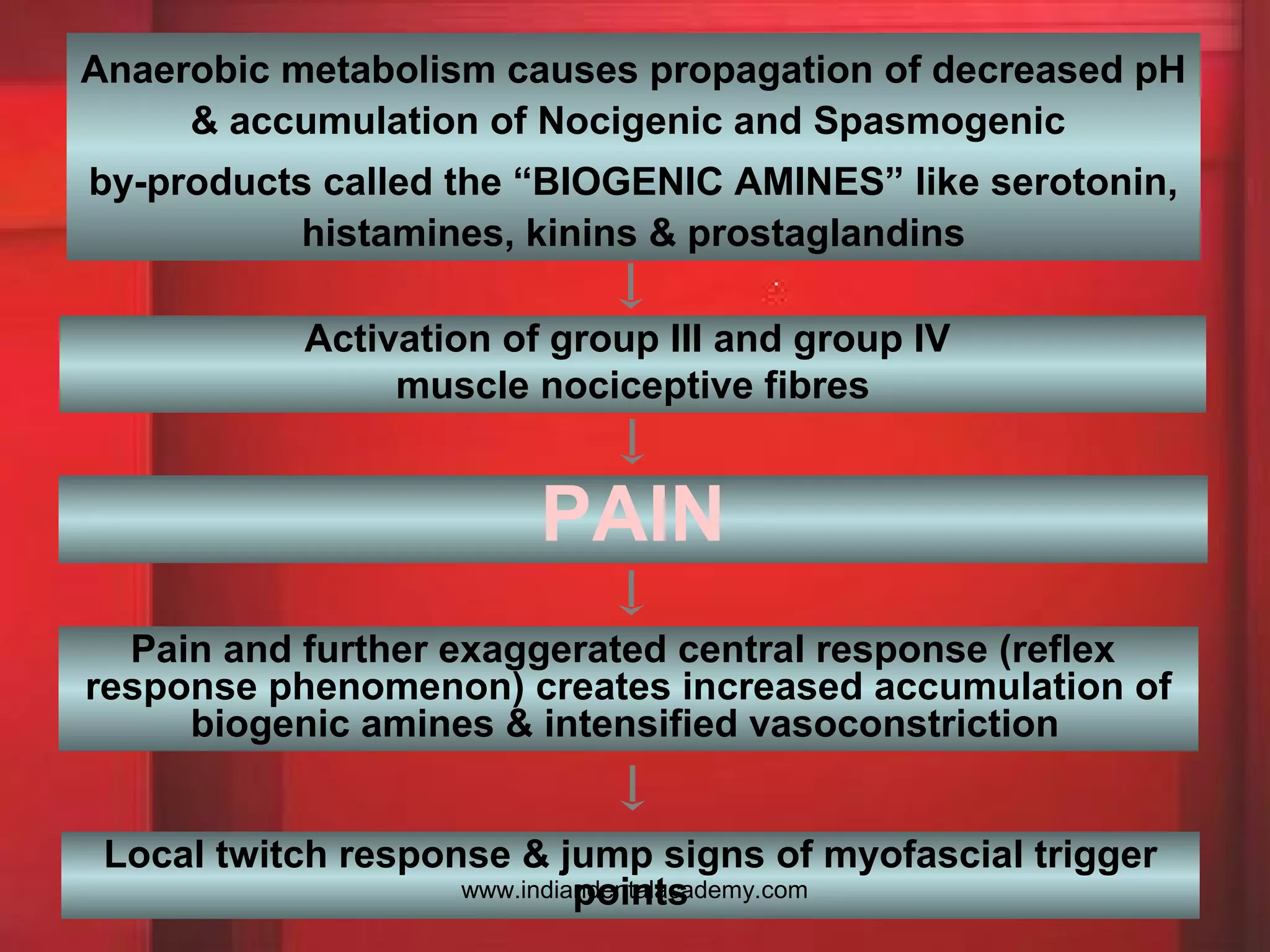
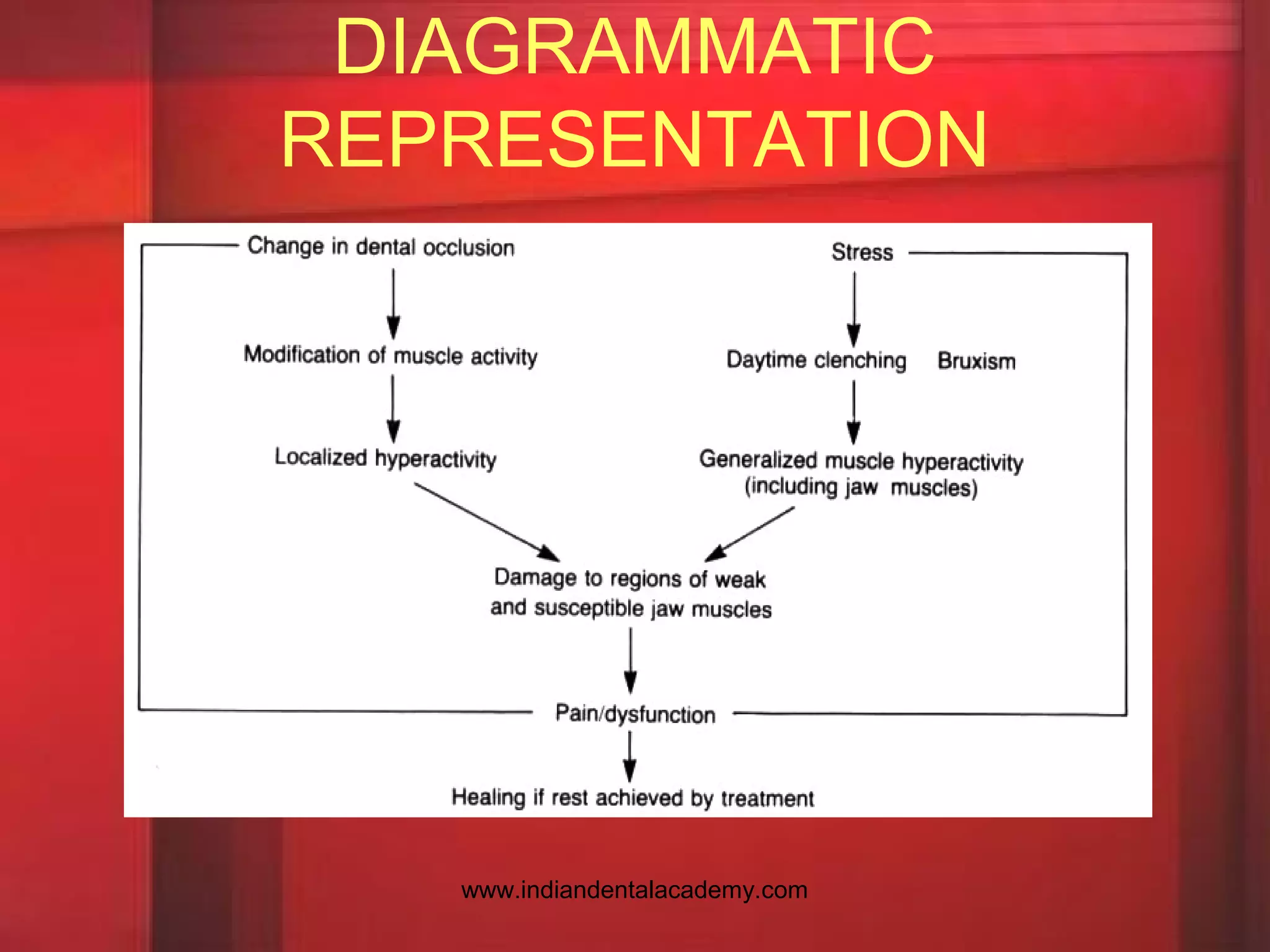
The document discusses Myofascial Pain Dysfunction Syndrome (MPDS), outlining its etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment options. It highlights pain patterns, trigger points, and various diagnostic tests used to assess jaw movement and muscle function. Treatment approaches include physical therapy, pharmacotherapy, self-care strategies, and the use of occlusal splints, addressing both physical and psychological aspects of the condition.