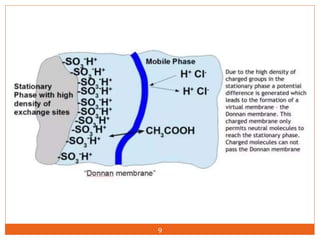
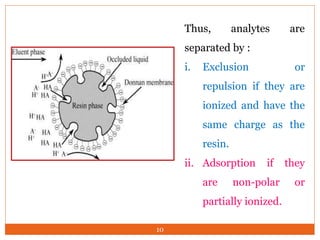
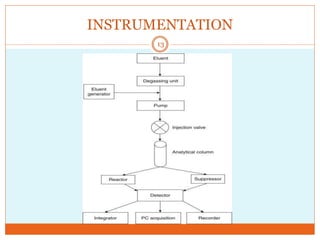
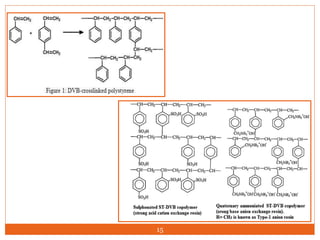
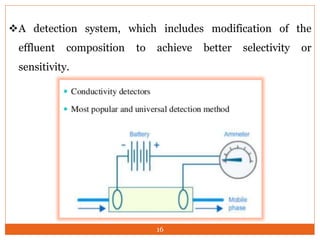
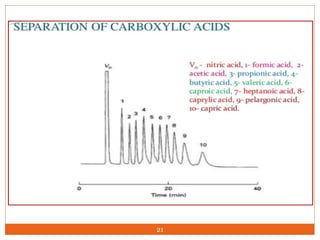
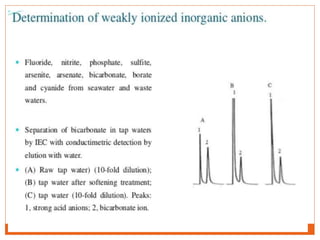
Ion exclusion chromatography (IEC) is a technique for separating ionic from non-ionic compounds and is characterized by the quick passage of ionic substances through the column while non-ionic substances are delayed. Its mechanism relies on a Donnan exclusion process where the formation of a pseudo semi-permeable membrane around the resin phases facilitates the separation based on charge interactions. IEC has applications in the analysis of weak acids, carbohydrates, phenols, and amino acids, and features low organic solvent use for environmental compatibility.