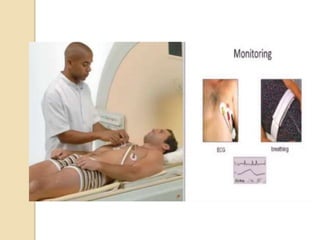
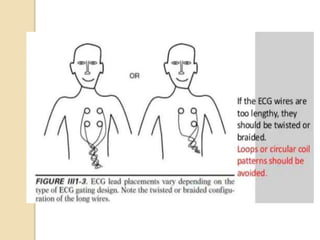
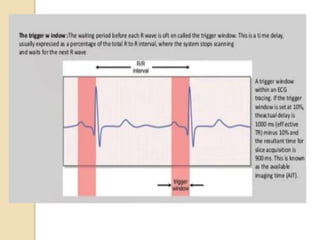
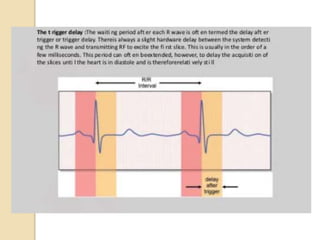
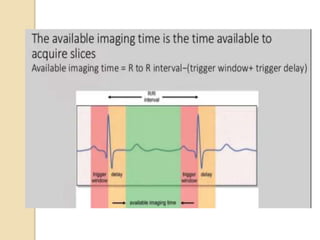
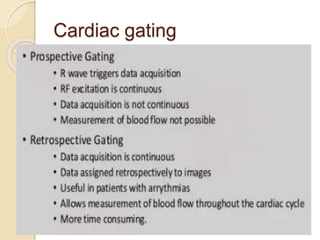
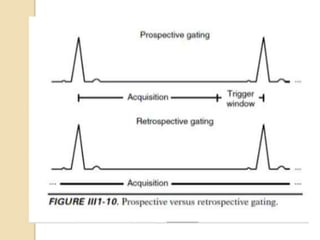
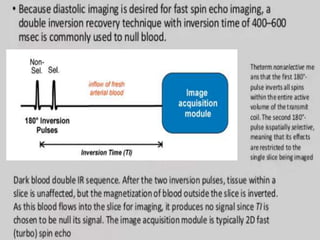
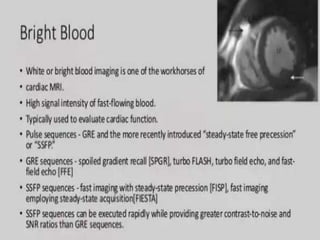
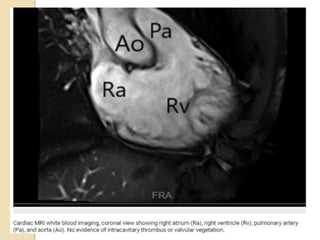
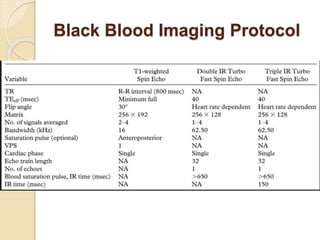
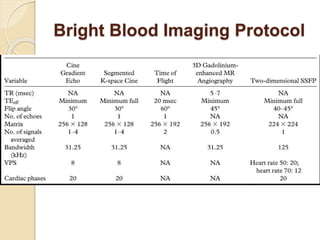
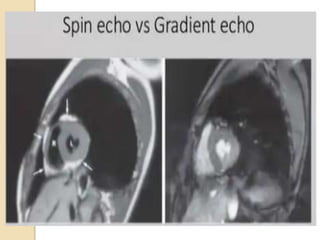
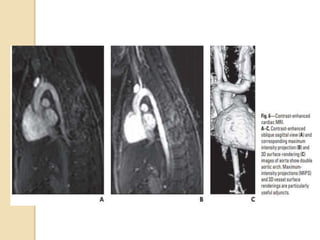
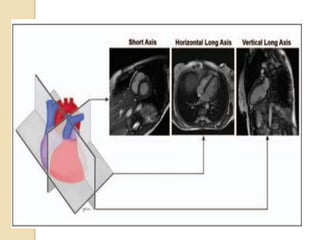
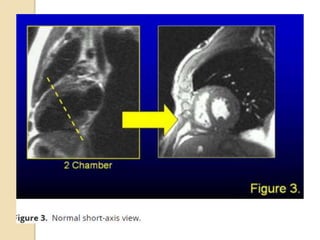
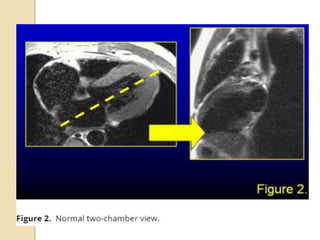
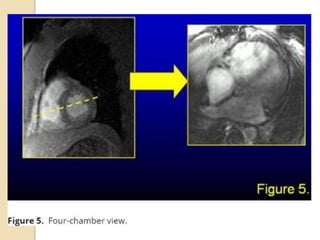
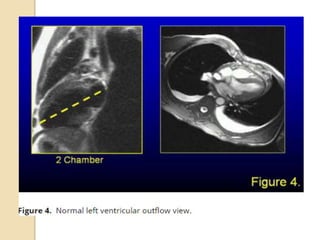
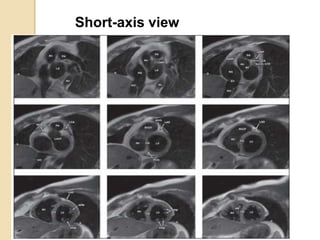
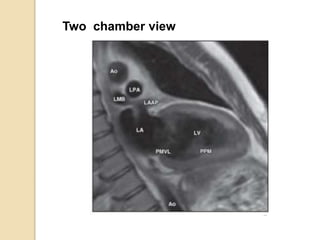
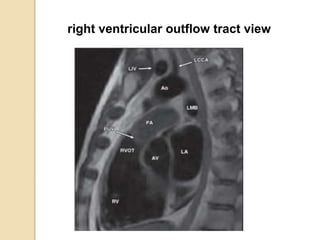
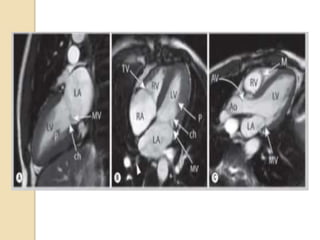
Cardiac MRI uses MRI techniques to study the heart's anatomy, physiology, and pathology. It offers improved soft tissue definition compared to other modalities and does not use ionizing radiation. The basic sequences include black blood imaging for anatomy and bright blood imaging for assessing flow and motion. Black blood sequences like spin echo are used while bright blood uses gradient echo. Cine imaging captures motion throughout the cardiac cycle. Contrast-enhanced techniques like perfusion and delayed enhancement imaging are used to identify infarcts and viability. Standard cardiac planes include the short axis, 4-chamber, and 2-chamber views.