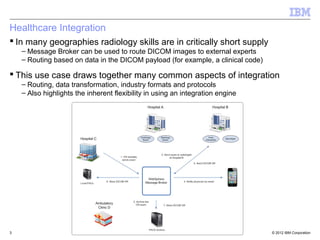
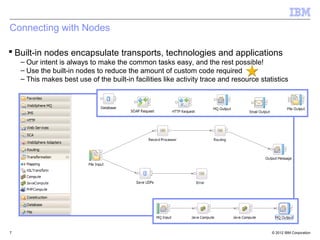
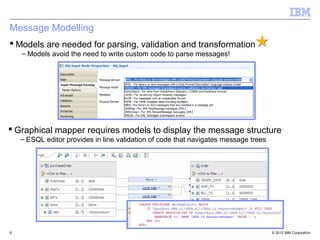
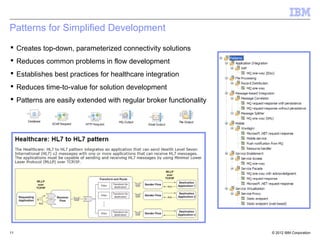
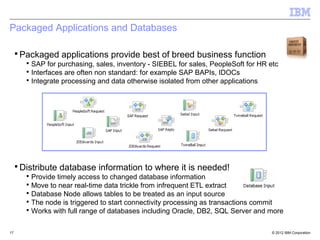
This document provides an introduction to IBM WebSphere Message Broker. It discusses how Message Broker can connect different enterprise systems and applications together through its support for various protocols, formats, and endpoints. It also highlights how Message Broker simplifies integration and avoids tightly coupled point-to-point connections. The document then provides overviews of key Message Broker concepts like nodes, transformations, message modeling, administration, patterns for development, and integration use cases.