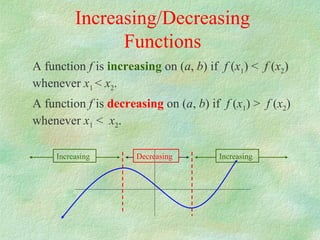
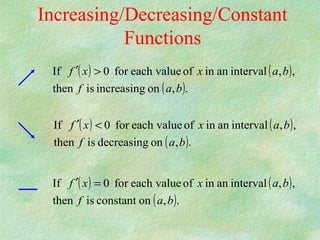
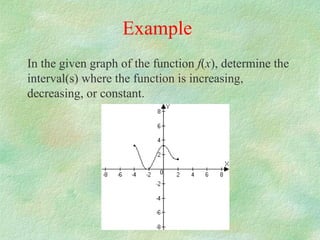
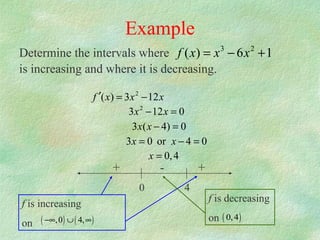
The document discusses how to determine if a function is increasing or decreasing on an interval using the derivative. It states that if the derivative is positive on an interval, the function is increasing on that interval, and if the derivative is negative, the function is decreasing. It provides steps to determine where a function is increasing or decreasing: 1) take the derivative, 2) find critical points where the derivative is 0 or undefined, 3) plot critical points to get intervals, 4) check sign of derivative in intervals. An example problem demonstrates finding the intervals where a cubic function is increasing or decreasing.