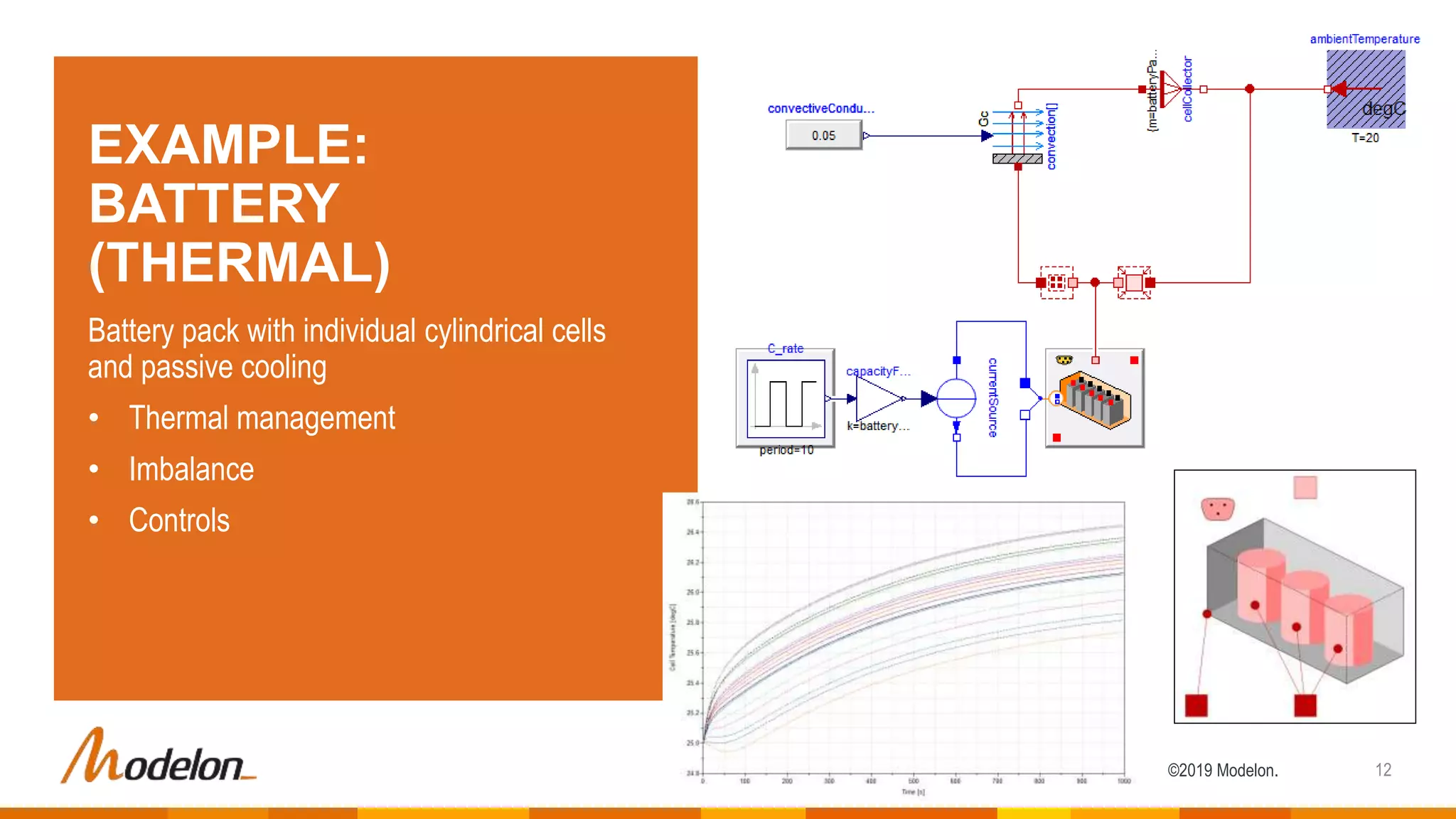
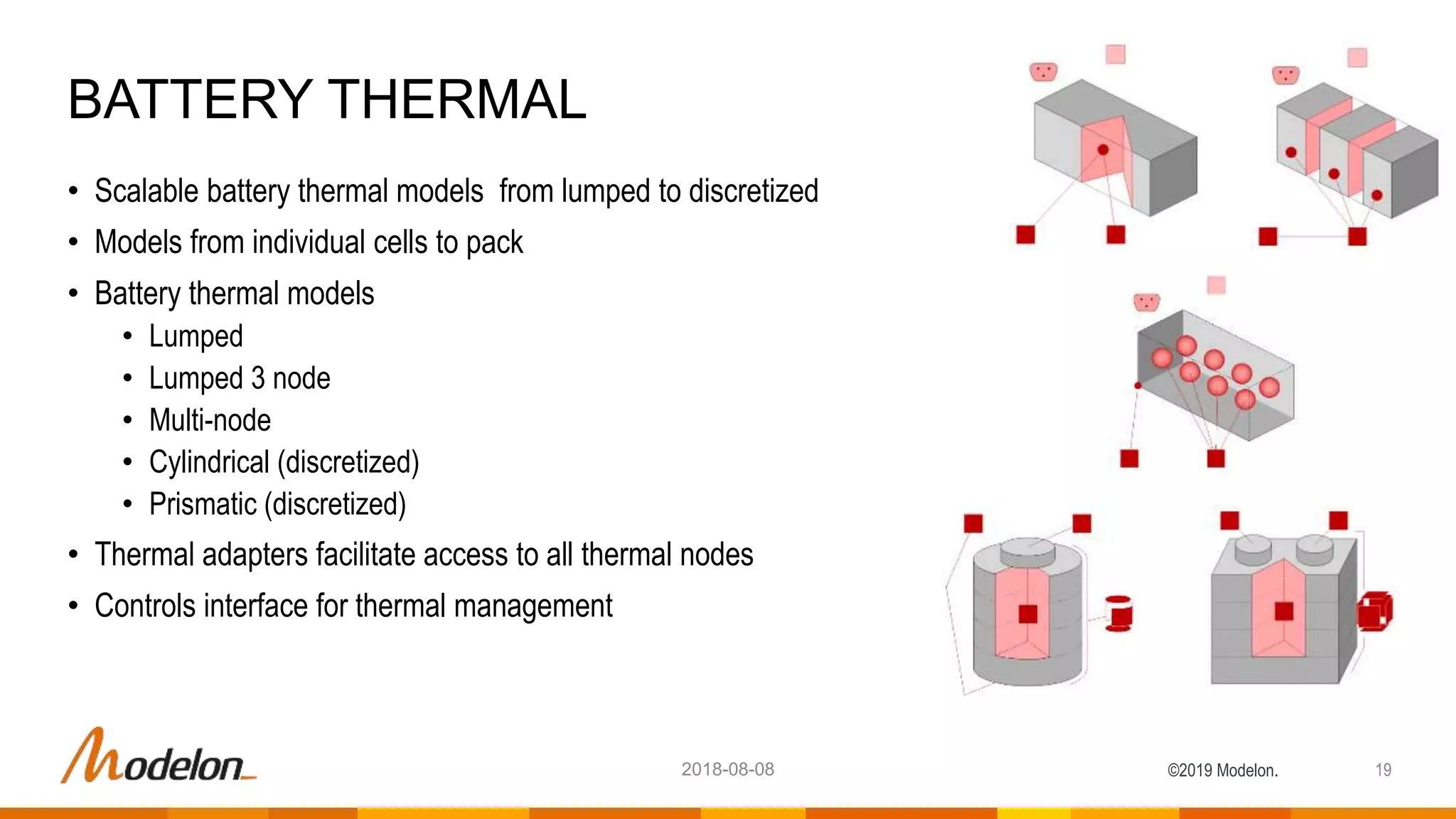
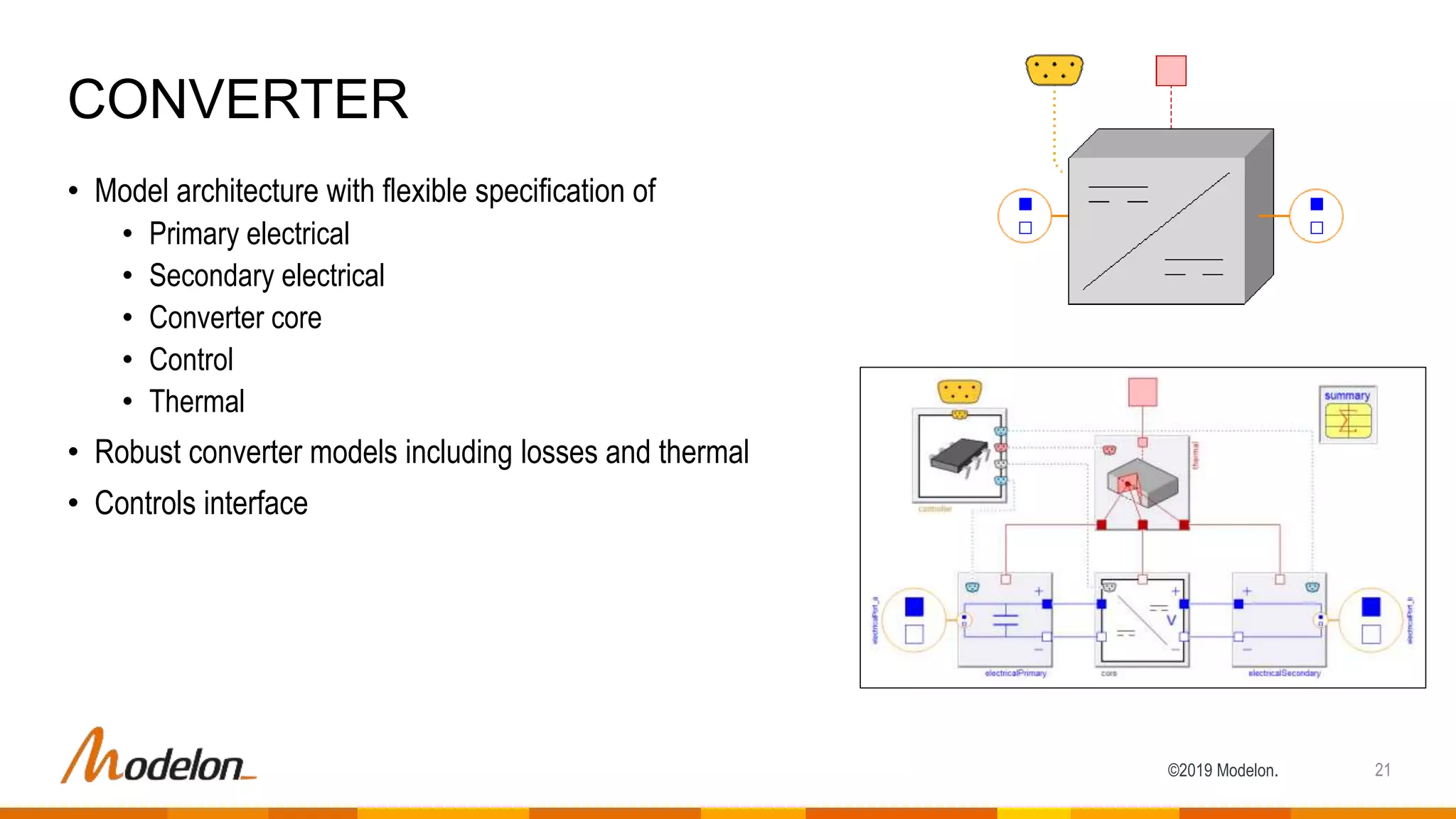
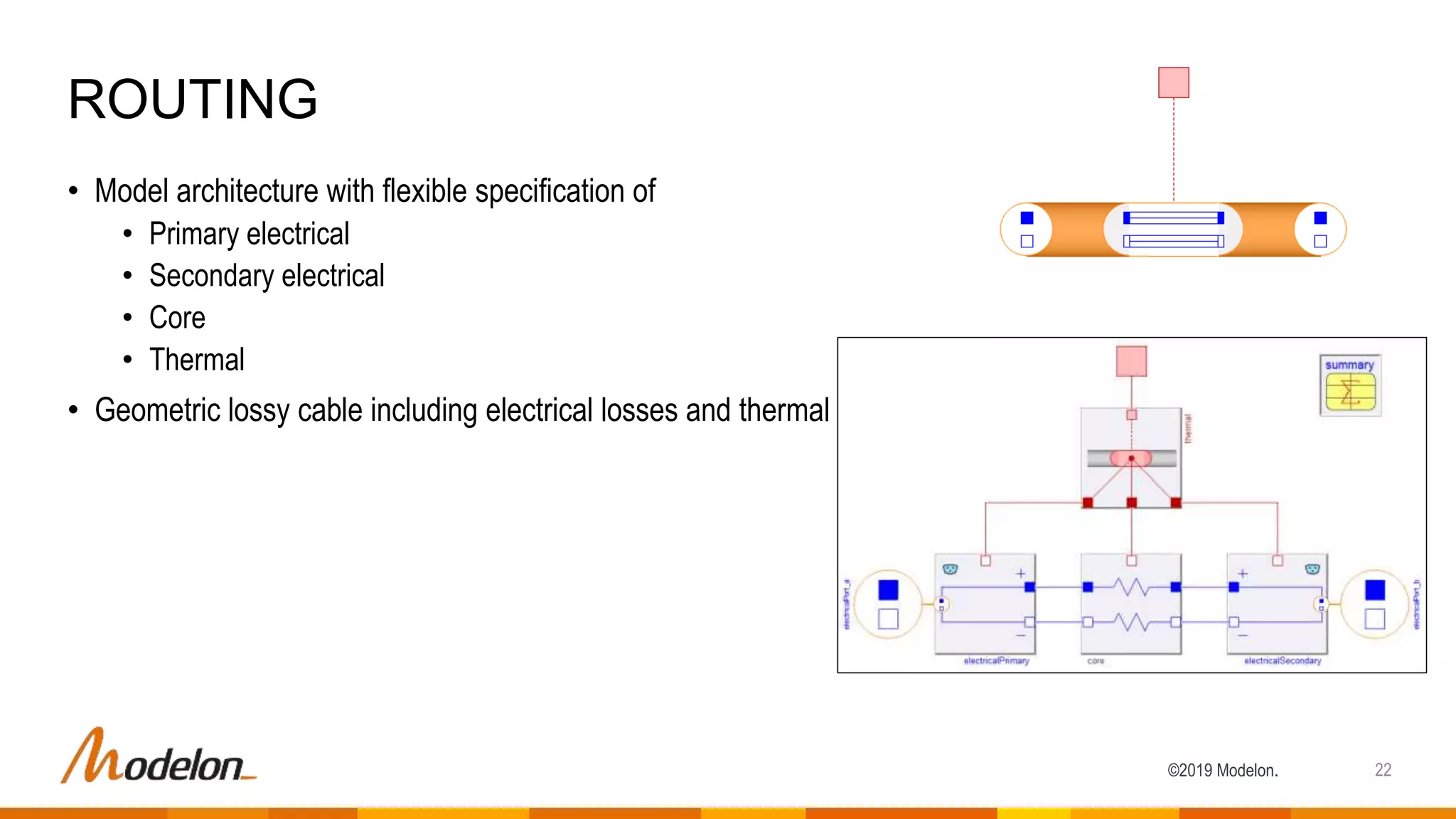
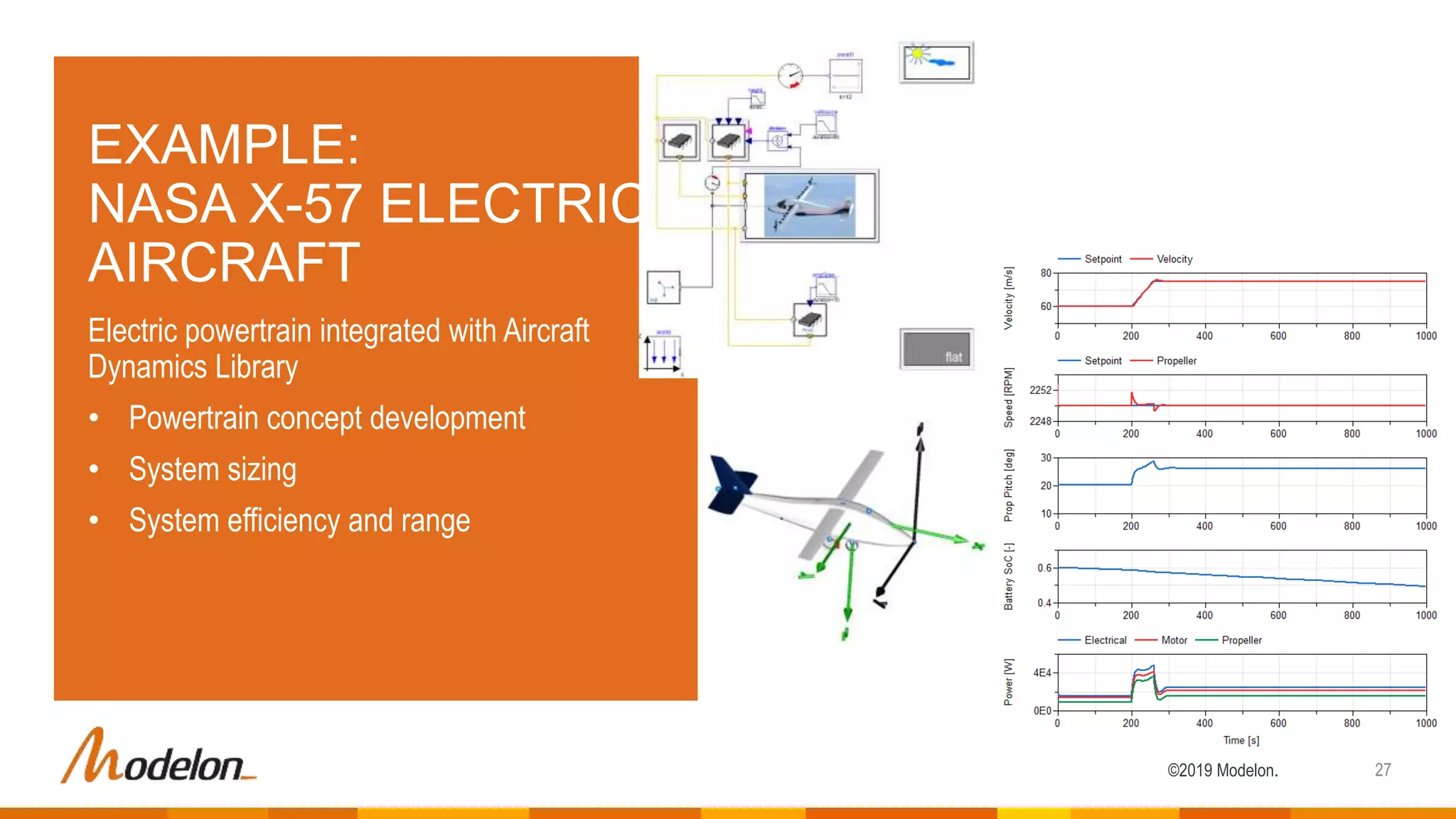
The document describes the Modelon Electrification Library, which provides component models for modeling electrified systems. The library contains scalable and reusable models of batteries, electric machines, power converters, and other components. It supports modeling of electrified vehicles, aircraft, and other applications across different engineering domains. The library allows for multidisciplinary and multilevel system modeling from components to subsystems to whole systems.