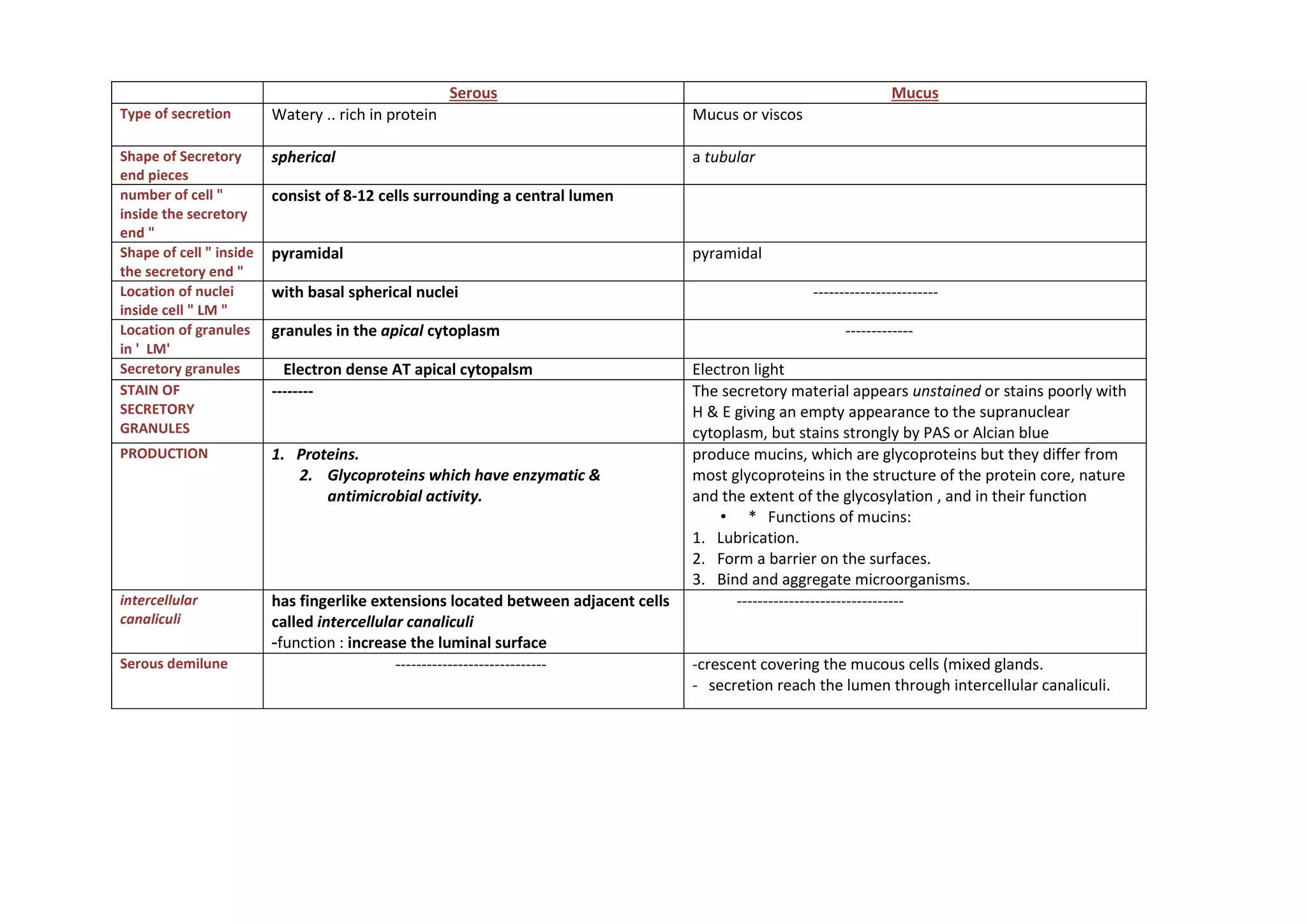
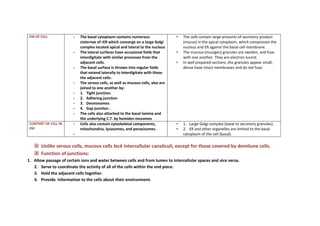
The document details the characteristics and functions of mucus-secreting cells, including the structure of secretory granules and their role in lubrication and barrier formation. It explains the cellular organization, including the presence of intercellular canaliculi, tight junctions, and various organelles such as Golgi complexes and endoplasmic reticulum. The document highlights the differences between serous and mucous cells in terms of their secretory mechanisms and cellular architecture.