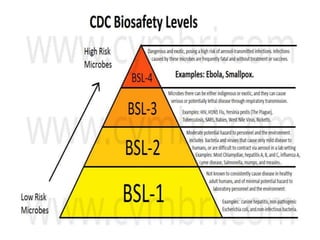
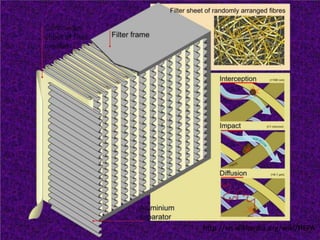
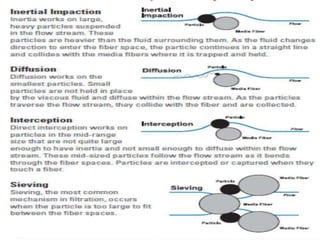
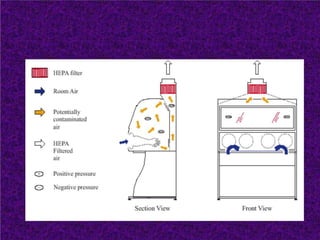
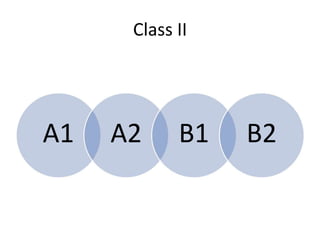
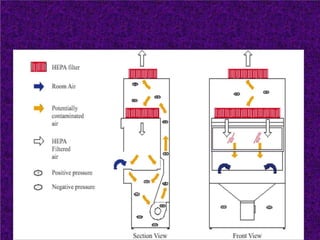
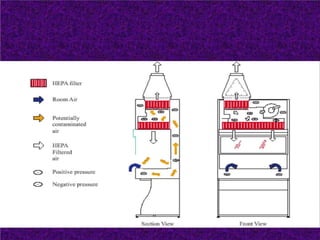
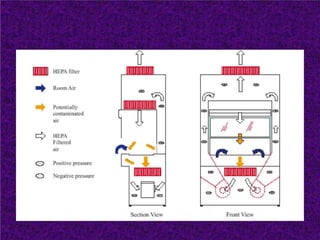
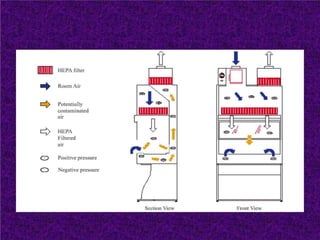
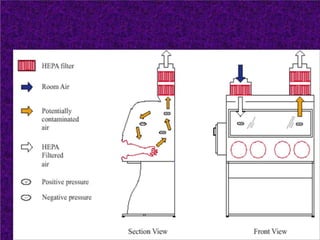
Biosafety levels and biosafety cabinets are essential for safely working with infectious agents in laboratories. There are four biosafety levels with increasing safety precautions for more dangerous pathogens. Biosafety cabinets provide personnel, environmental or product protection depending on the class. Class I provides personnel and environmental protection while Class II and III also provide product protection using laminar airflow and HEPA filtration of exhaust air. Proper work practices, maintenance, and decontamination methods are required when using biosafety cabinets.