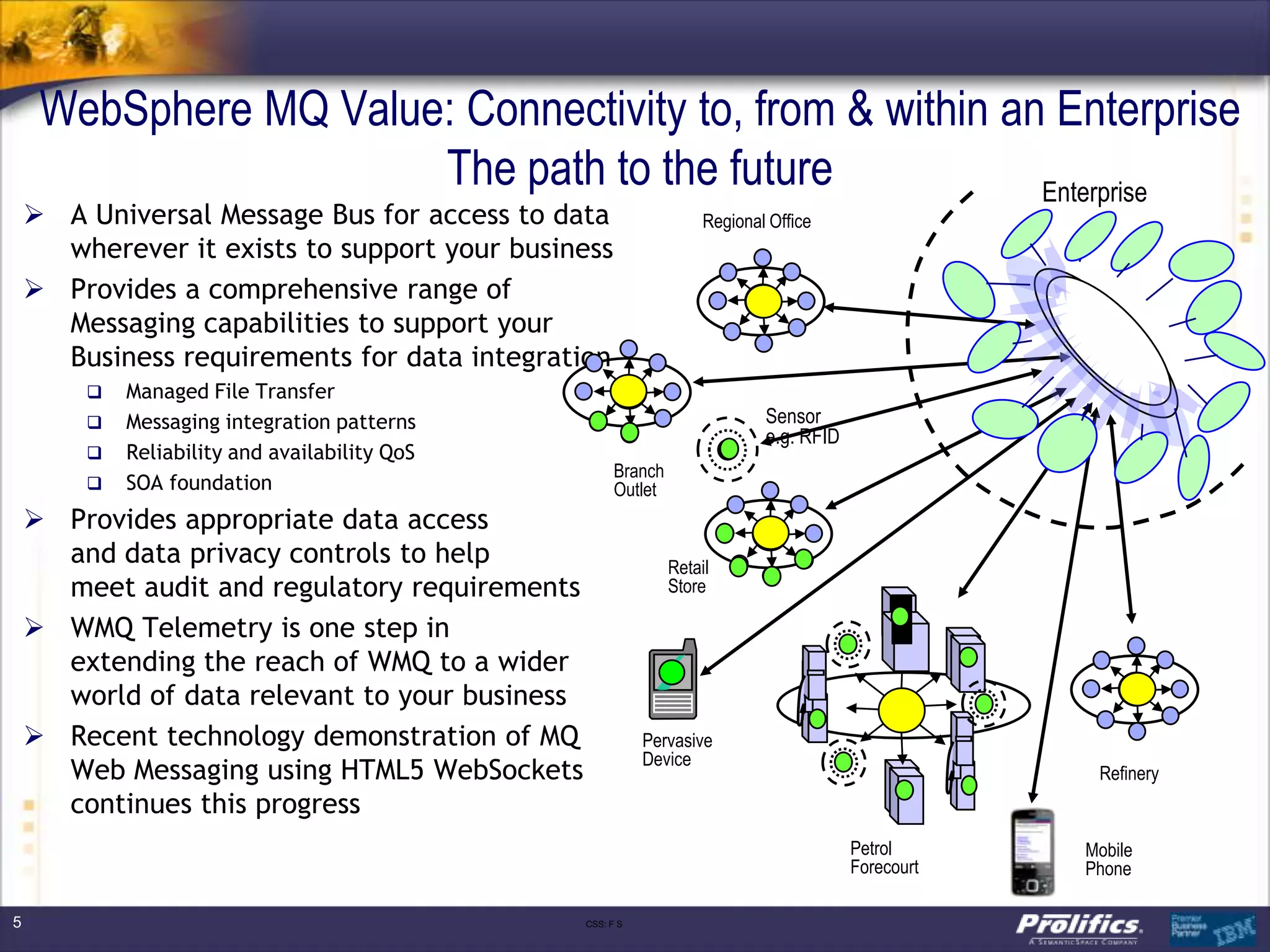
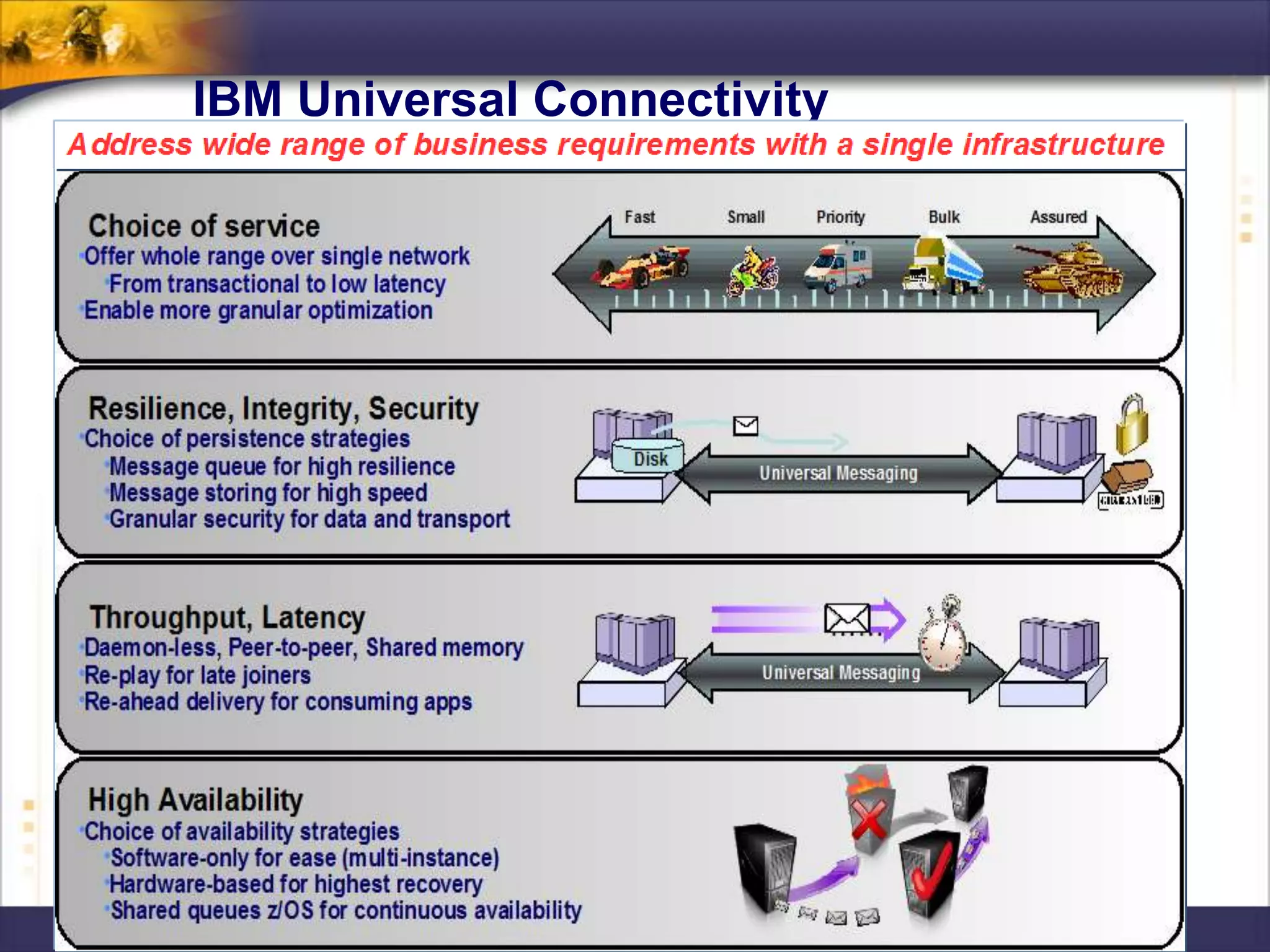
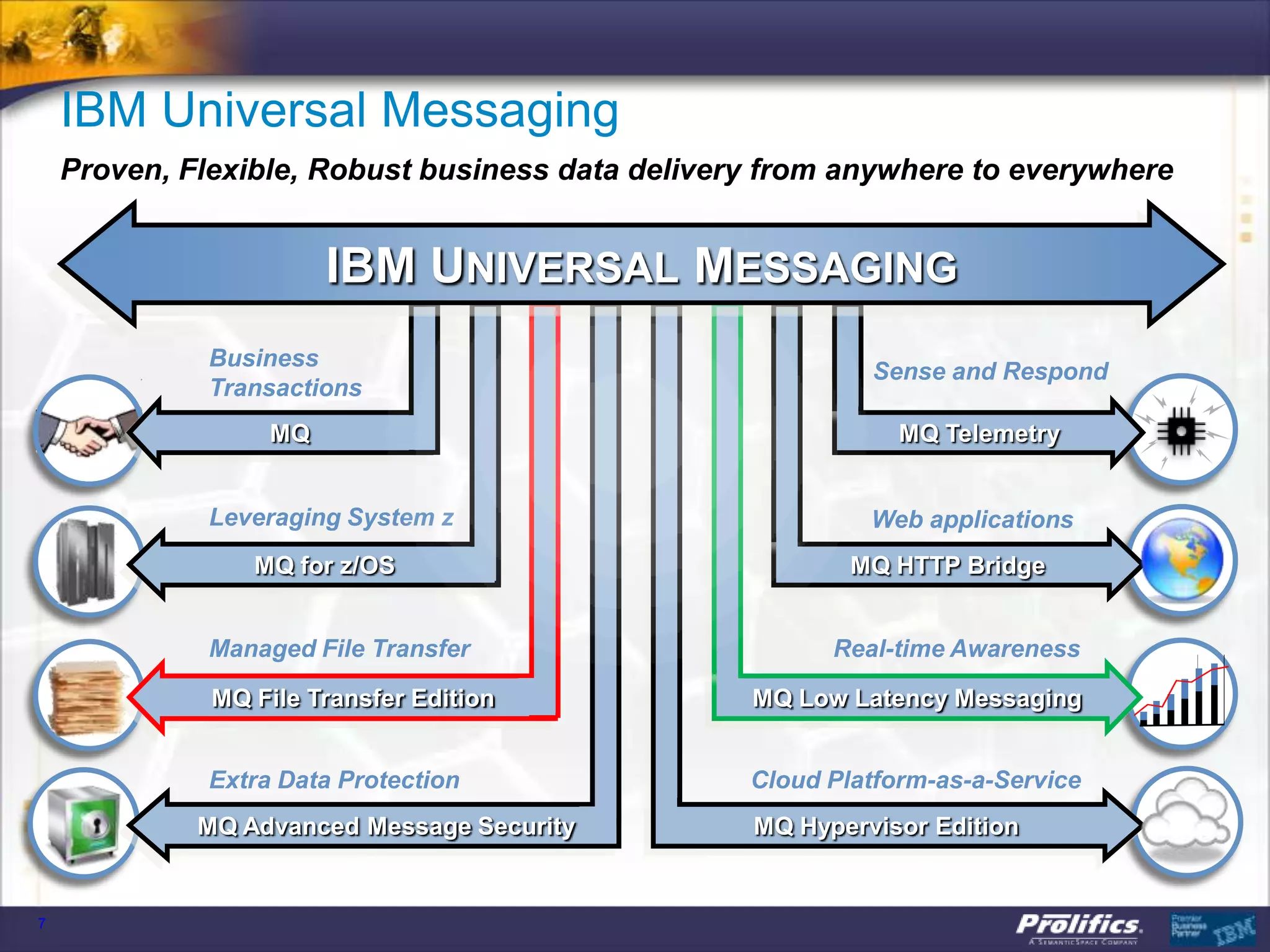
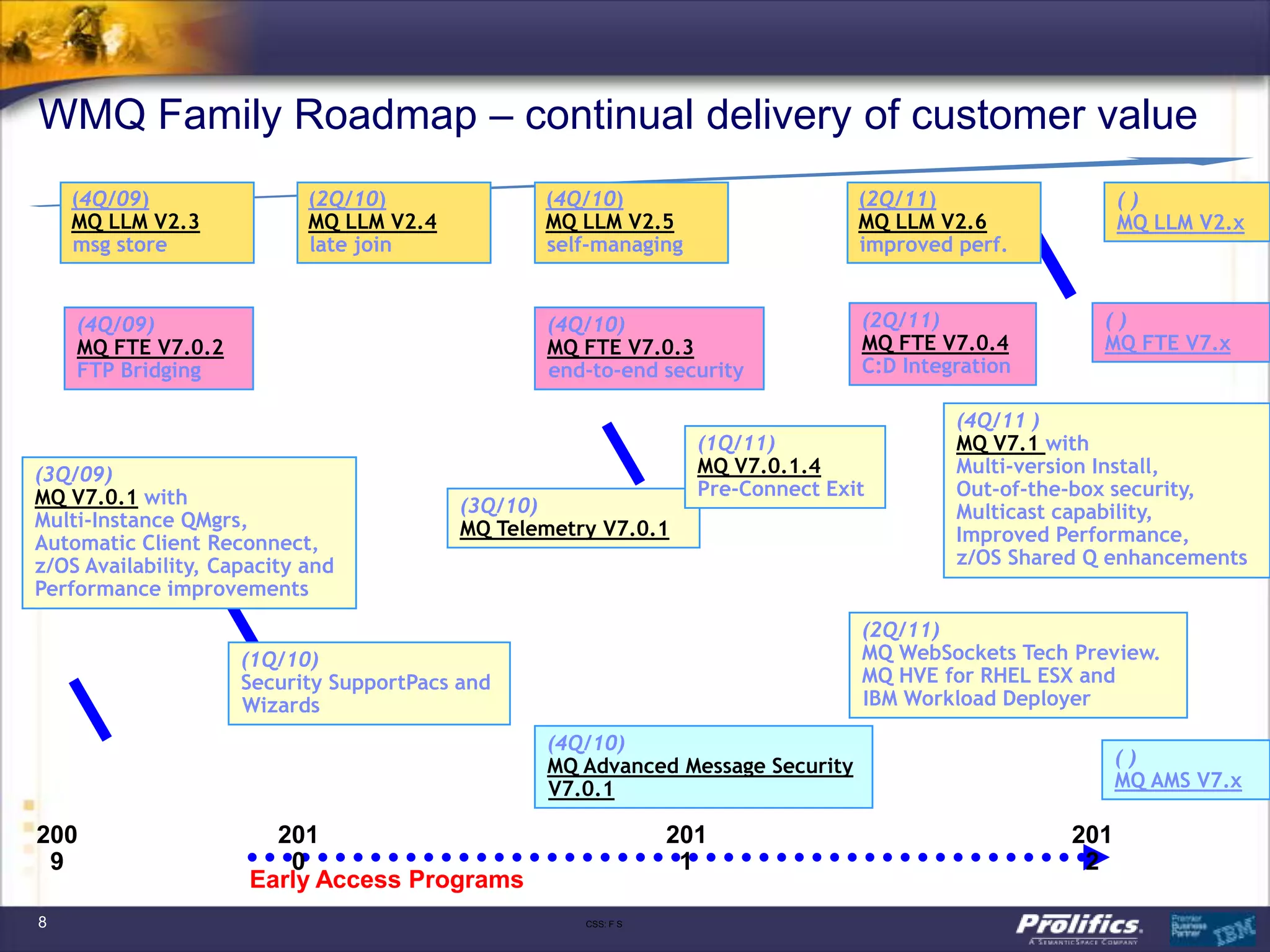
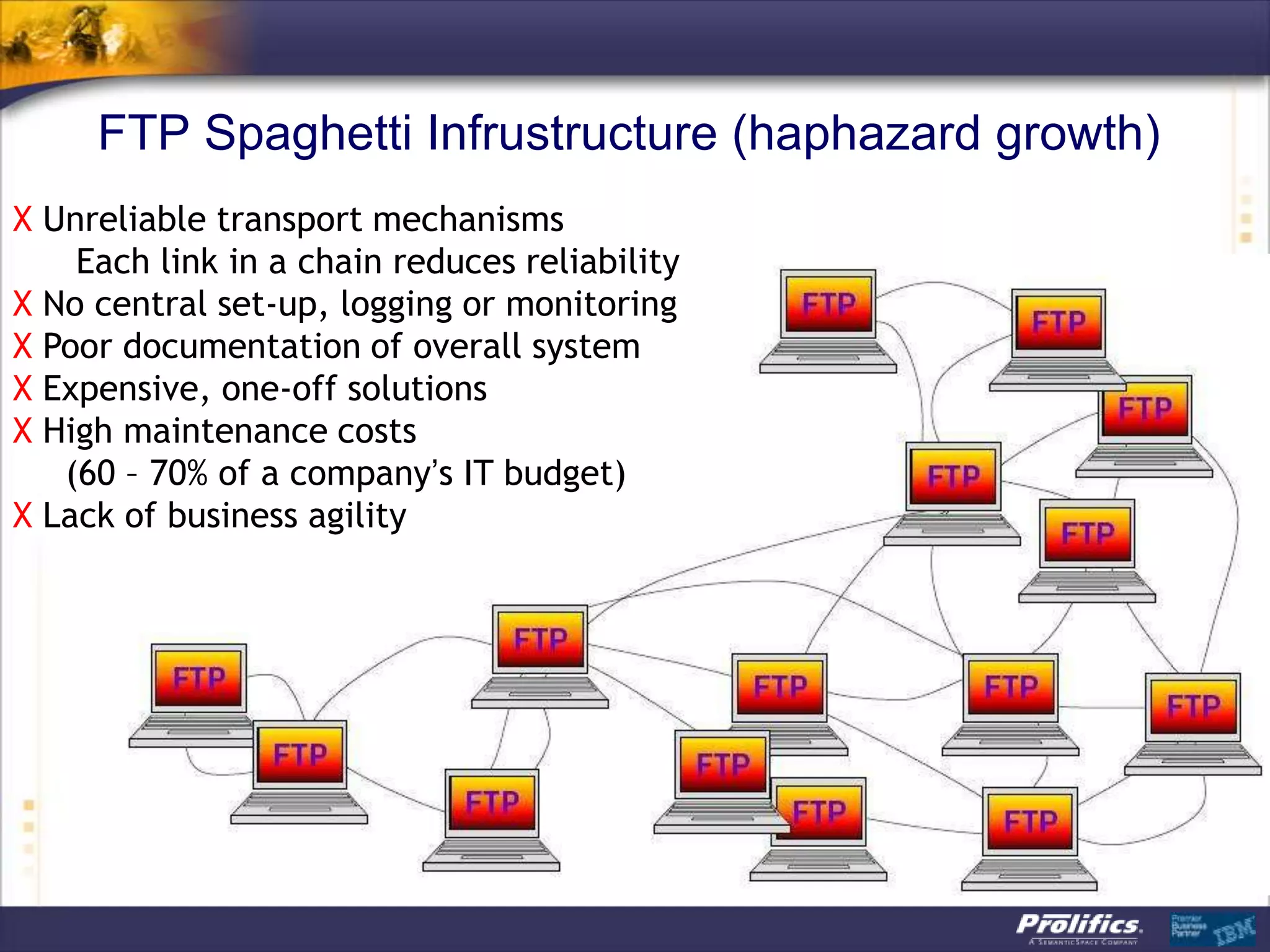
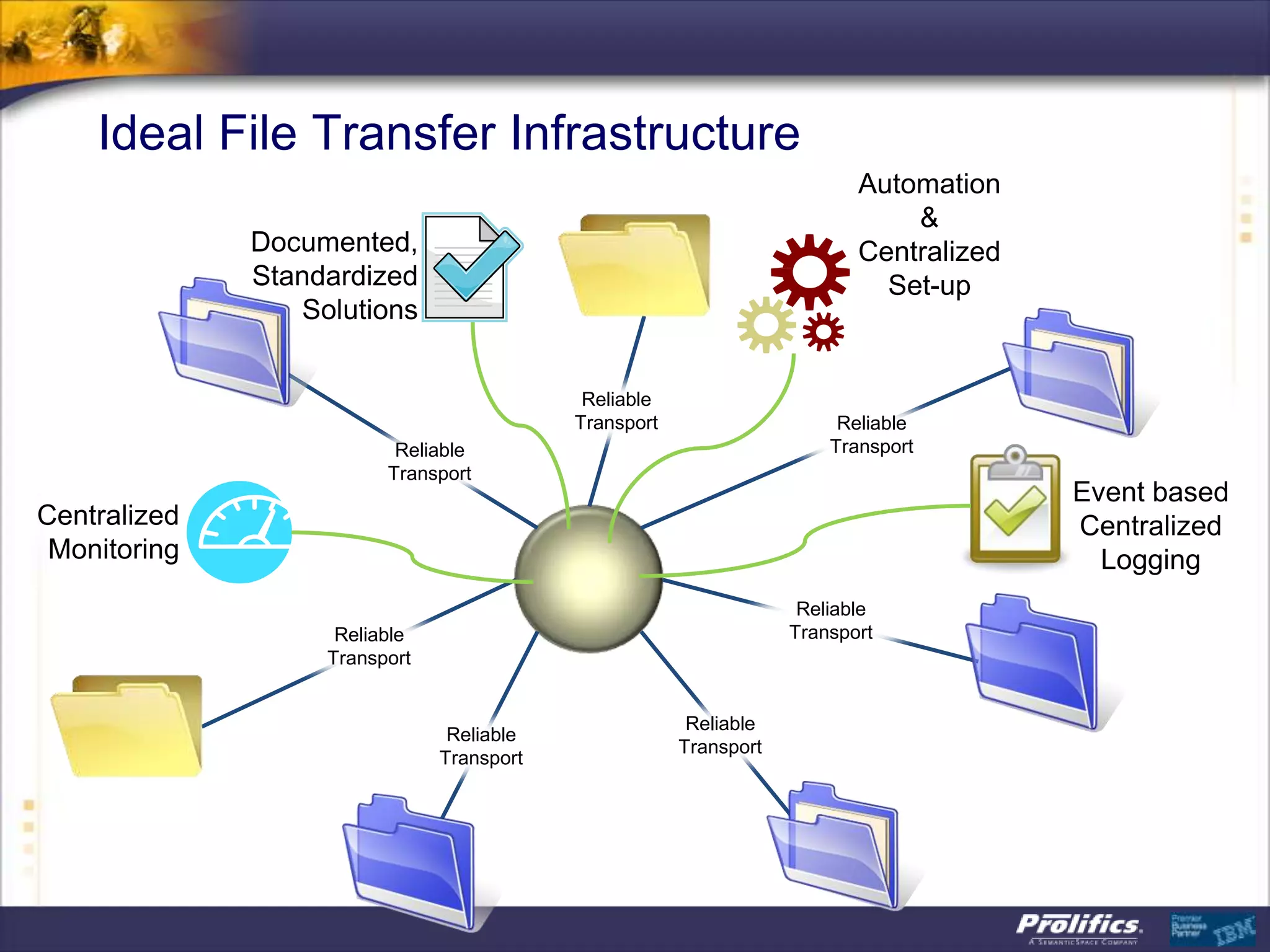
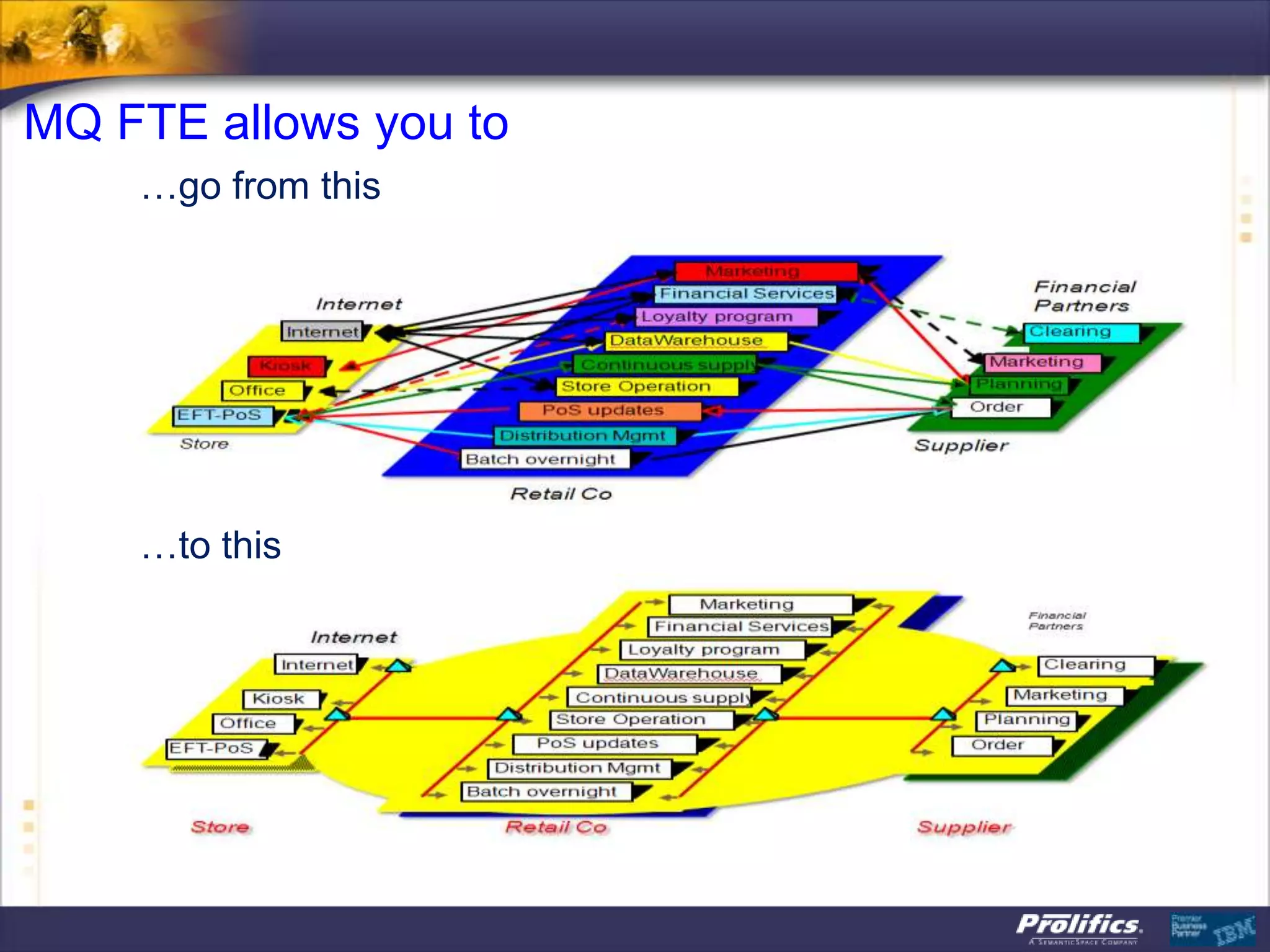
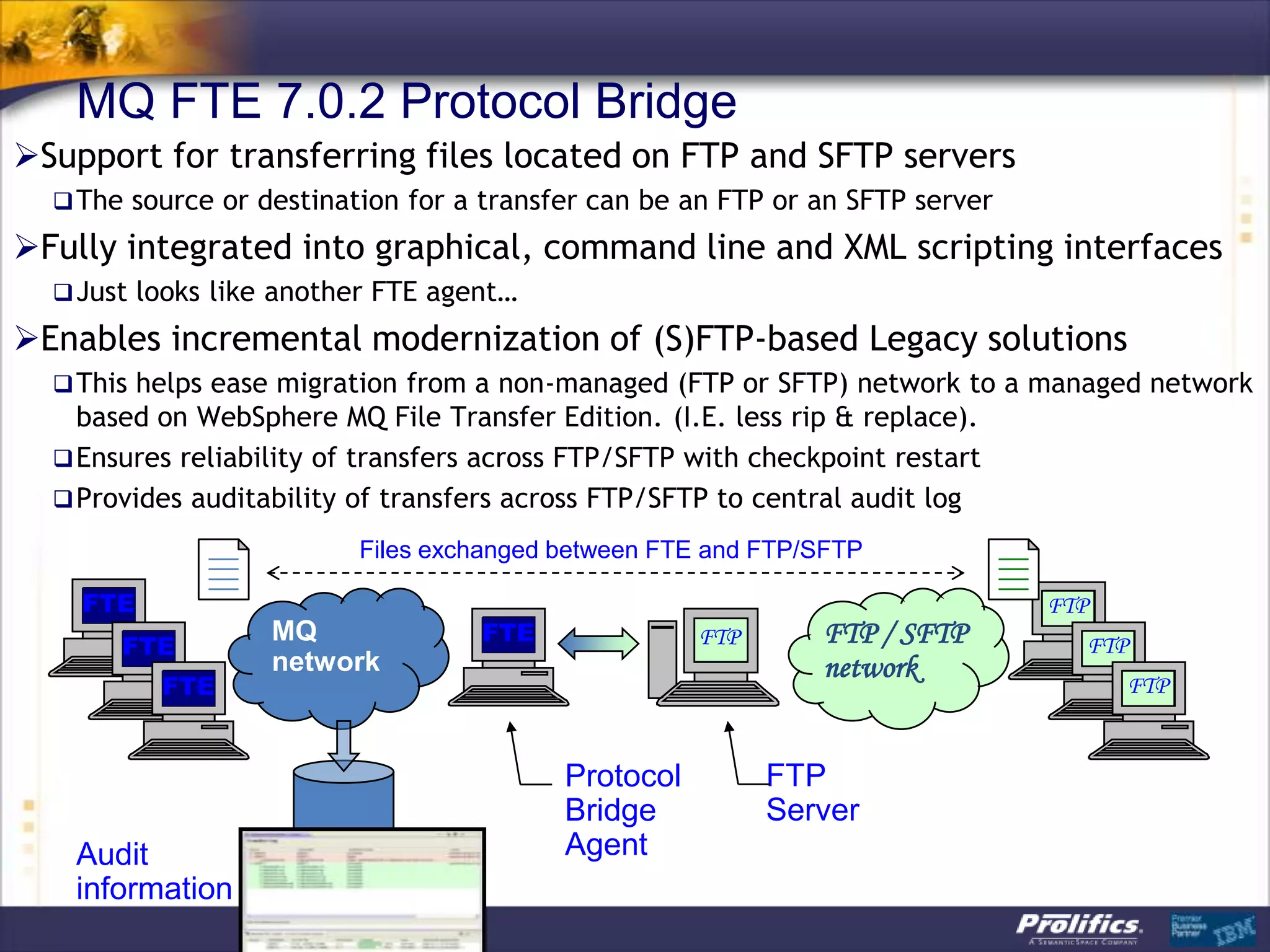
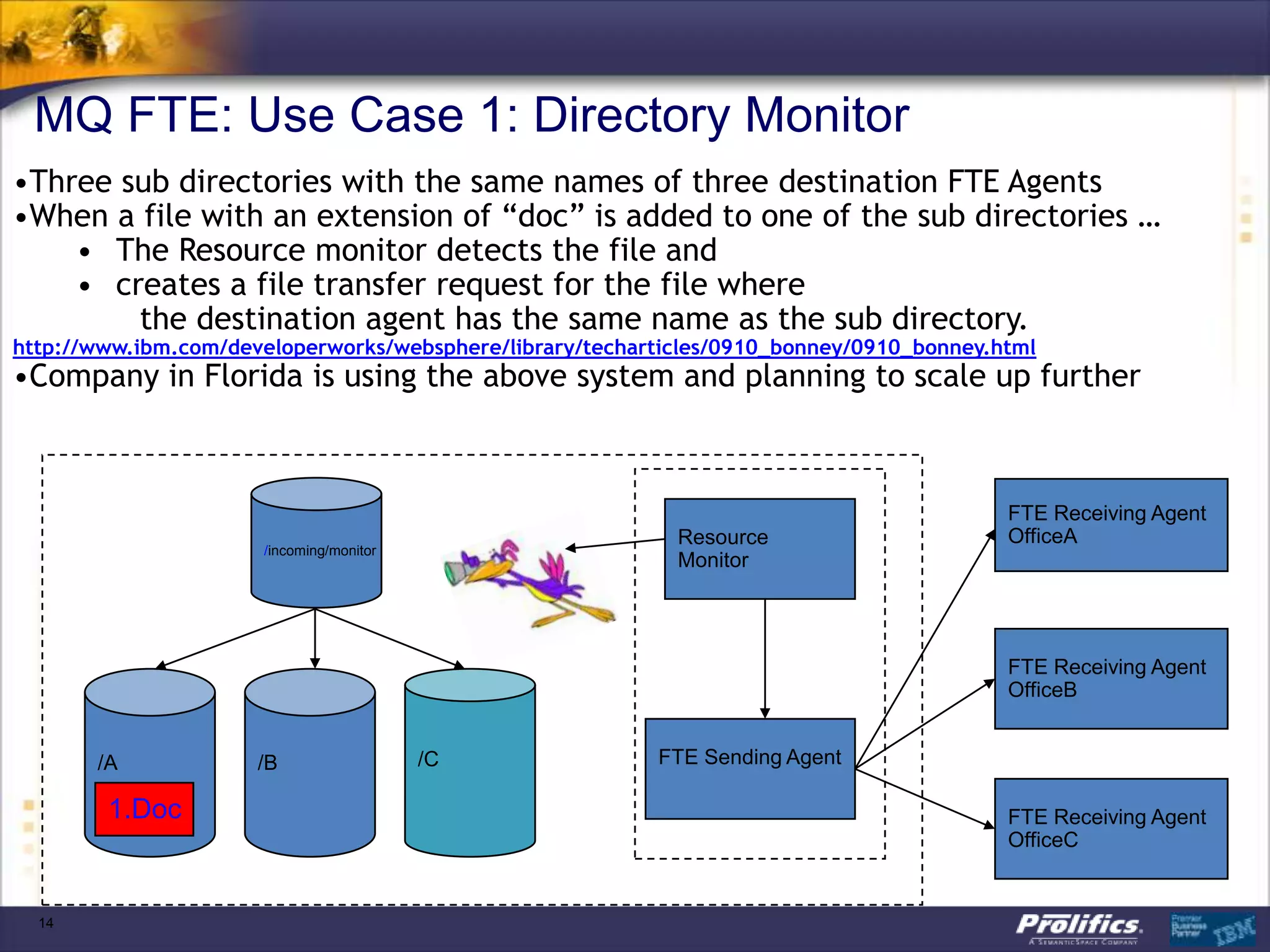
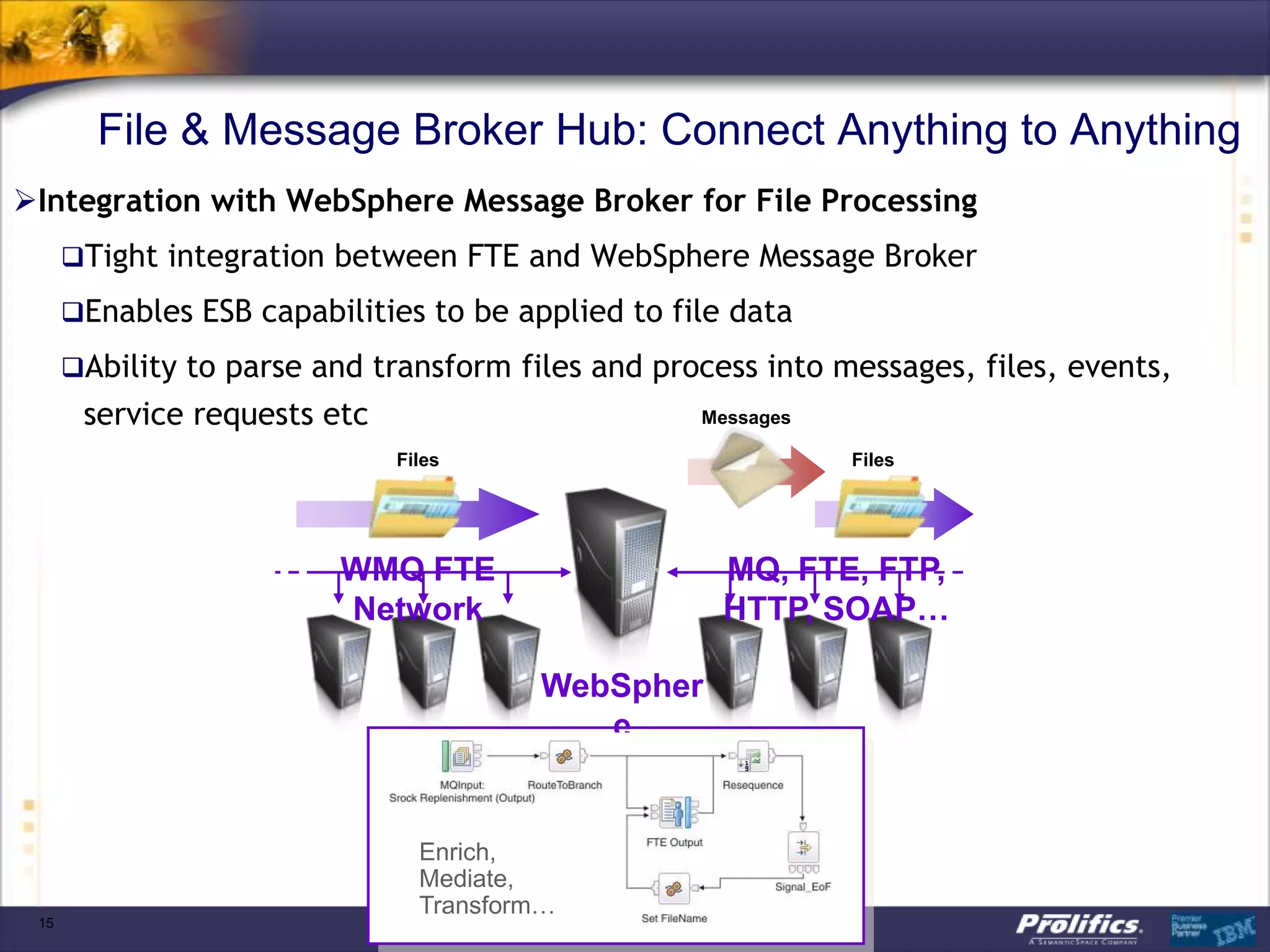
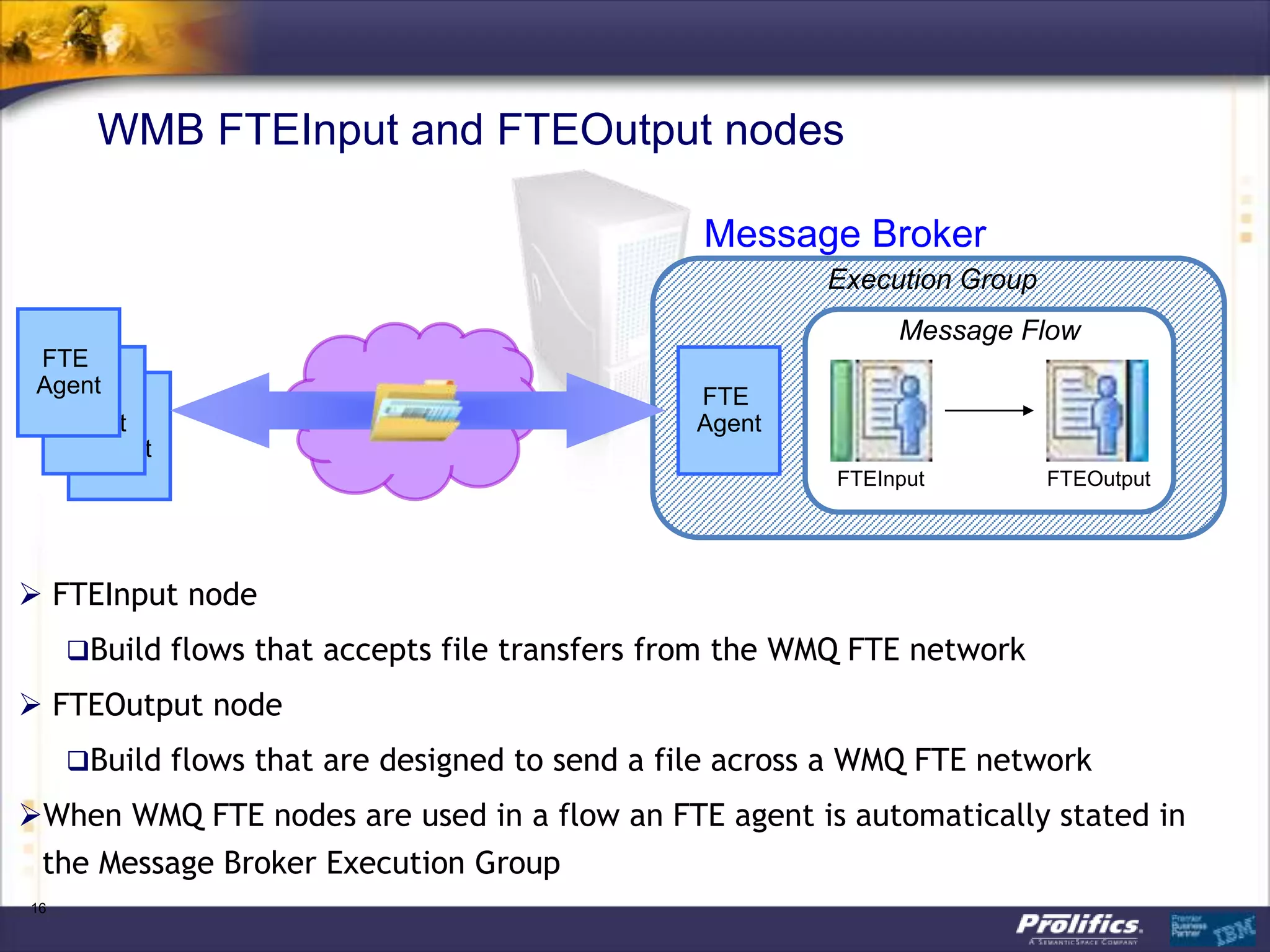
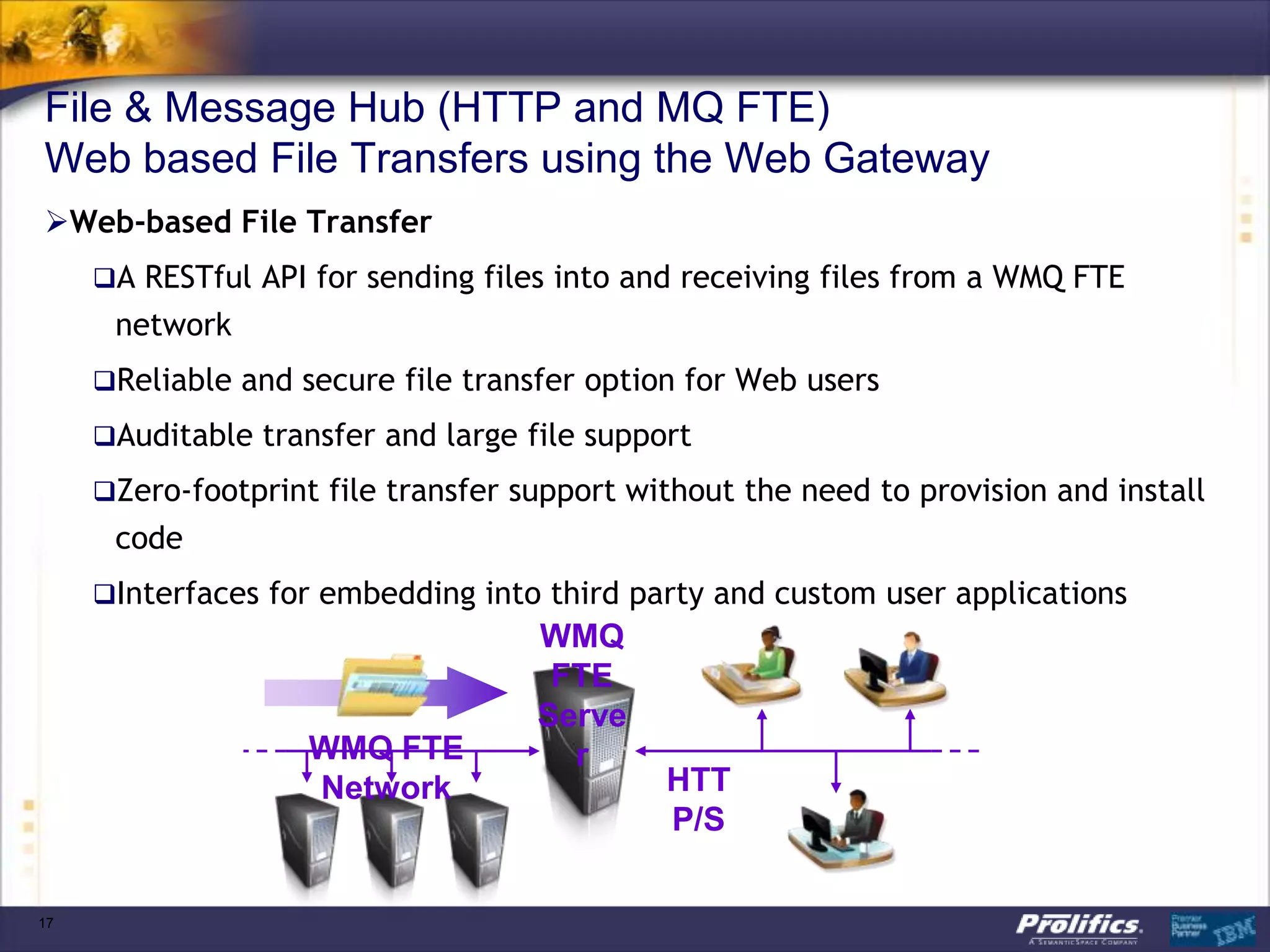
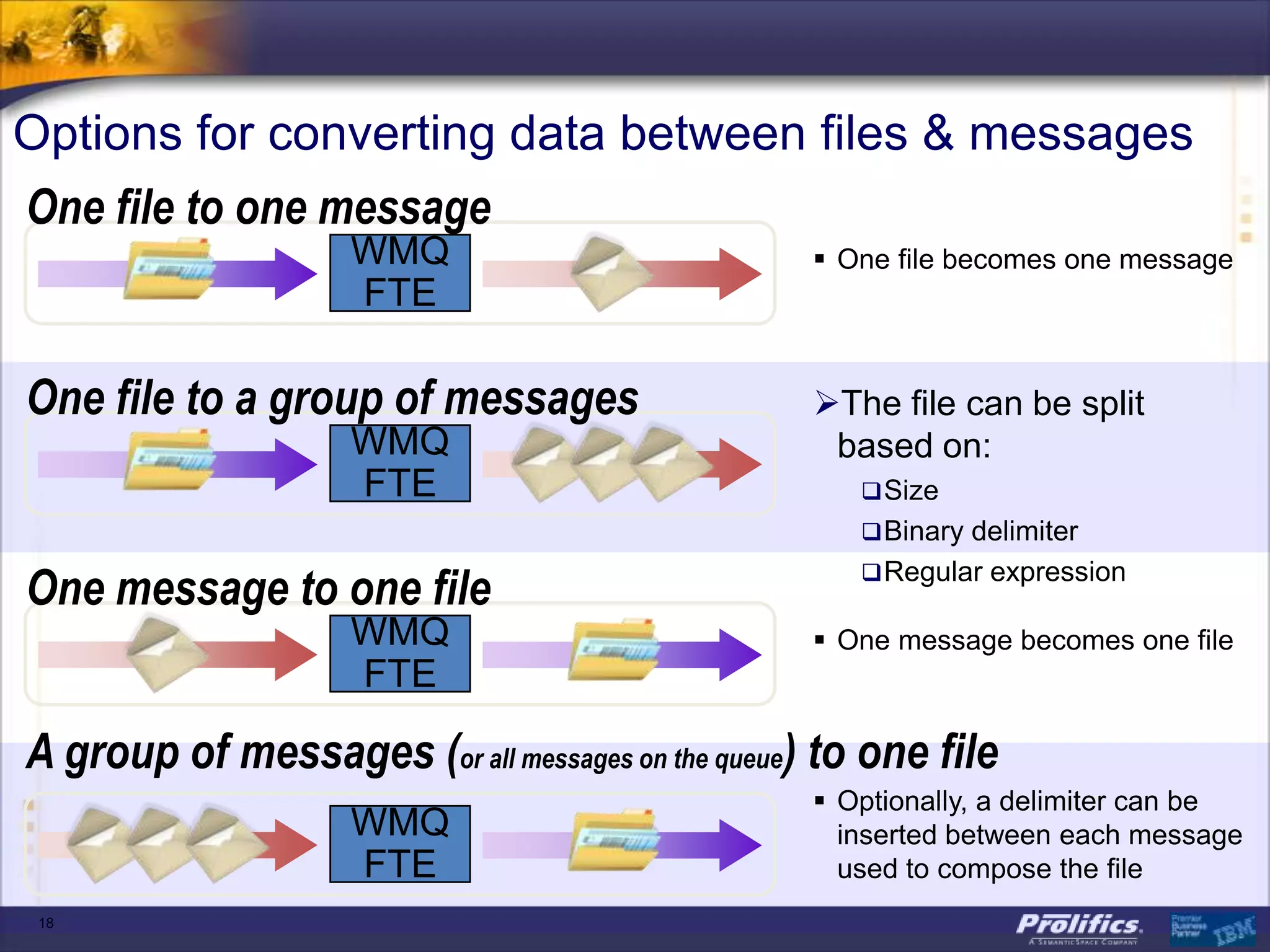
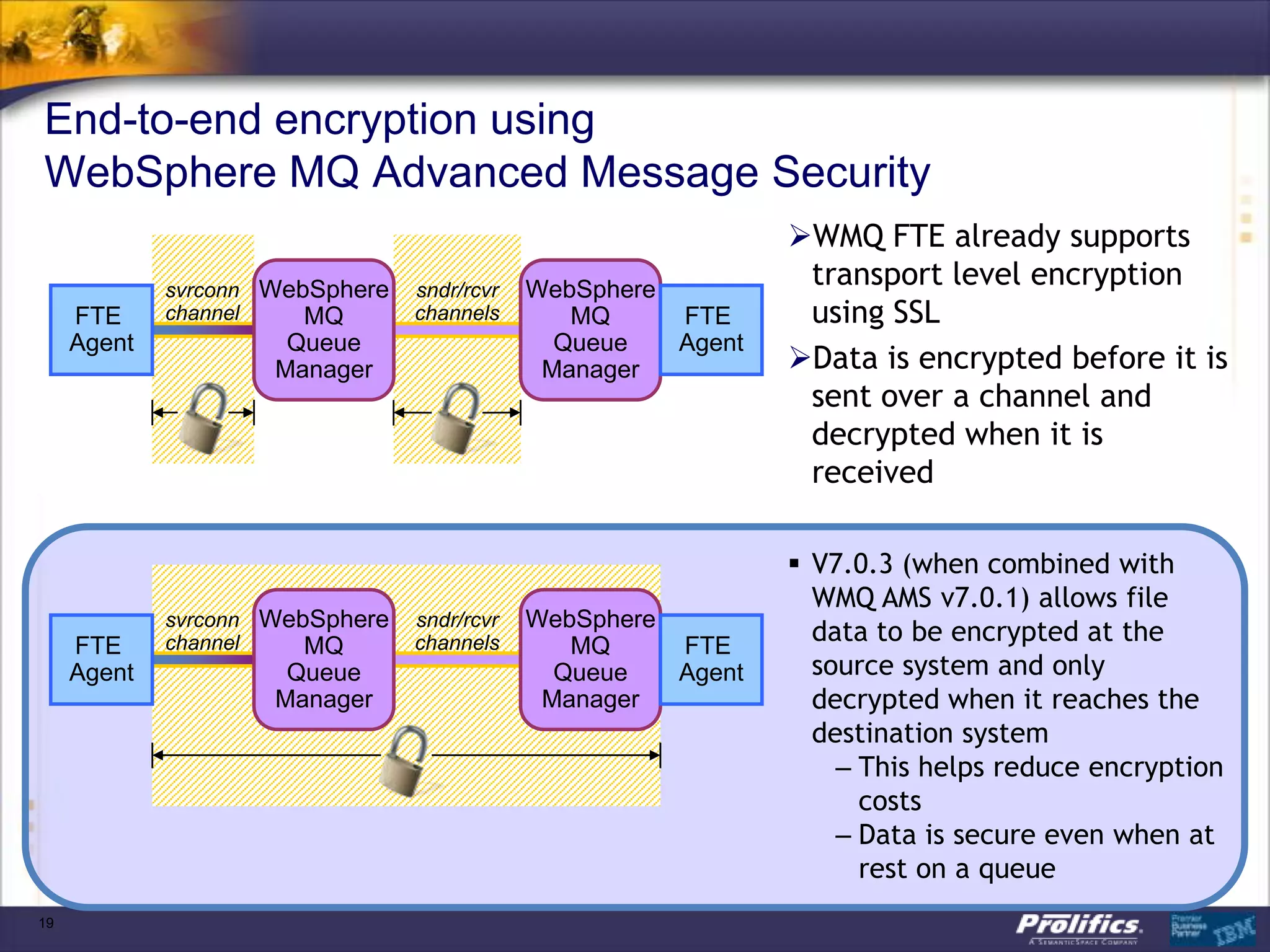
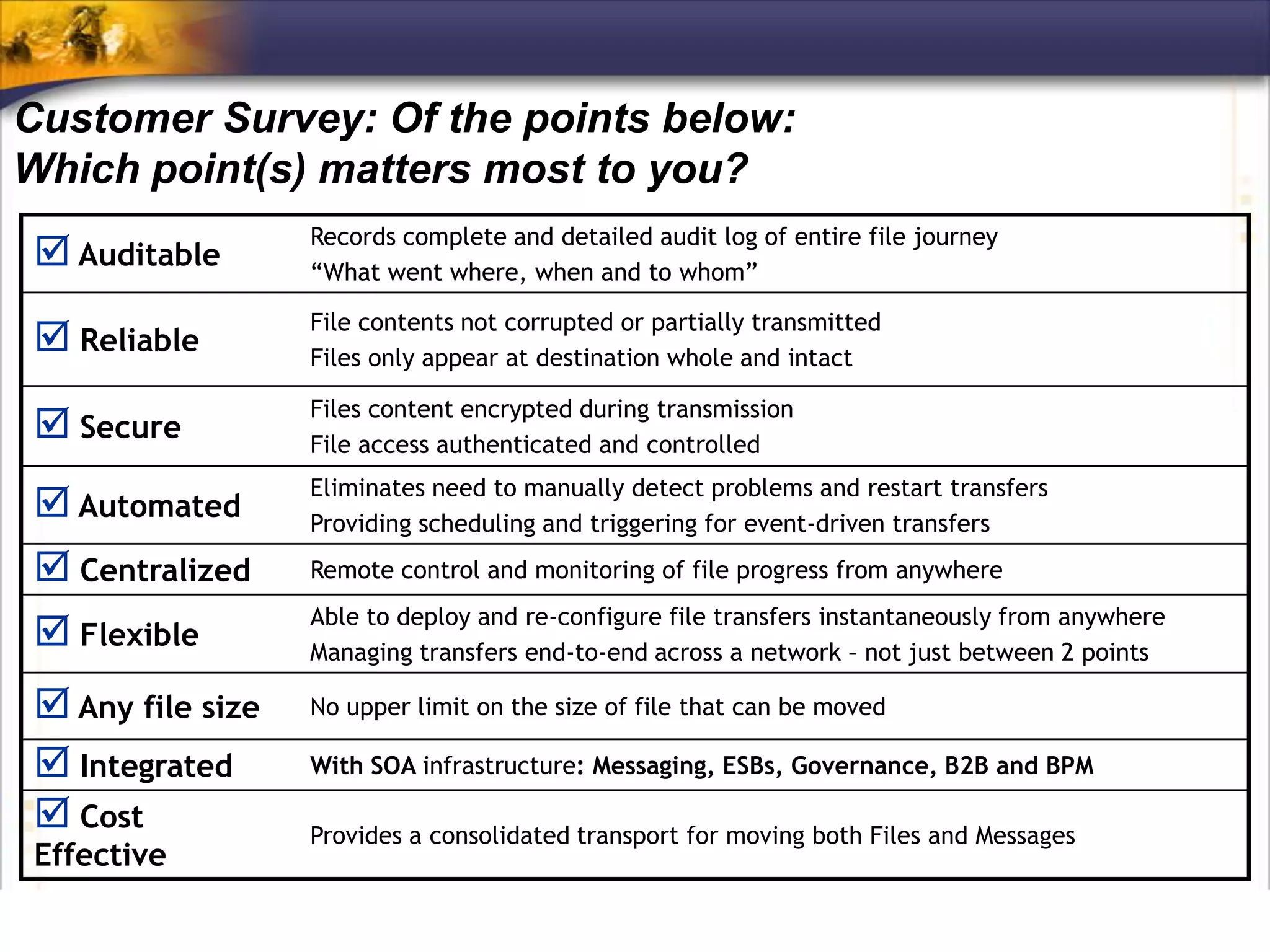
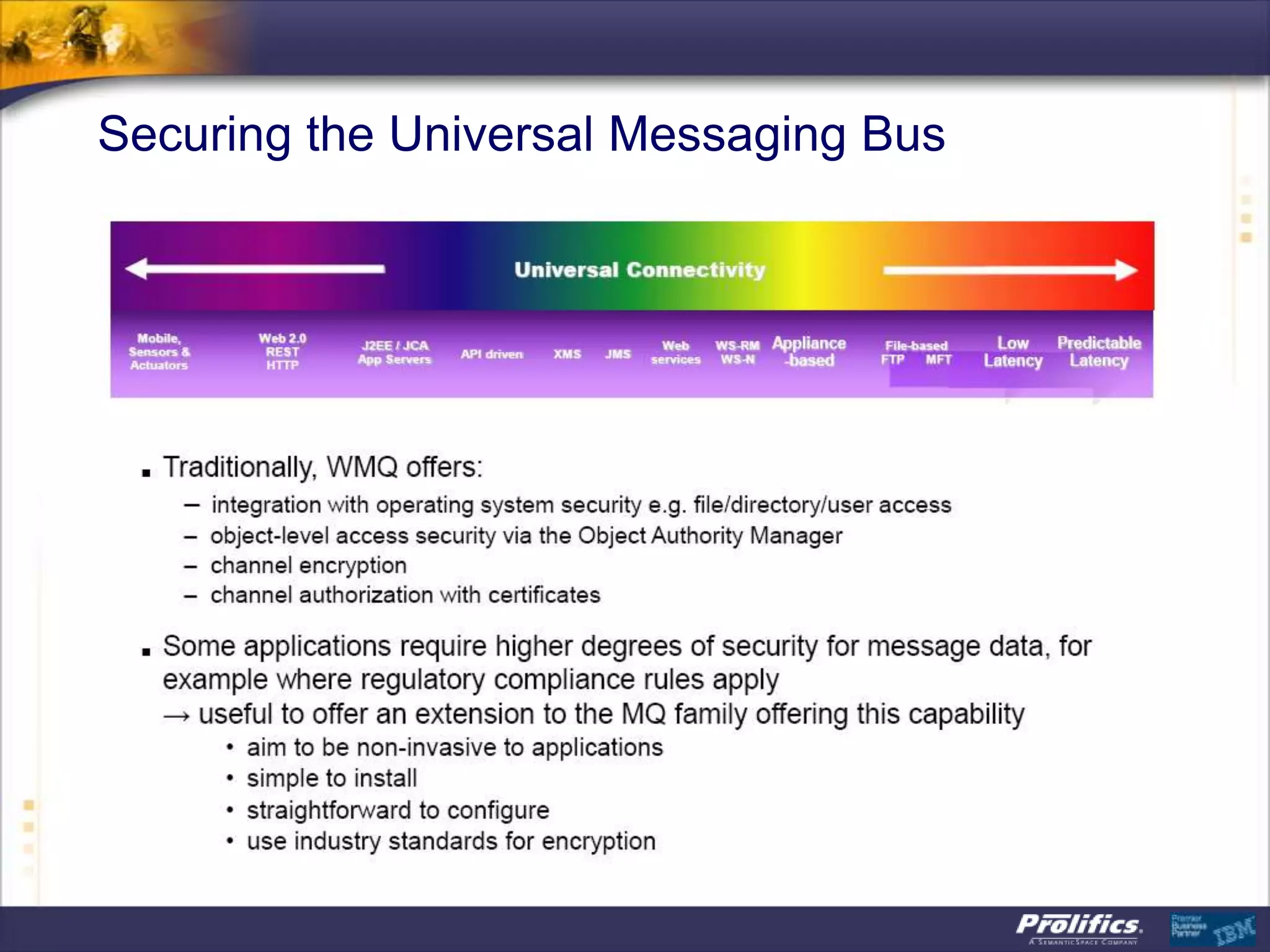
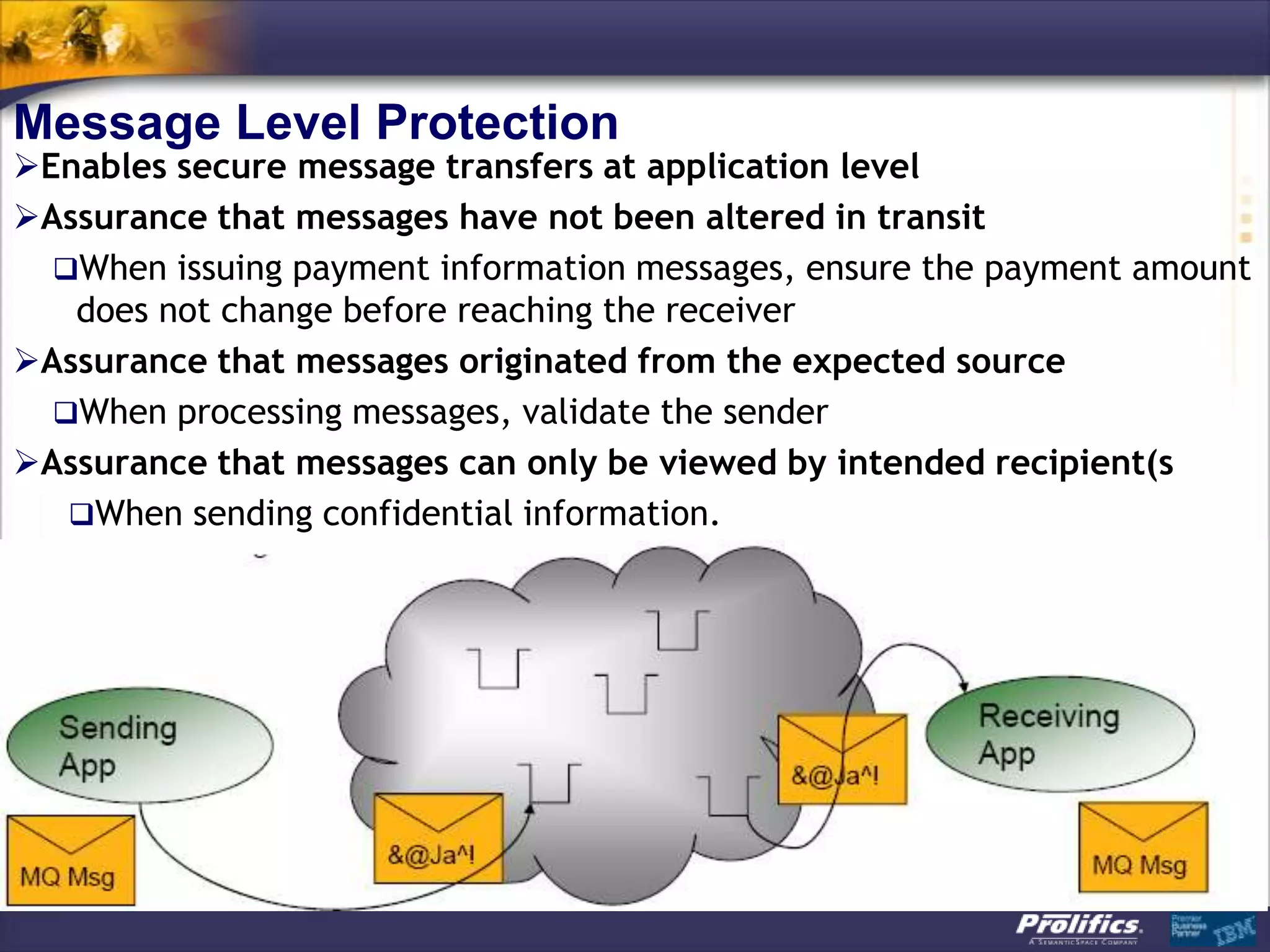
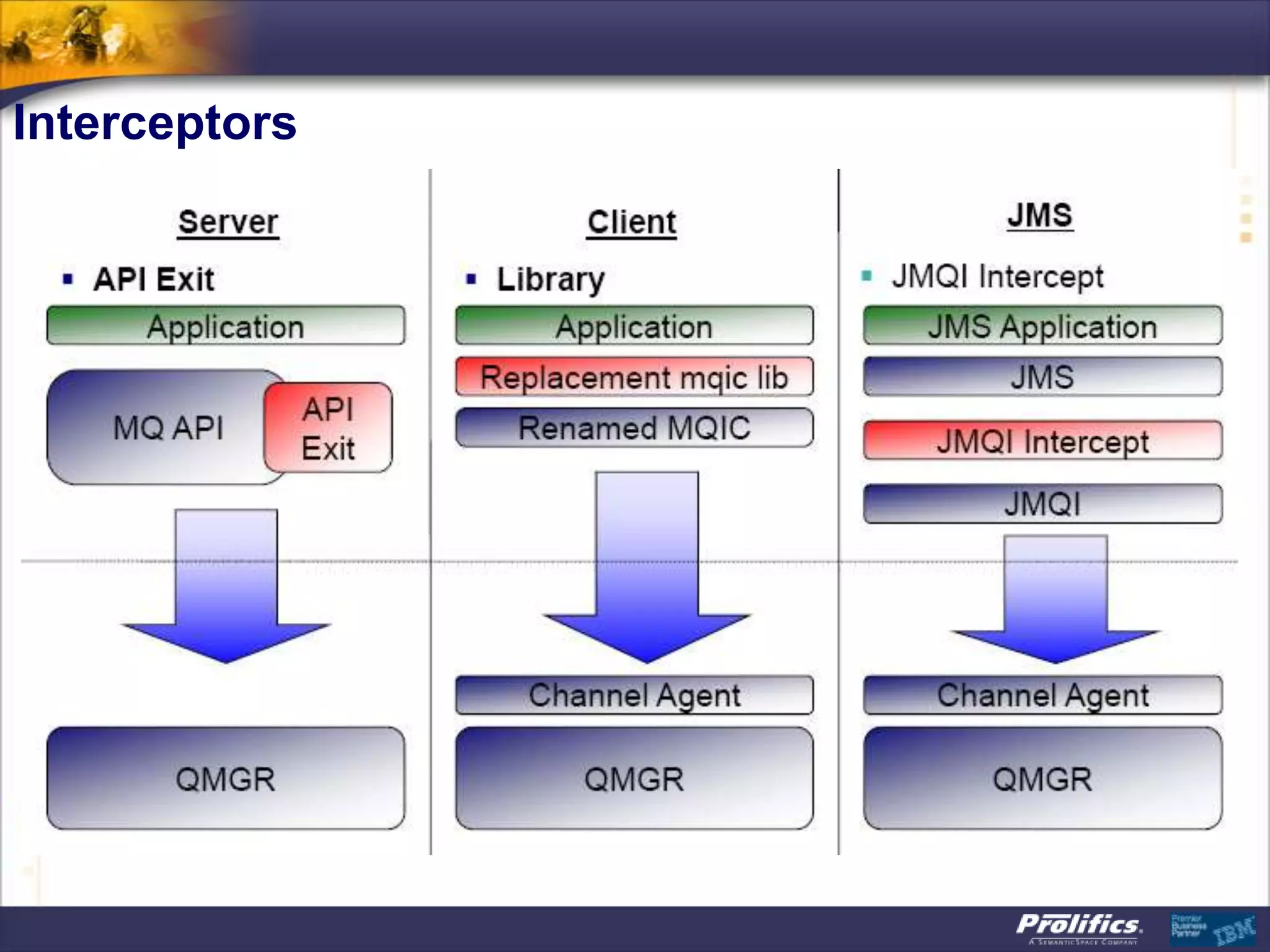
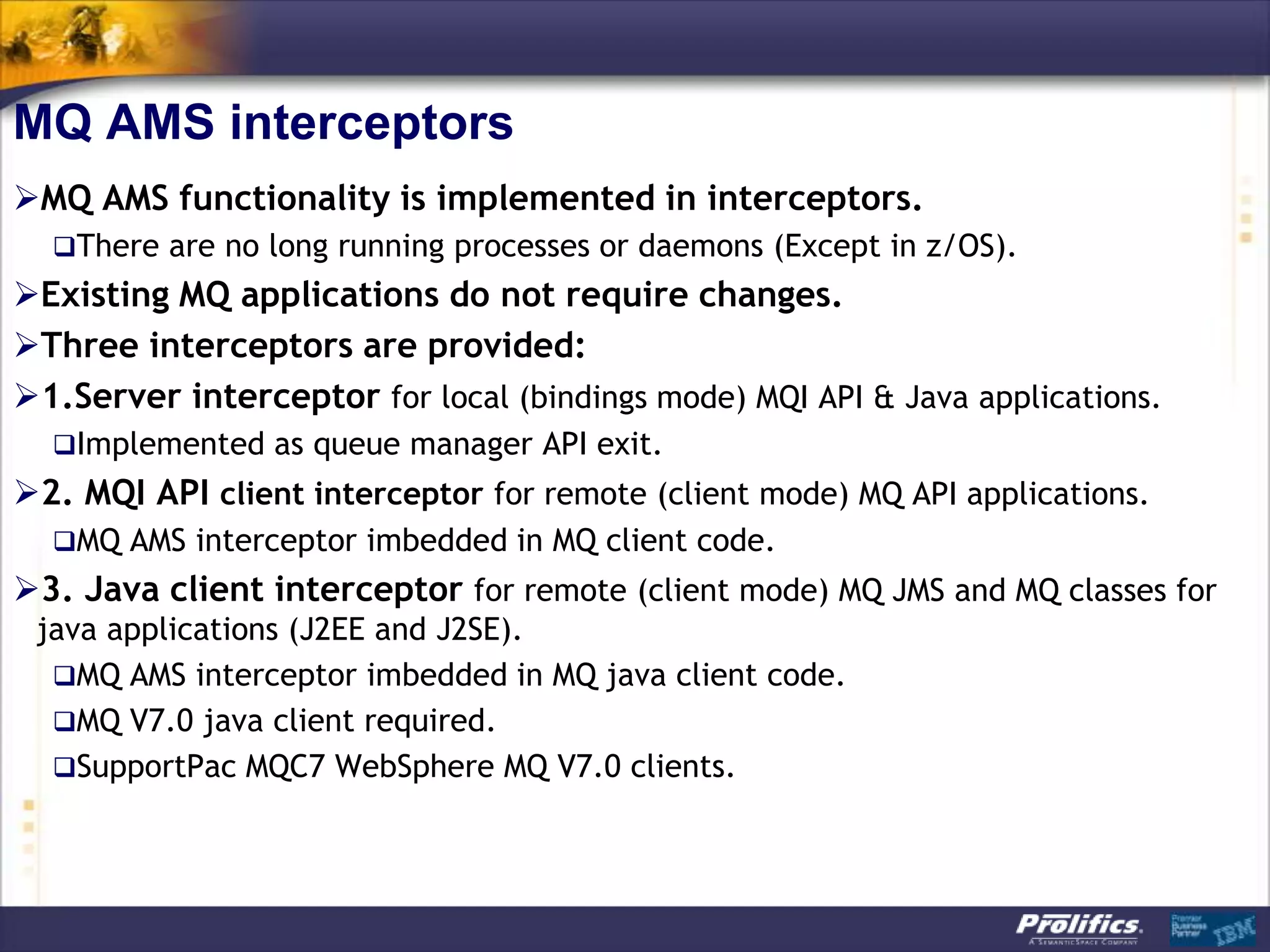
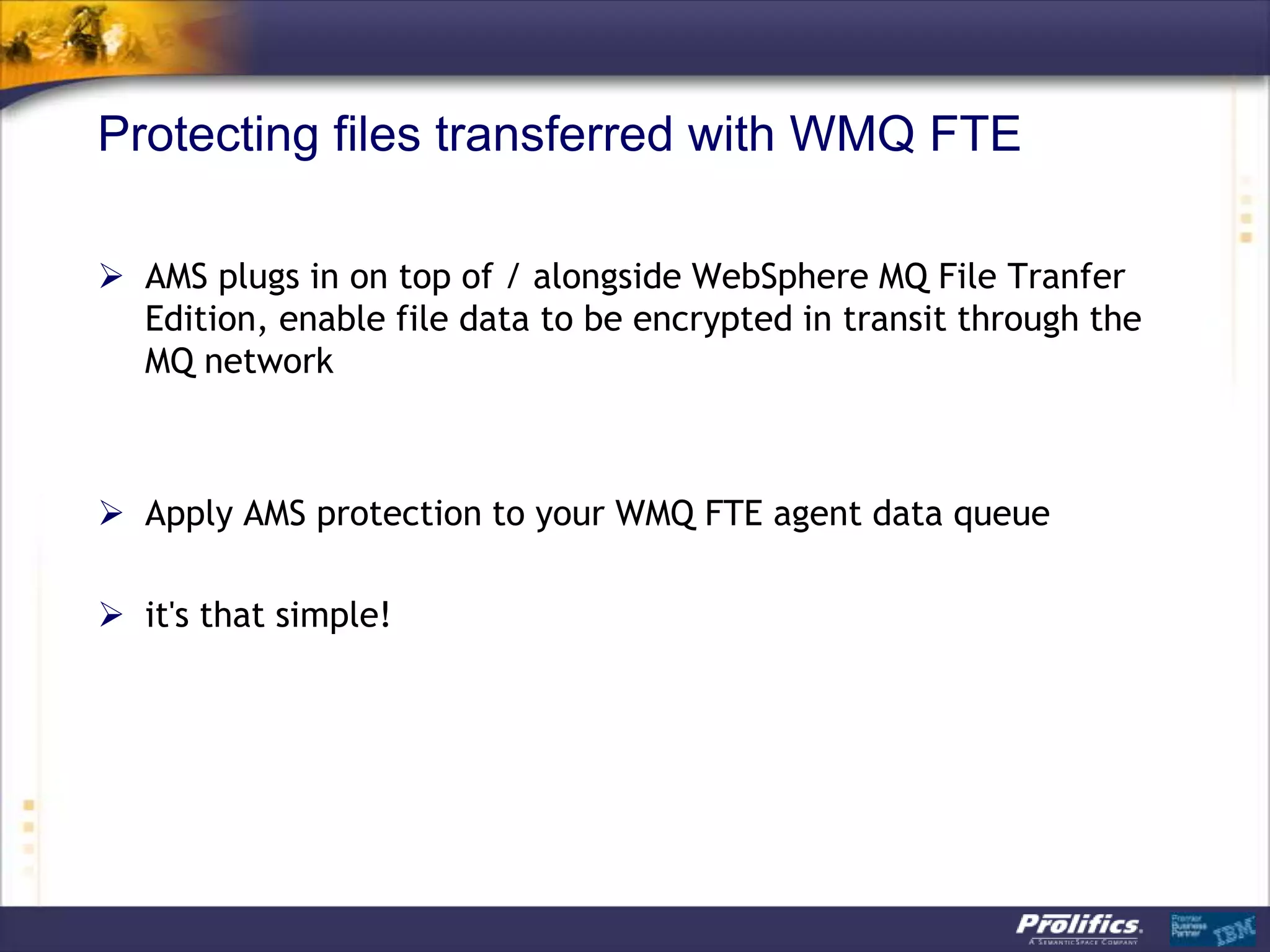
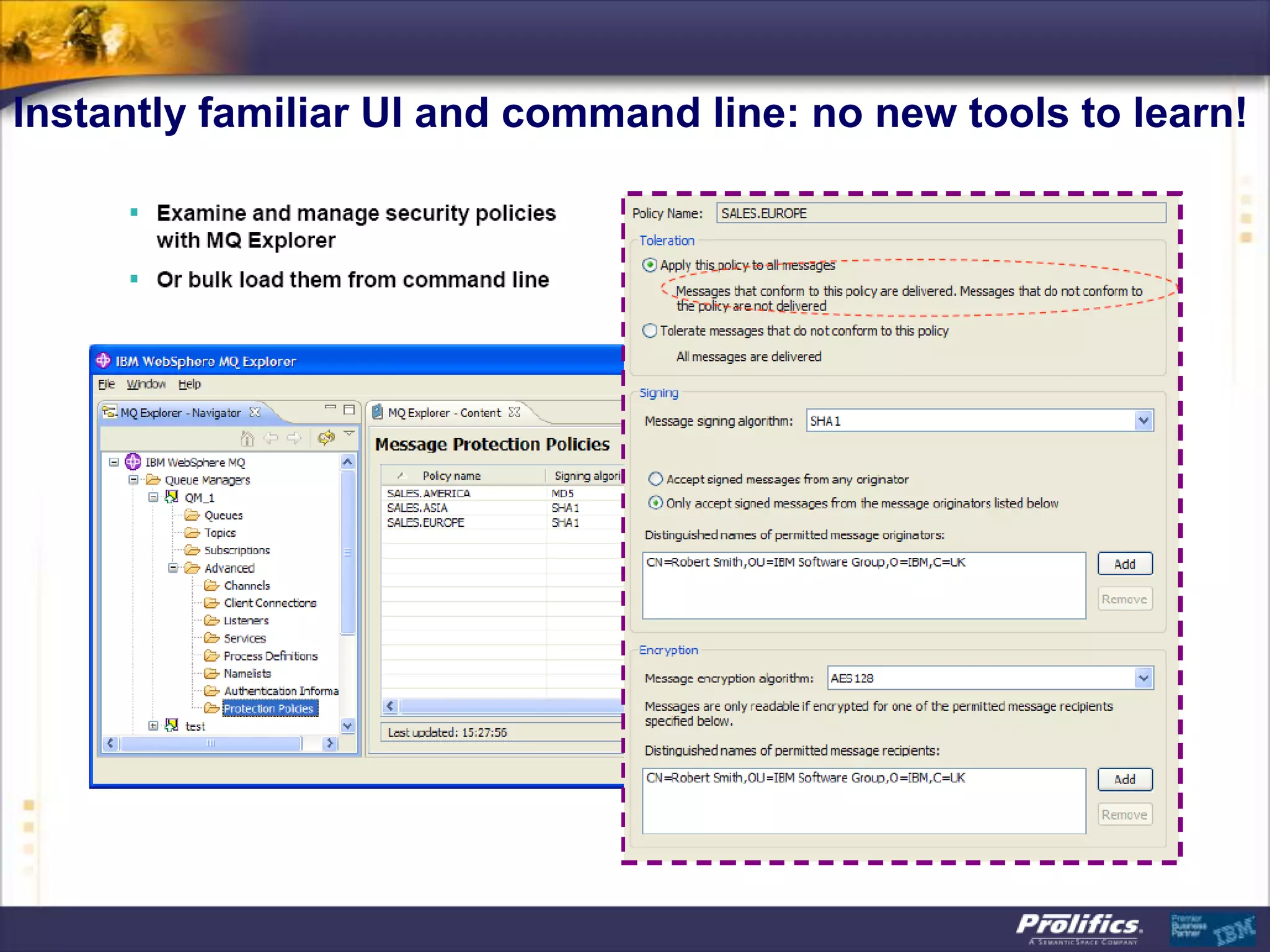
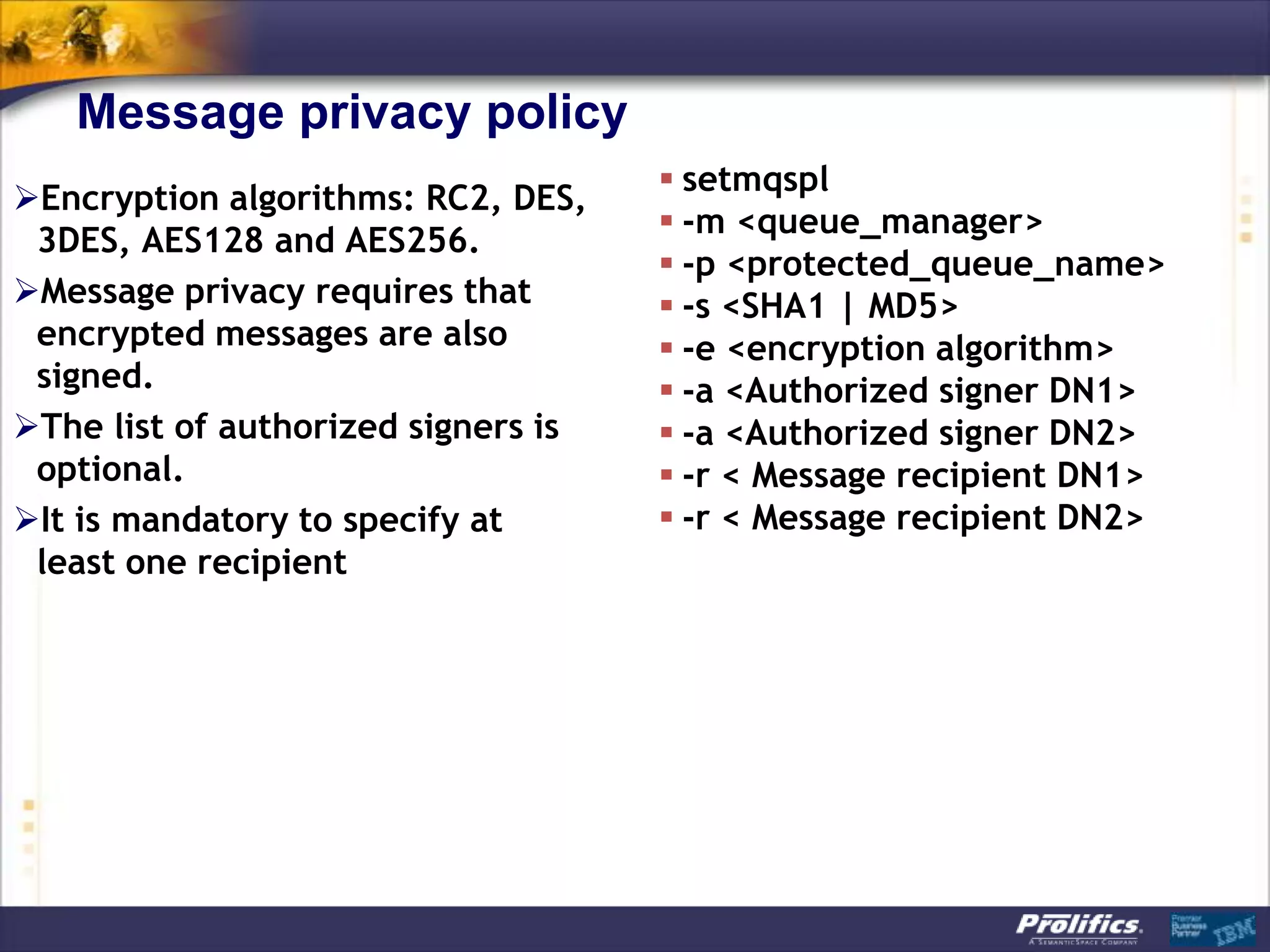
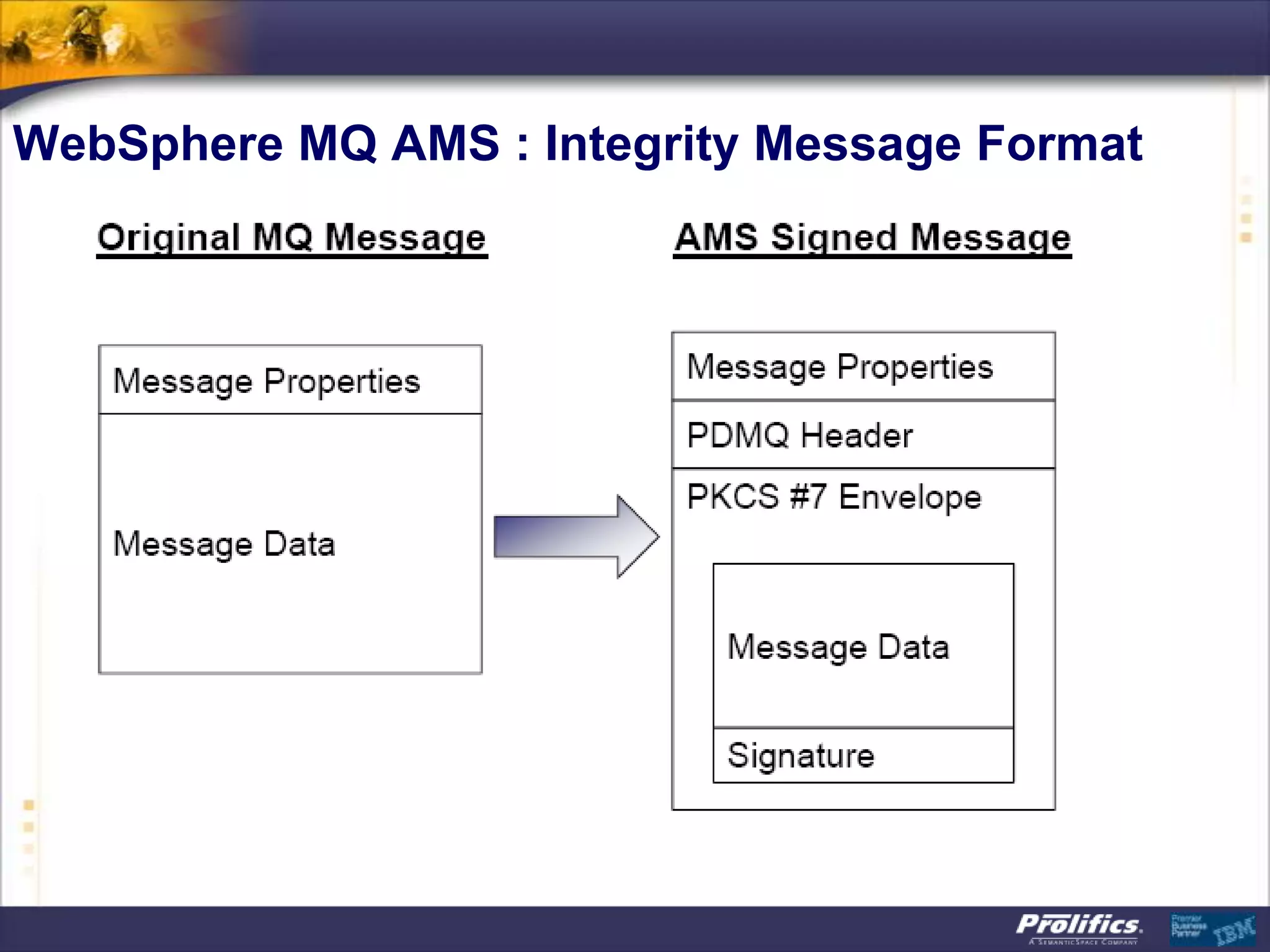
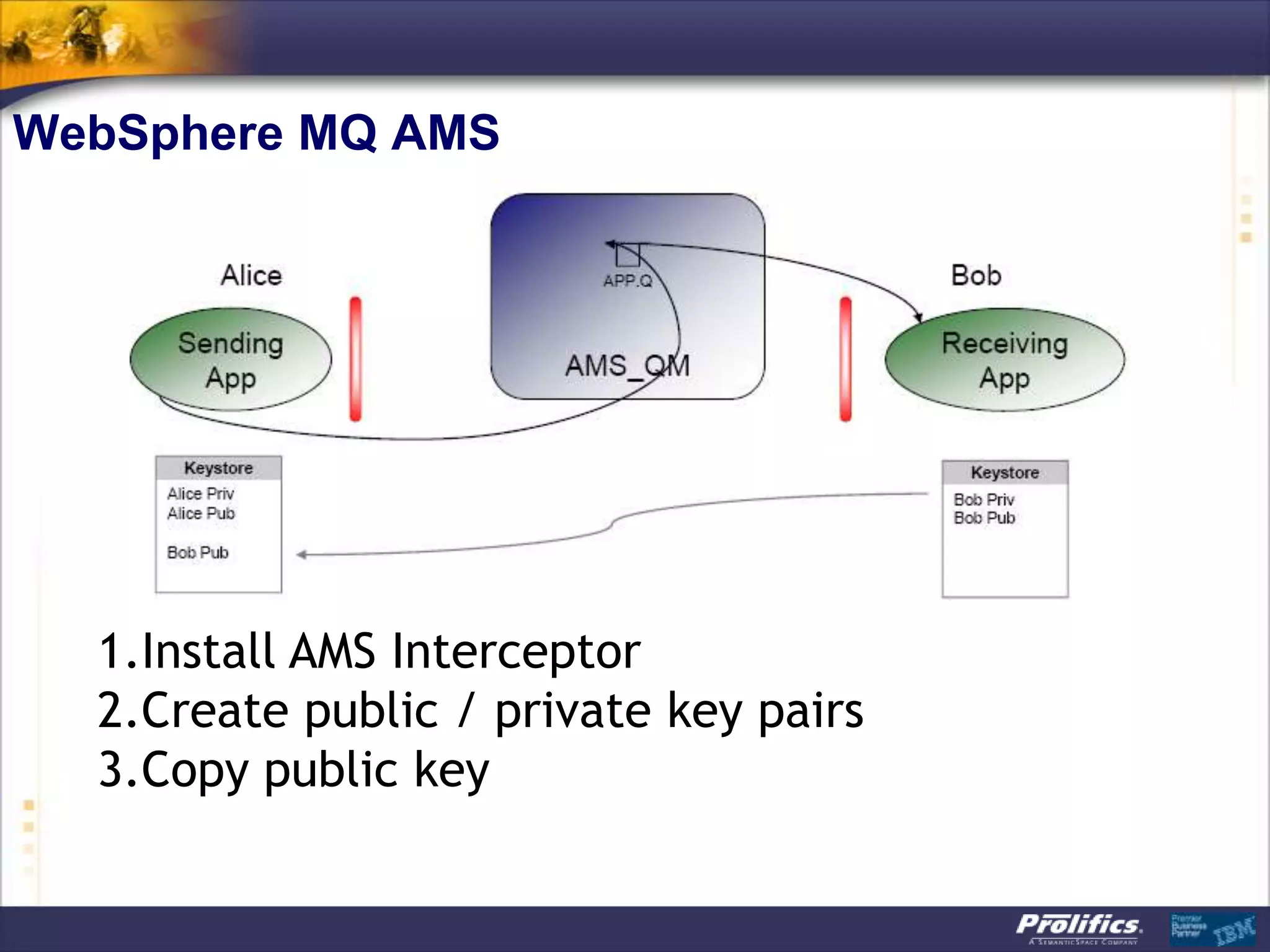
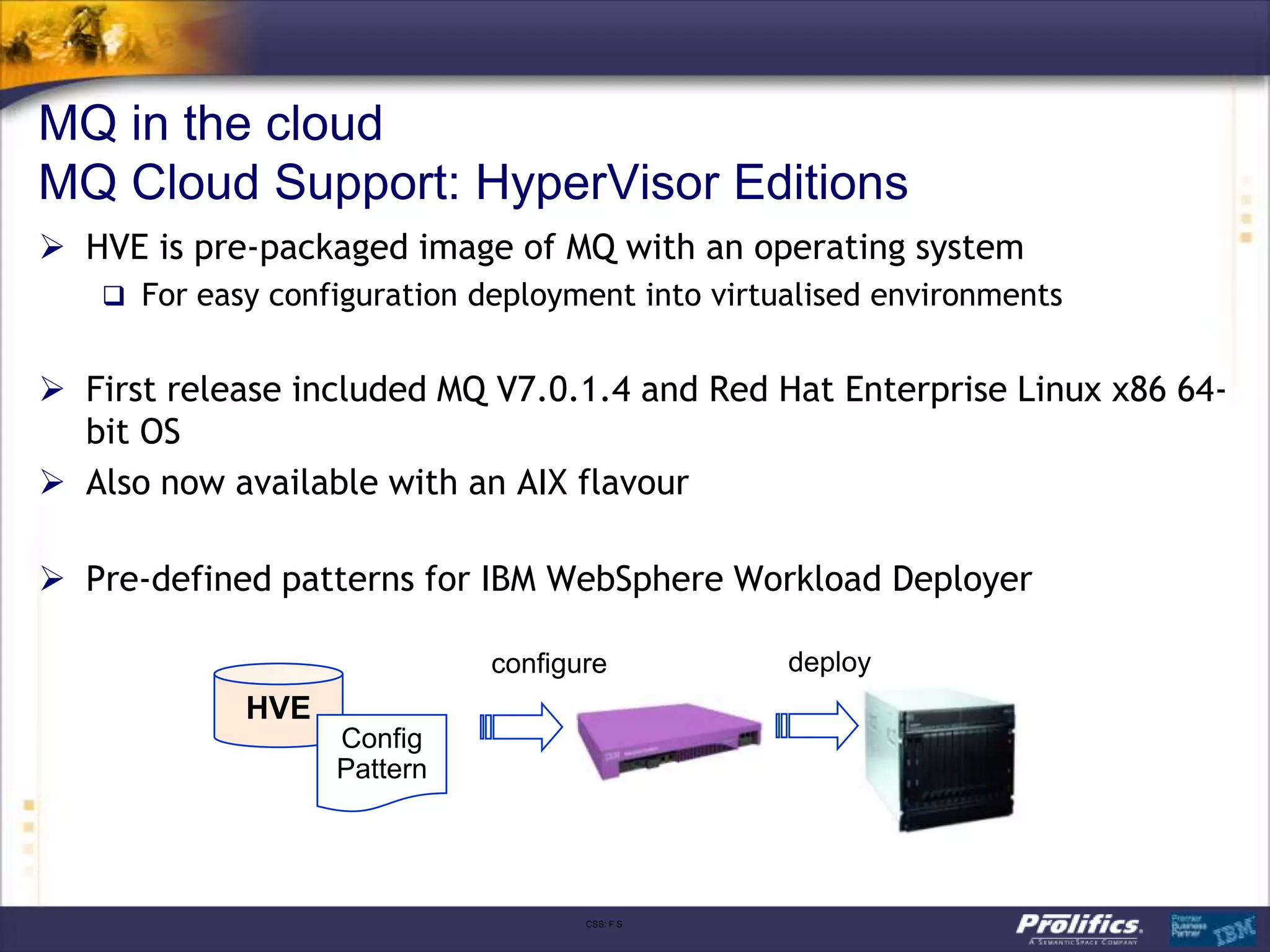
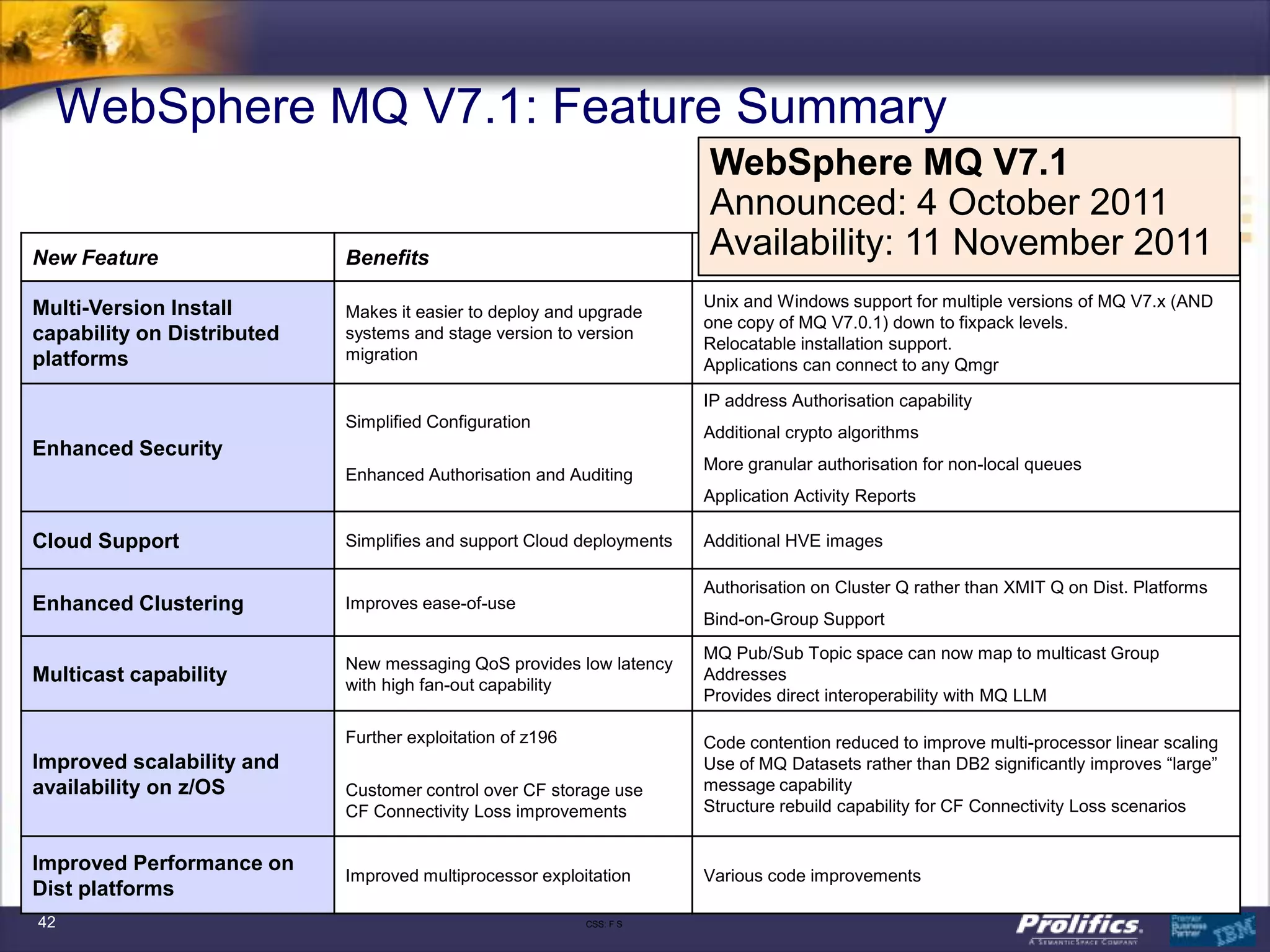
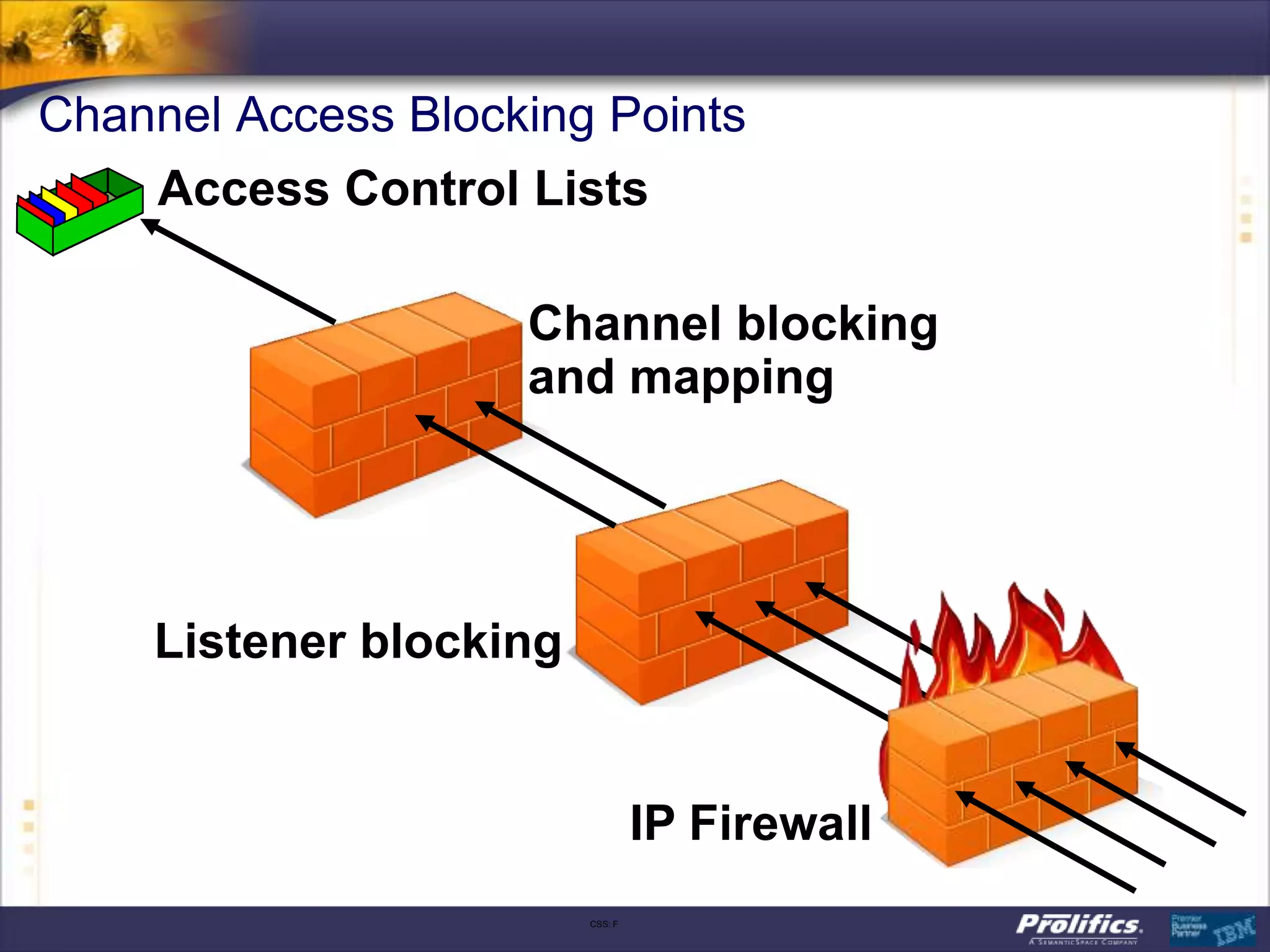
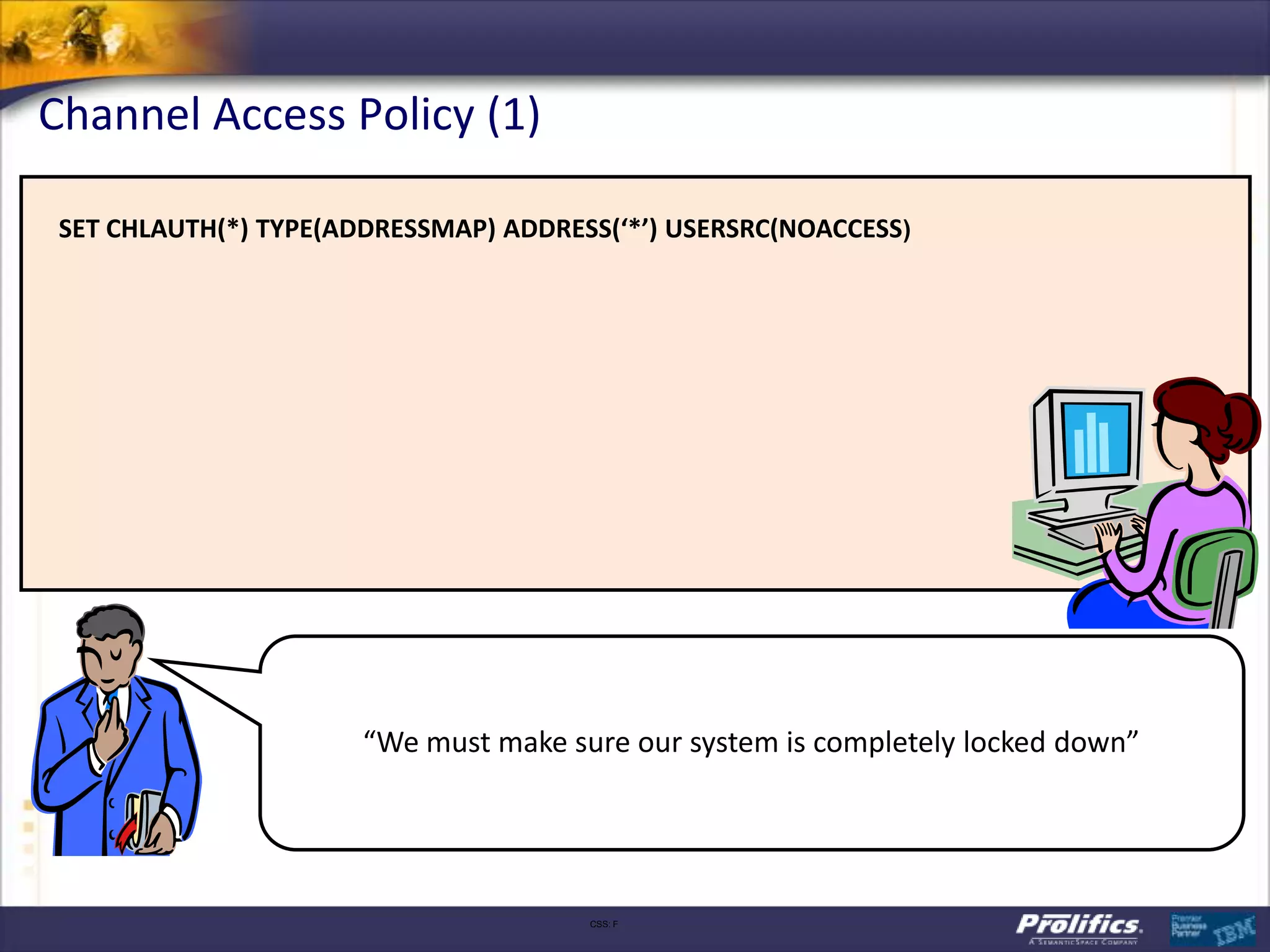
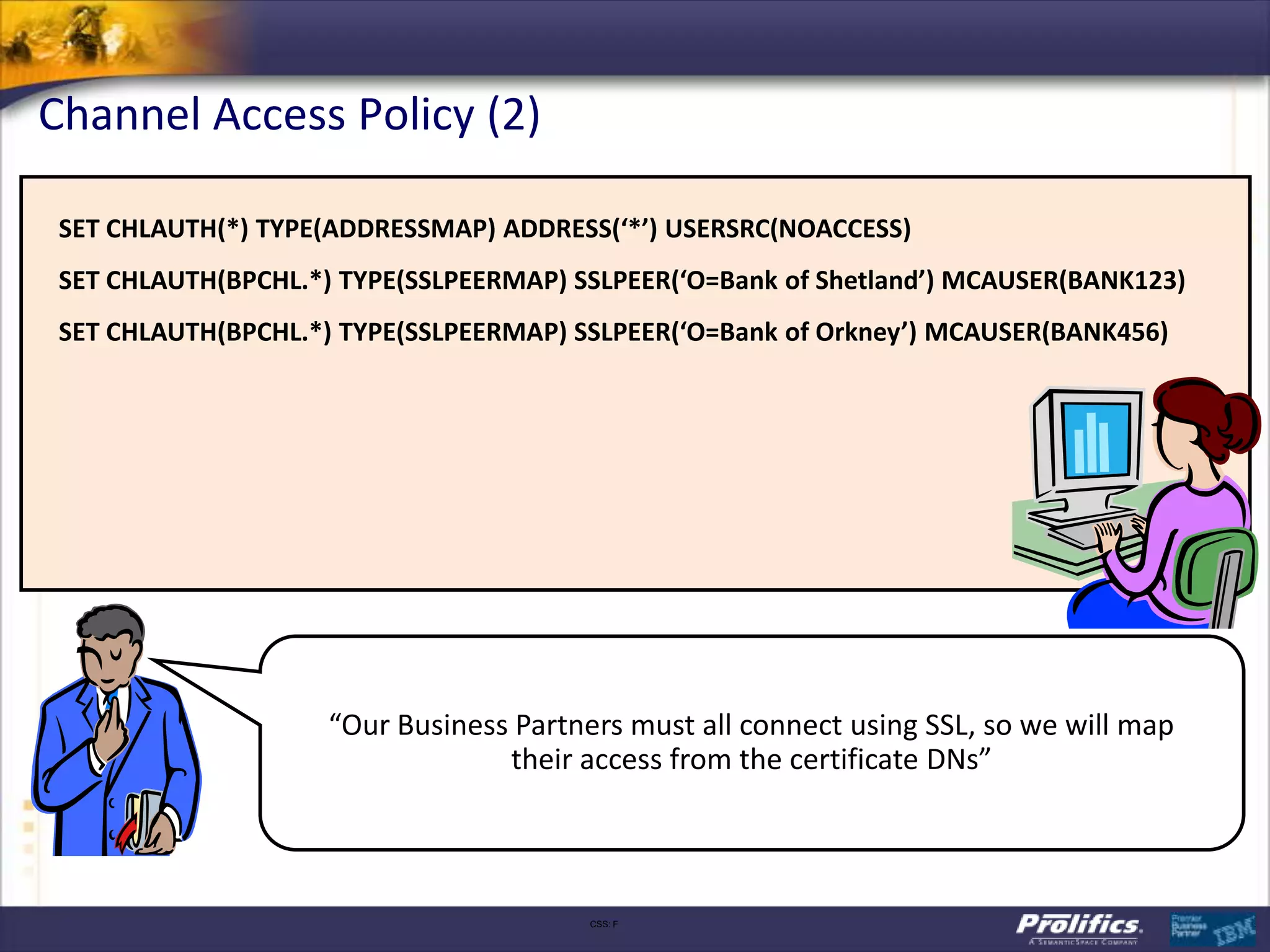
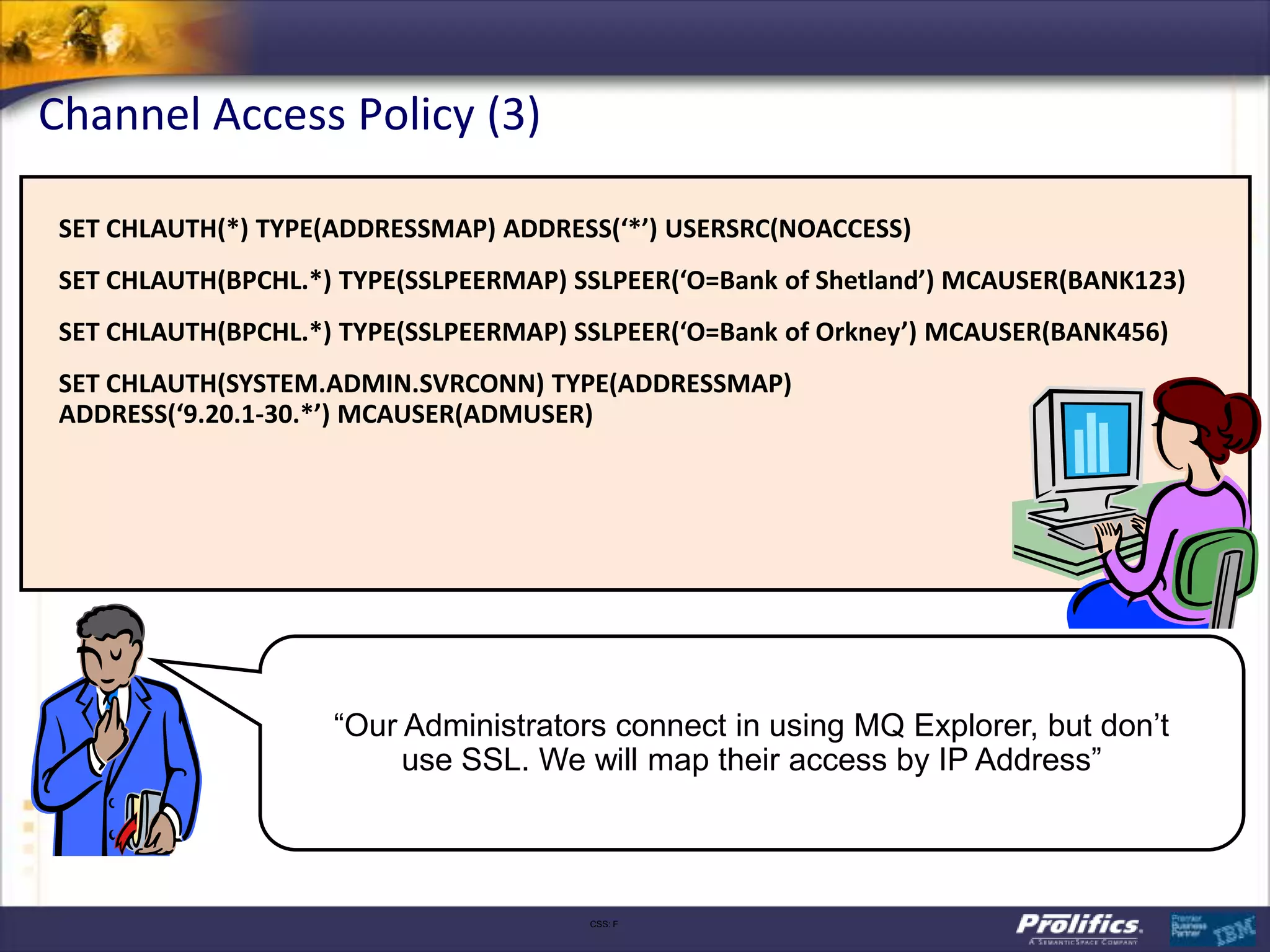
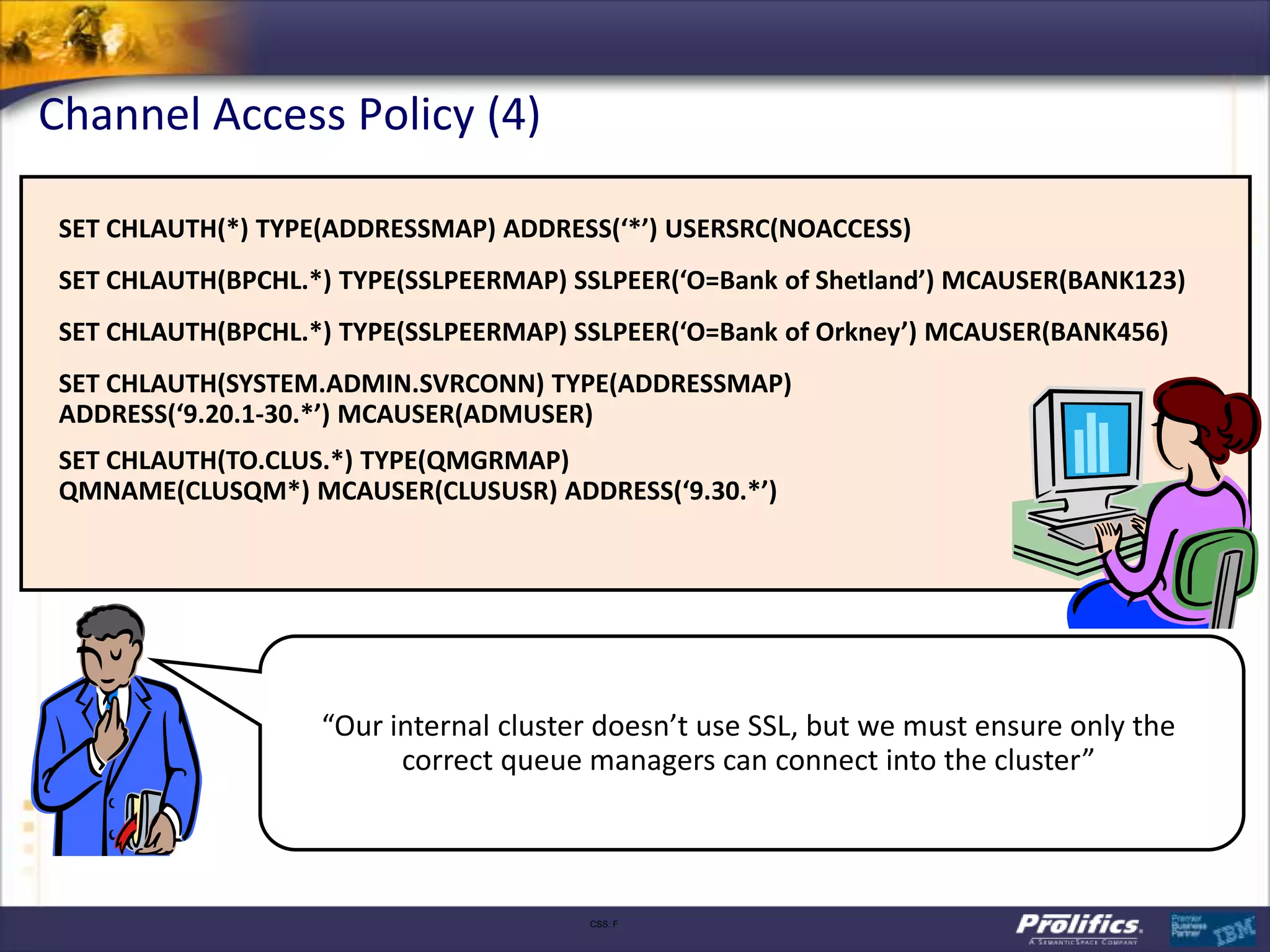
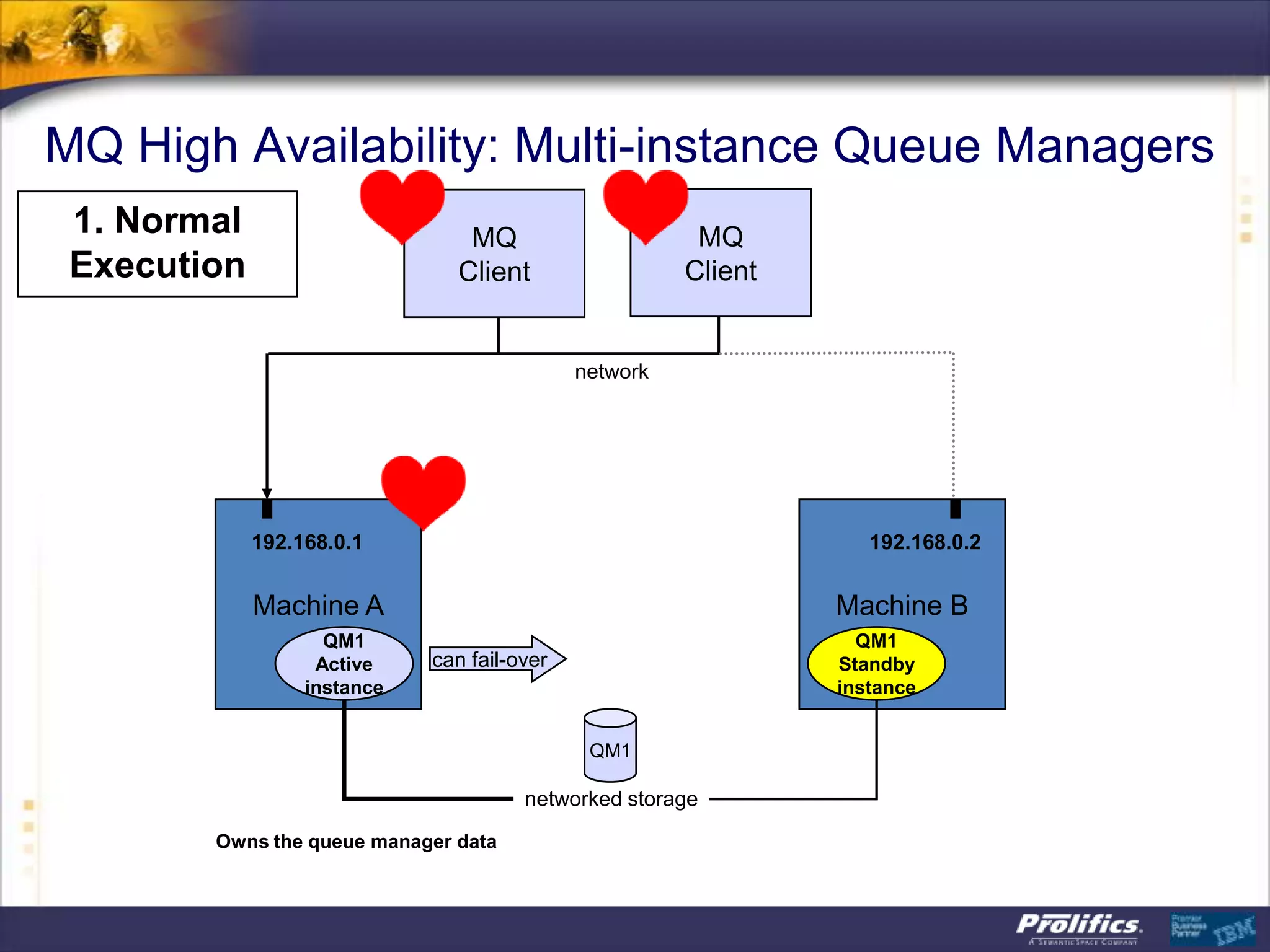
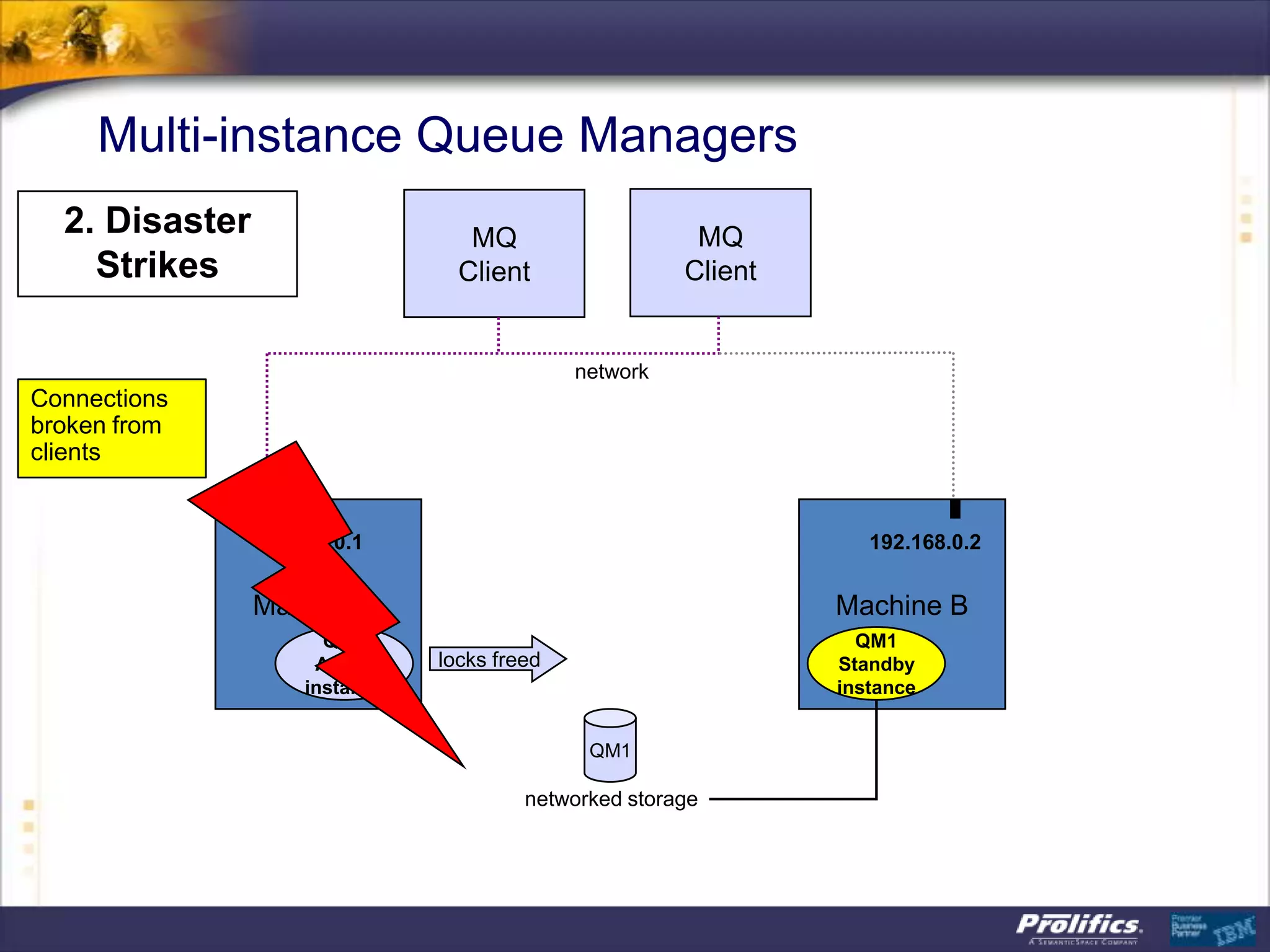
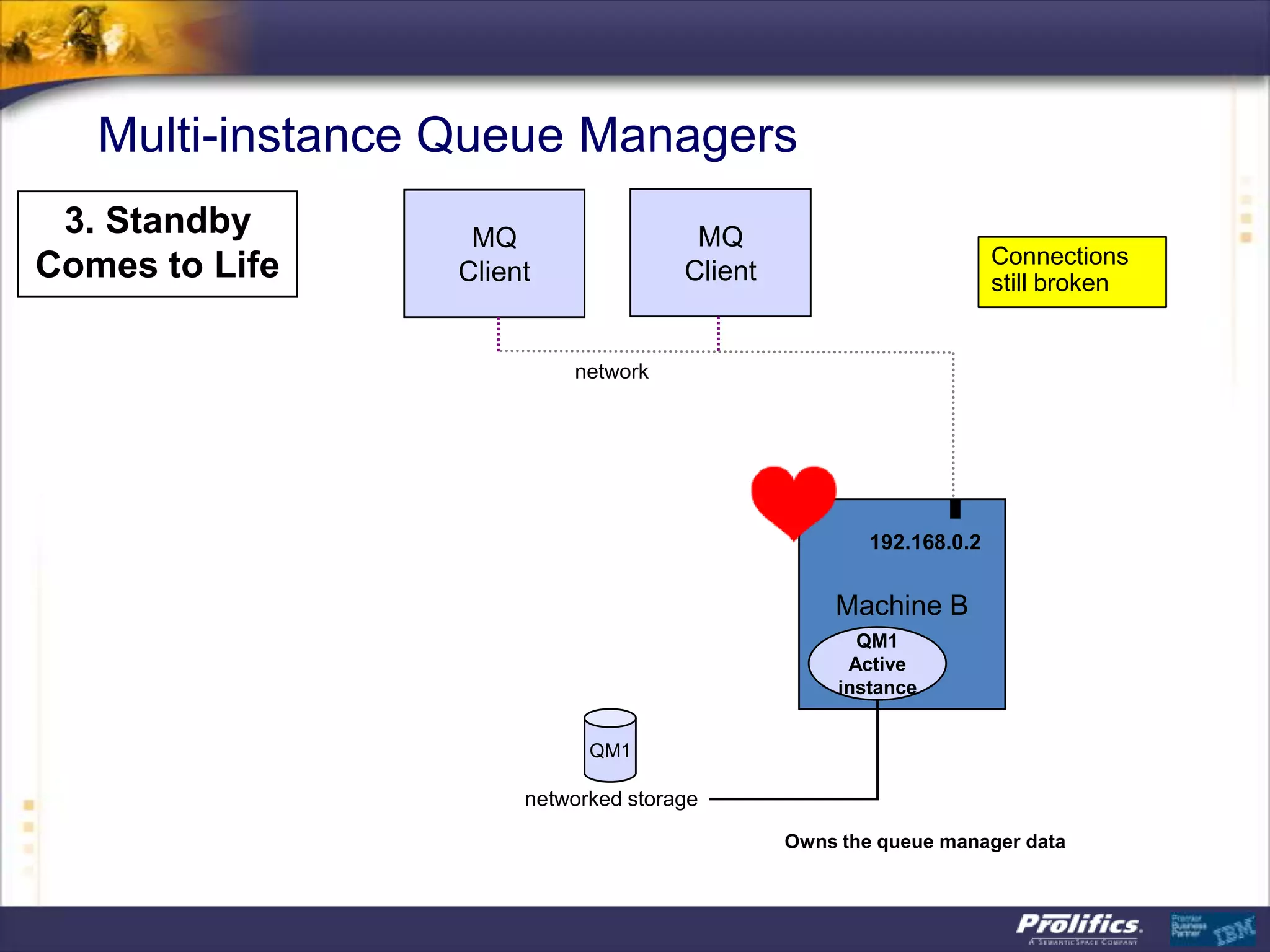
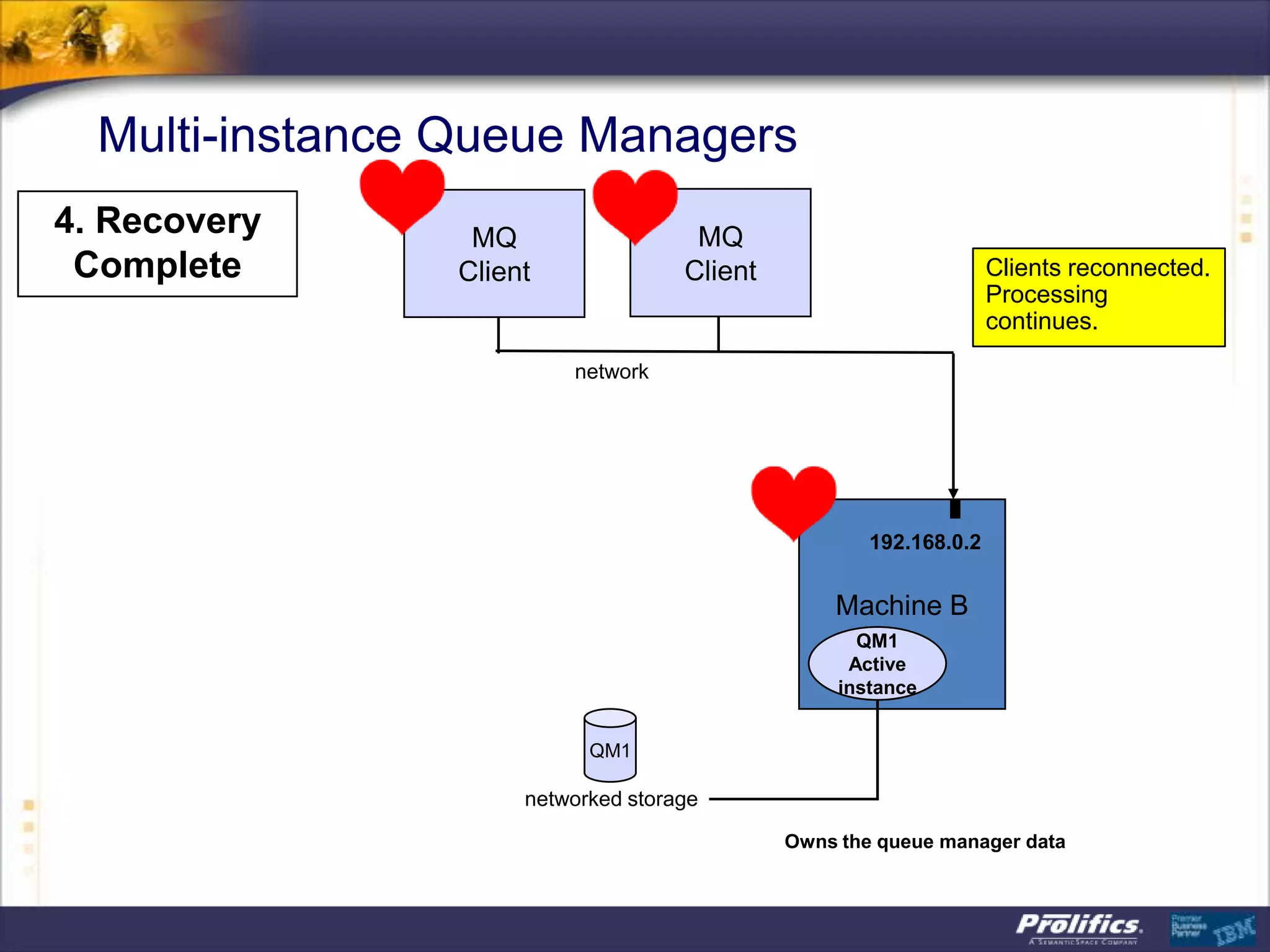
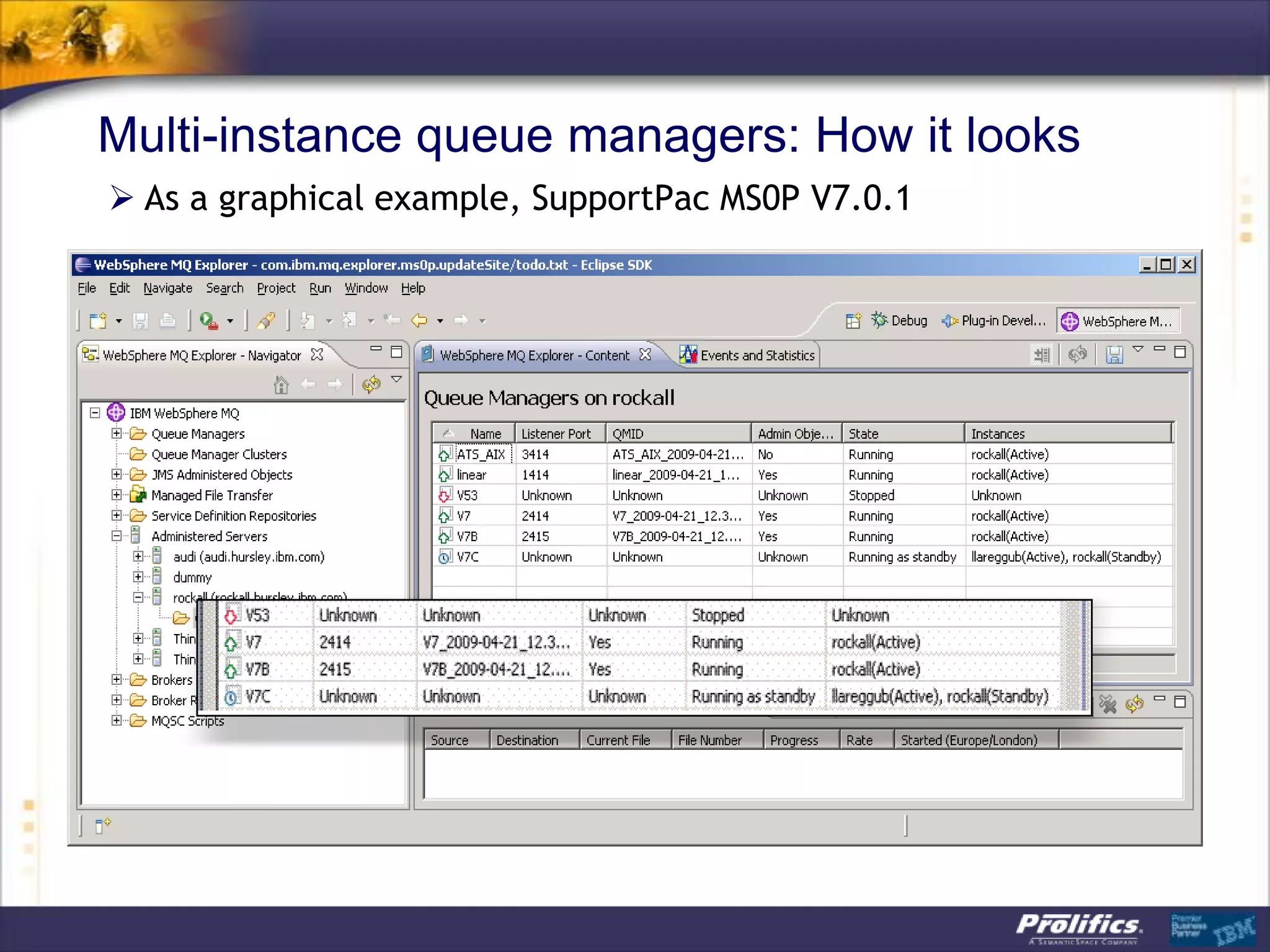
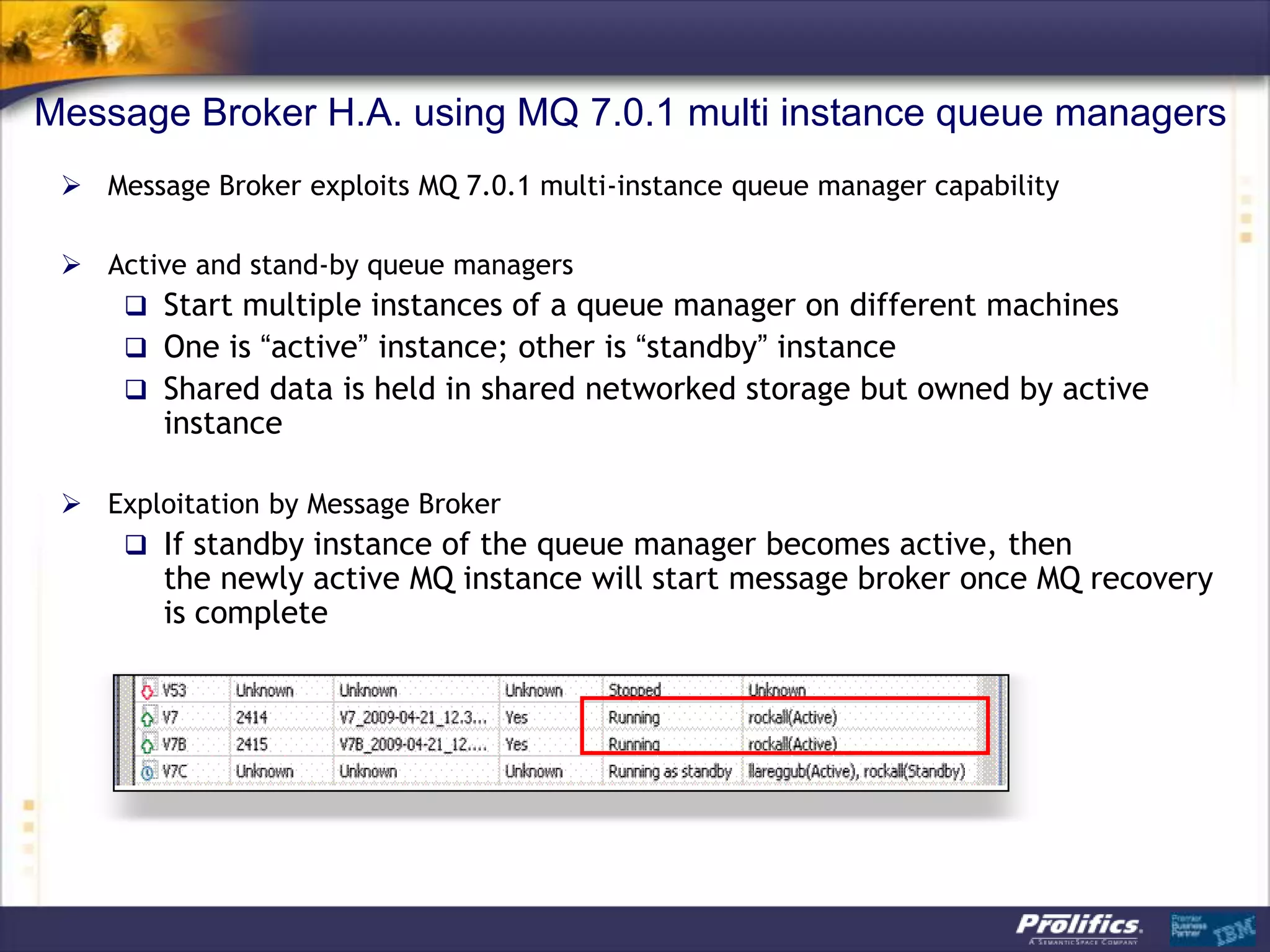
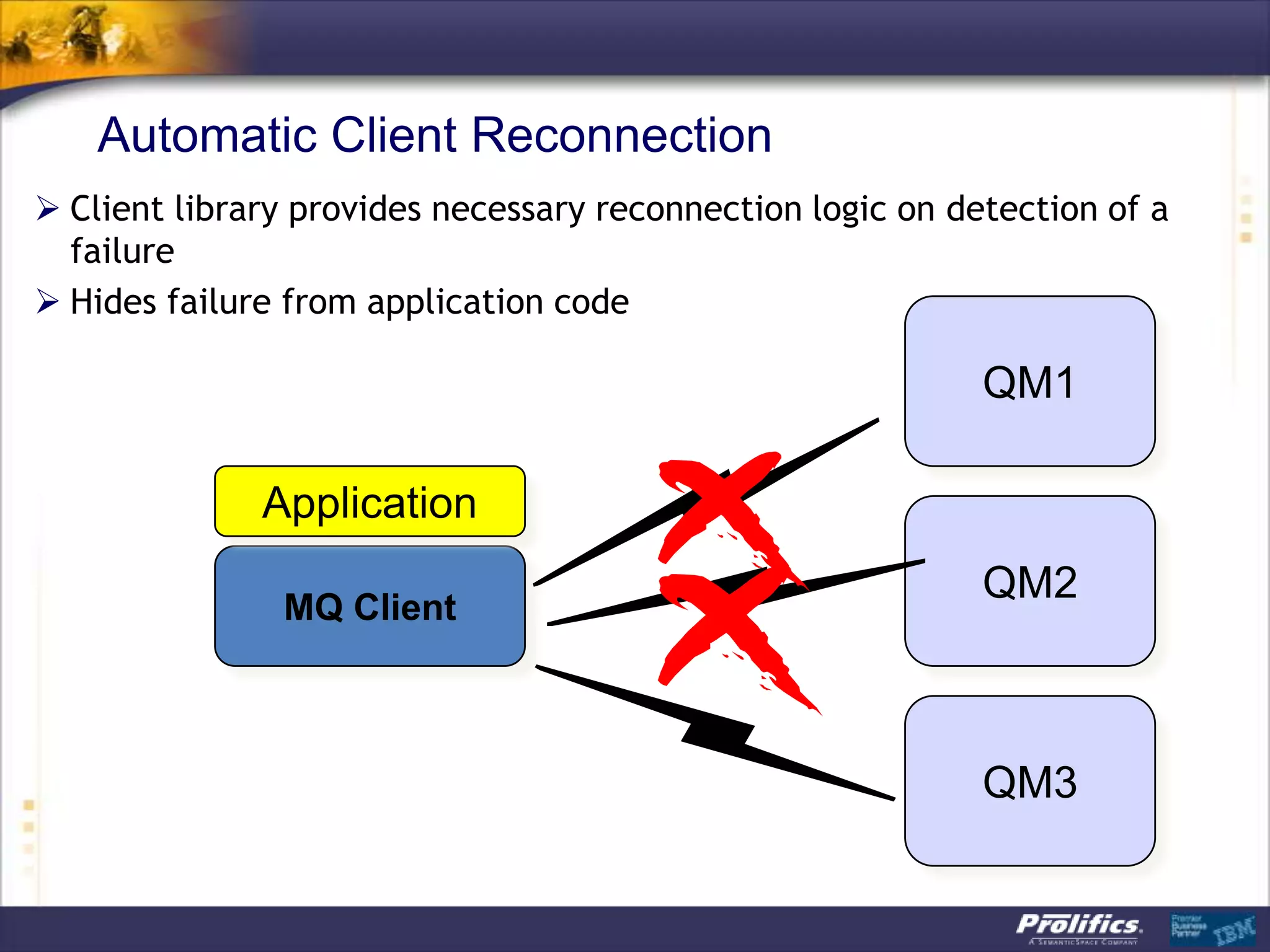
The document discusses IBM's MQ infrastructure including MQ 7.1, MQ AMS, and MQ FTE. It provides an agenda covering universal connectivity with MQ, MQ File Transfer Edition, MQ security with MQ AMS, and features of MQ 7.1 including security policies. The document is presented by AJ Aronoff from Prolifics and focuses on MQ infrastructure for security and high availability.