1) The document discusses the rhythmicity and automaticity of the heart, which refers to the heart's ability to beat regularly and generate impulses without external stimuli.
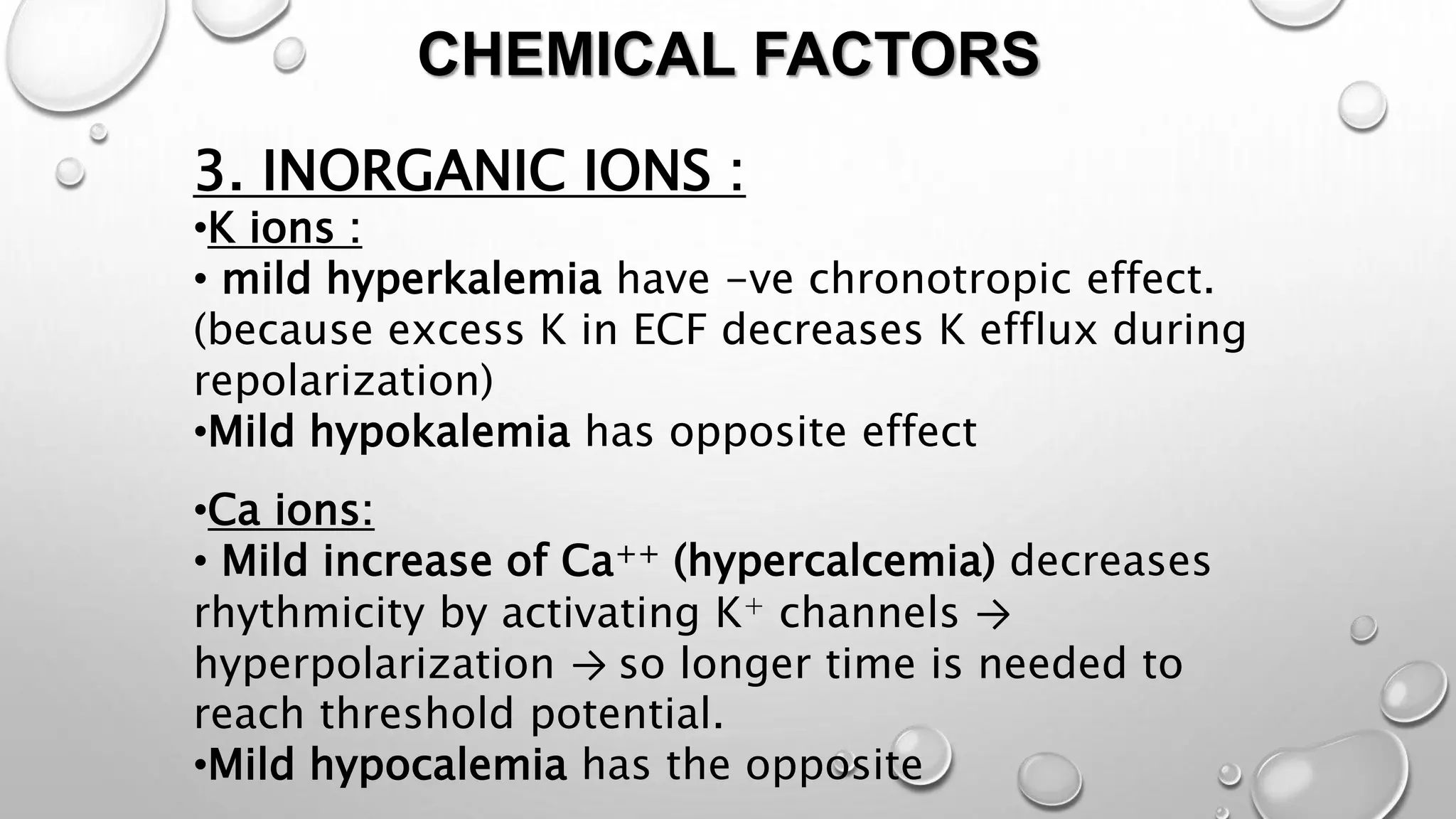
2) It originates from within the heart itself (myogenic, not neurogenic) and several factors can influence the heart rate such as the autonomic nervous system, temperature, drugs, blood gases, and inorganic ions.
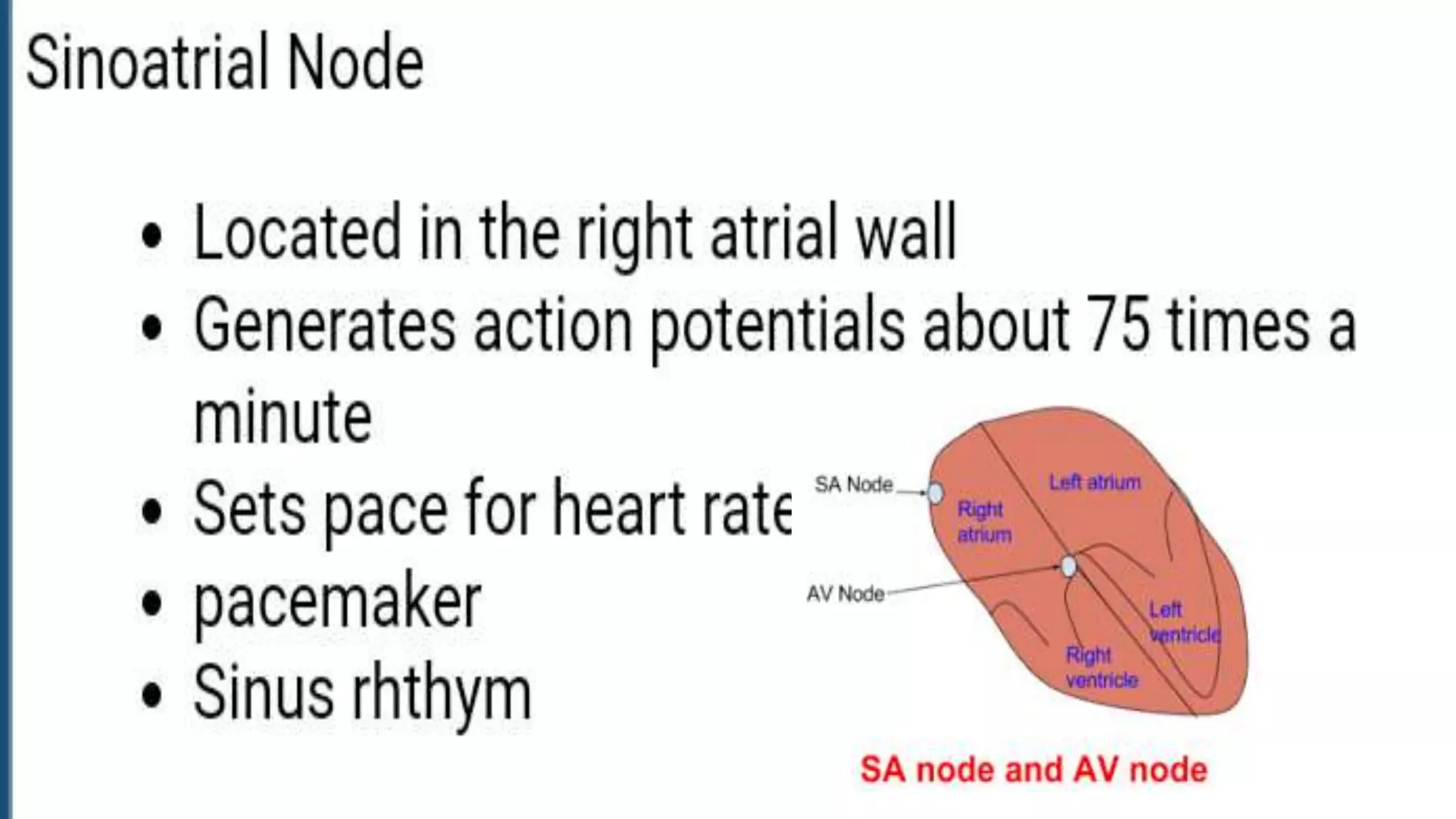
3) The sinoatrial node acts as the pacemaker for the heart and has membrane properties that allow it to spontaneously depolarize, initiating the heartbeat via an action potential involving sodium, calcium, and potassium ion fluxes.