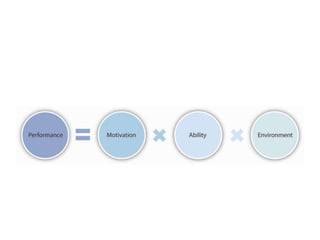
The document discusses different theories of motivation. It provides definitions and explanations of several motivation theories:
1. Hertzberg's Two-Factor Theory proposes there are motivator and hygiene factors that influence satisfaction and motivation. Motivator factors like achievement and recognition increase satisfaction, while hygiene factors like salary and working conditions prevent dissatisfaction if absent.
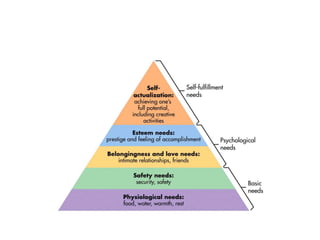
2. Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs suggests people must satisfy basic needs before pursuing higher level needs of esteem and self-actualization. Meeting each level of needs motivates pursuing the next.
3. The Hawthorne Effect found that simply being observed in studies improved worker productivity, not just physical changes, as workers felt more valued from attention.