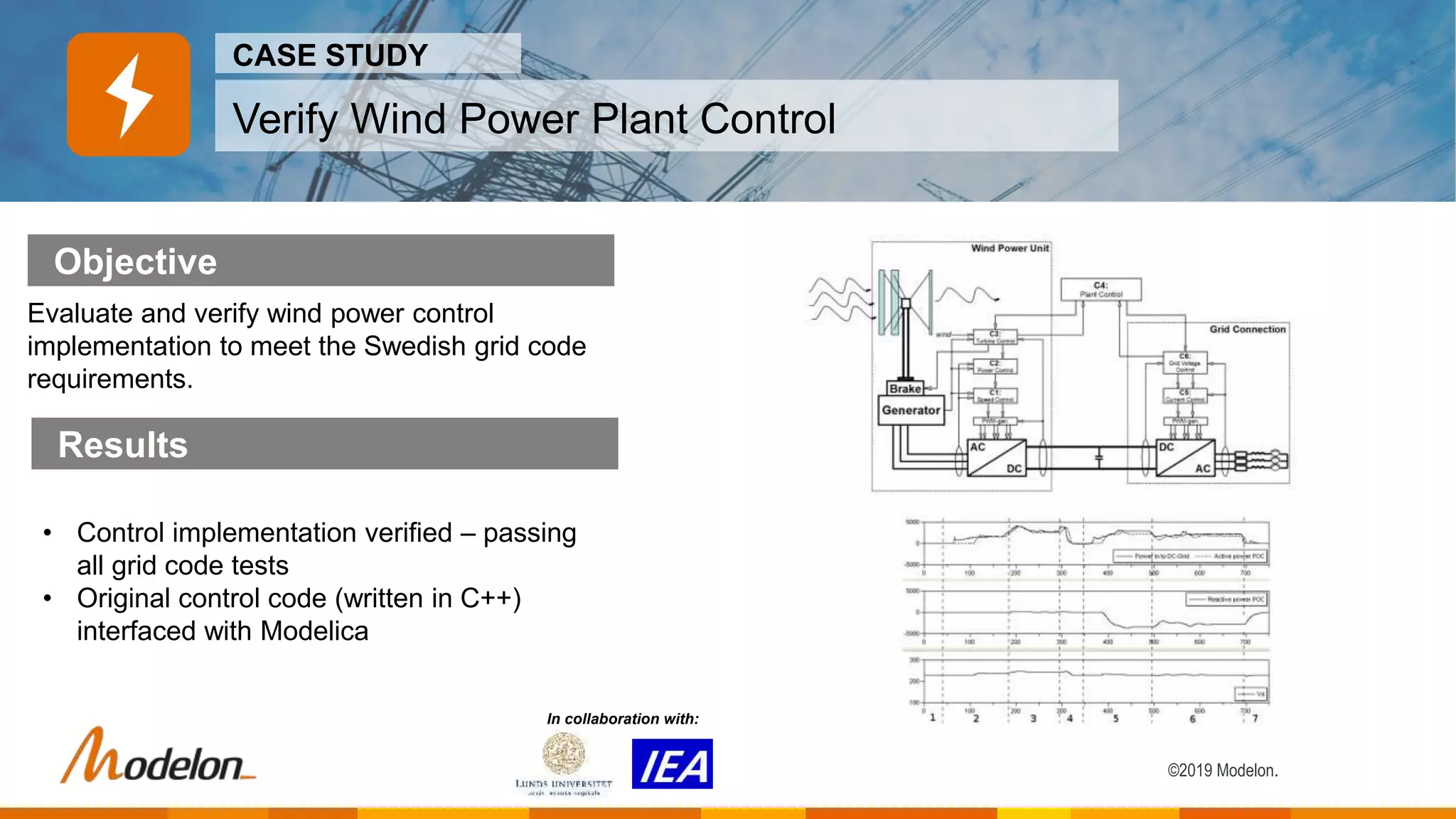
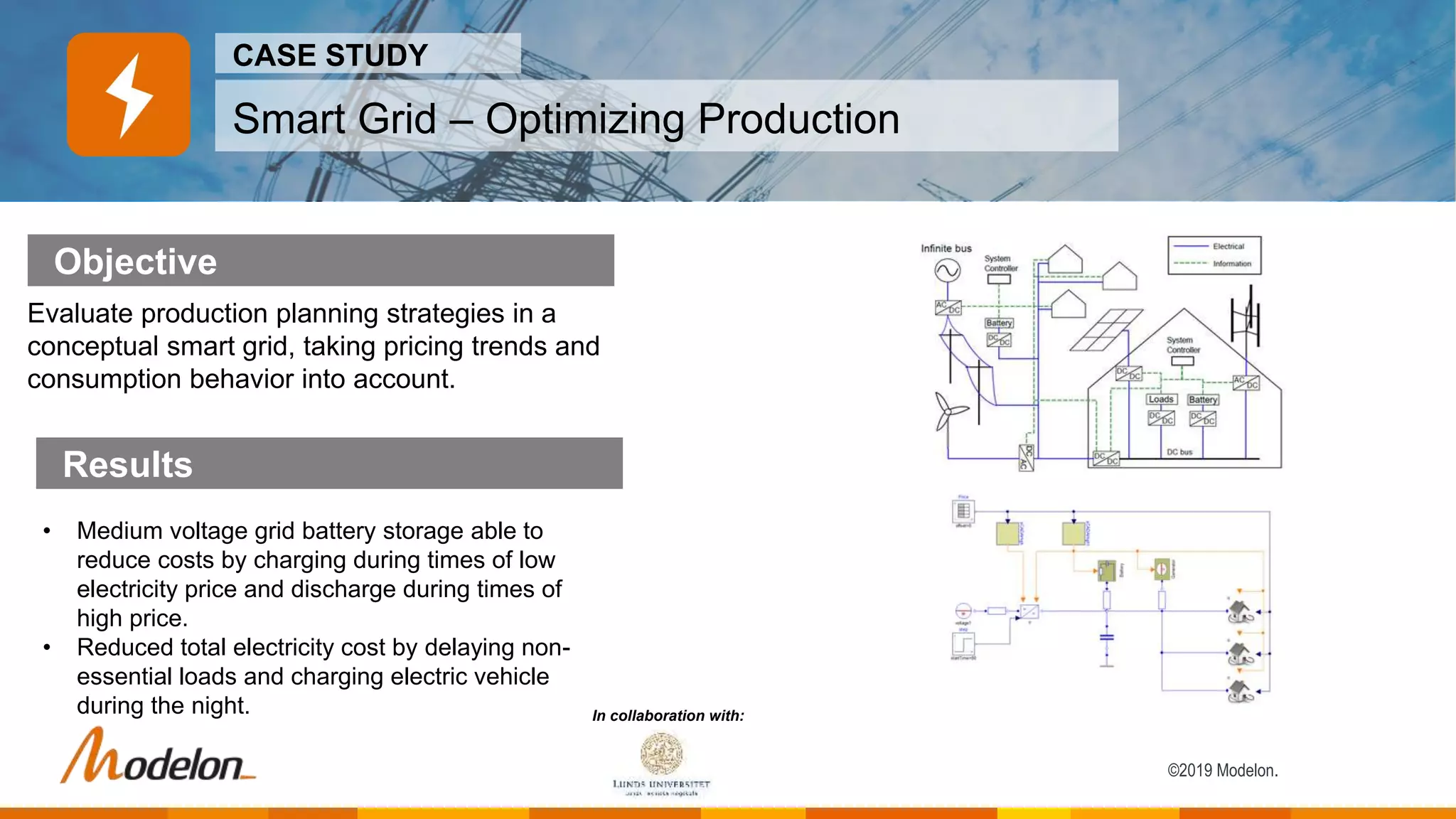
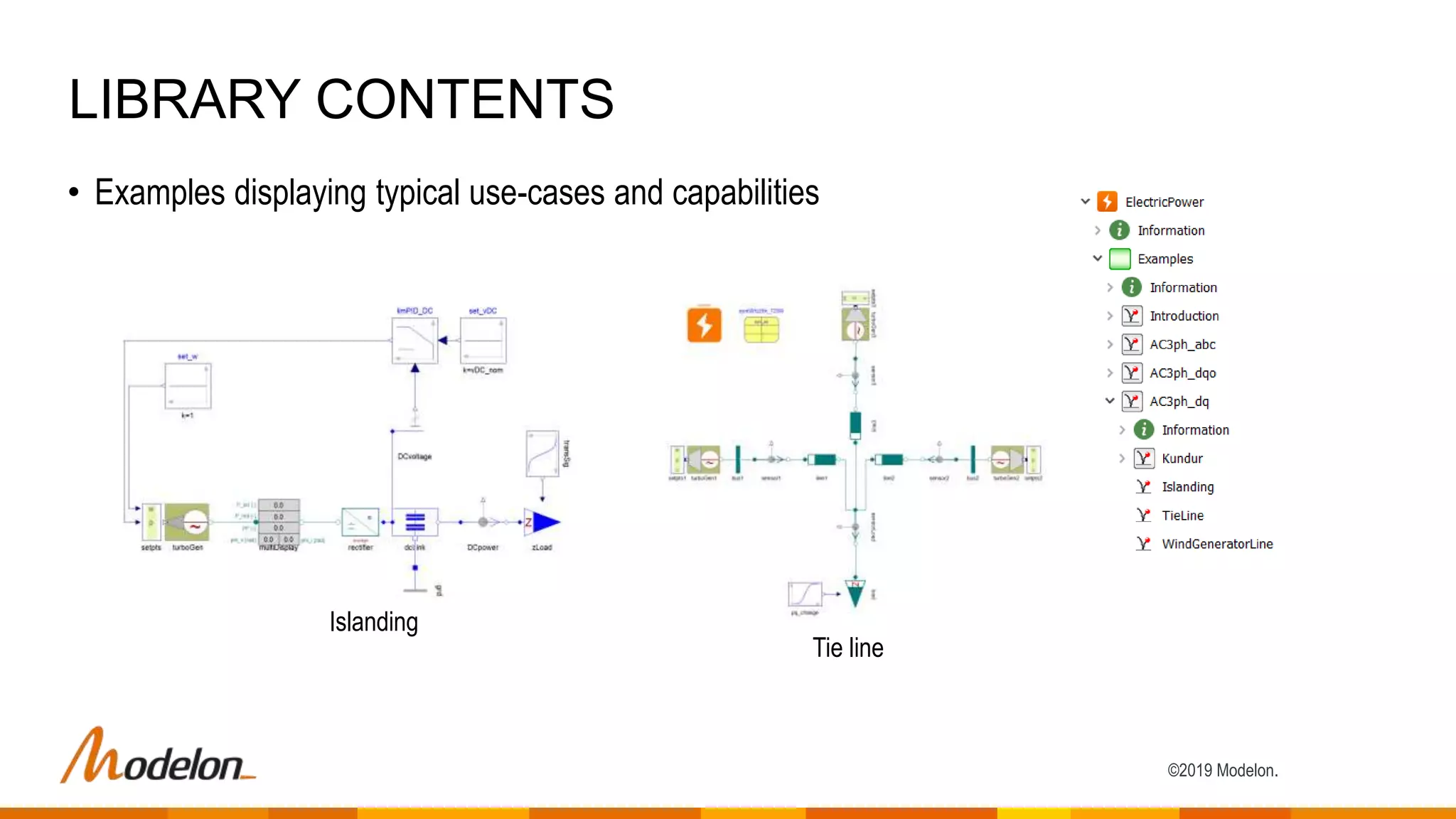
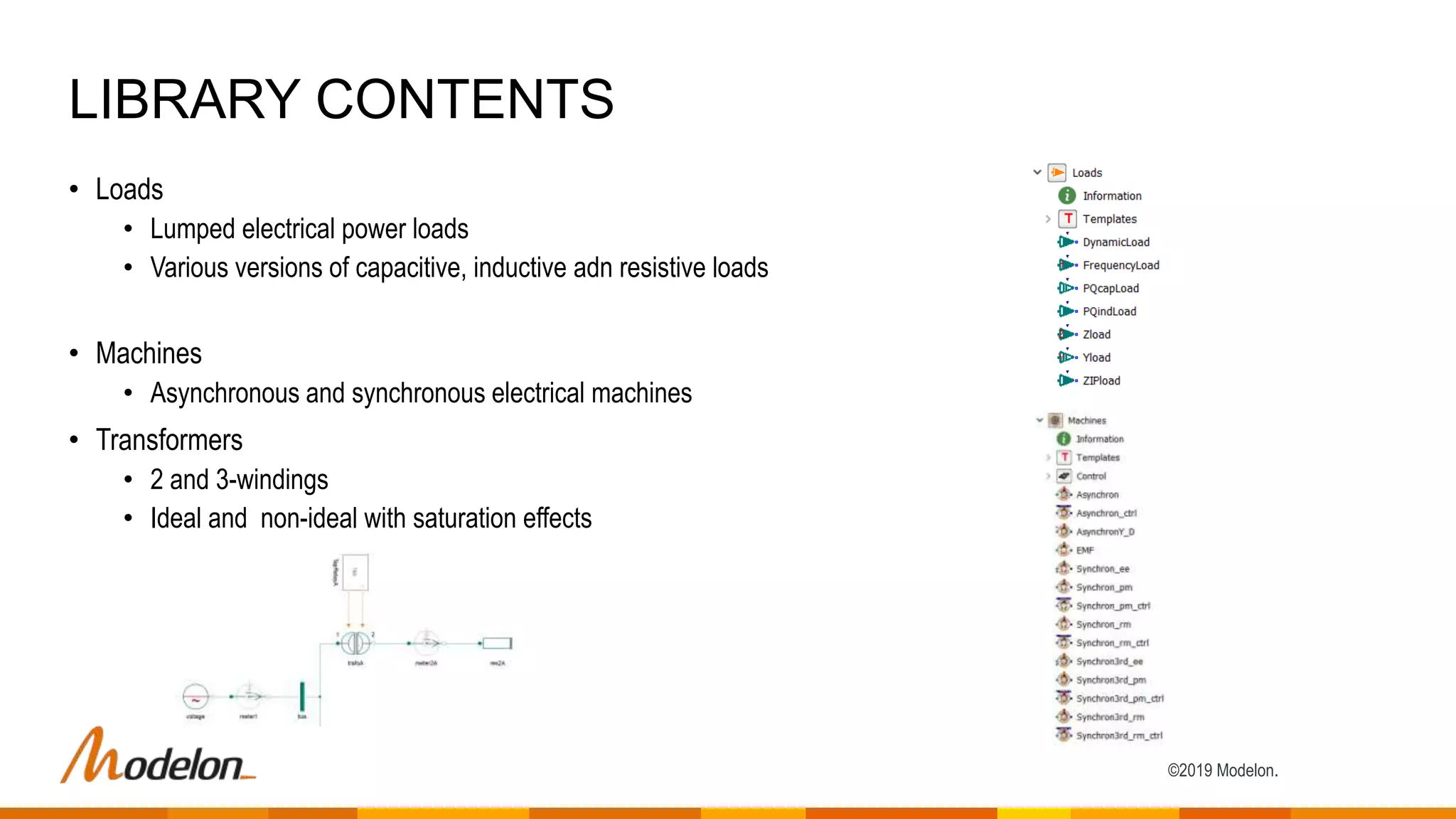
The Electric Power Library by Modelon facilitates the simulation of electric power systems, enabling testing, design verification, and analysis across various applications such as power generation and smart grids. It features multi-domain capabilities, fast simulations, and is compatible with other libraries like the thermal and hydro power libraries, providing a comprehensive tool for engineers and researchers. Case studies demonstrate its effectiveness in enhancing grid stability, investigating failures, and optimizing production planning strategies.