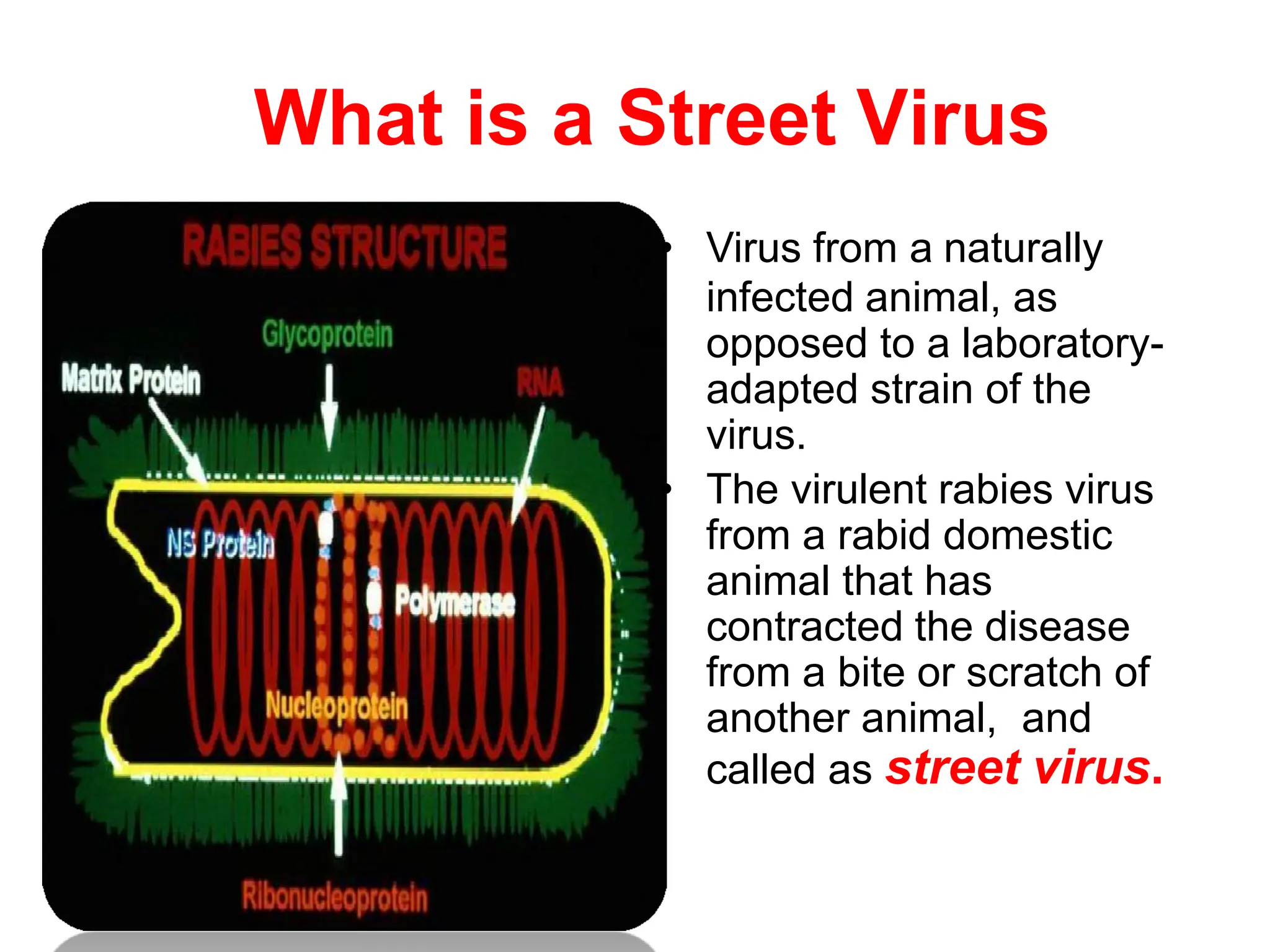
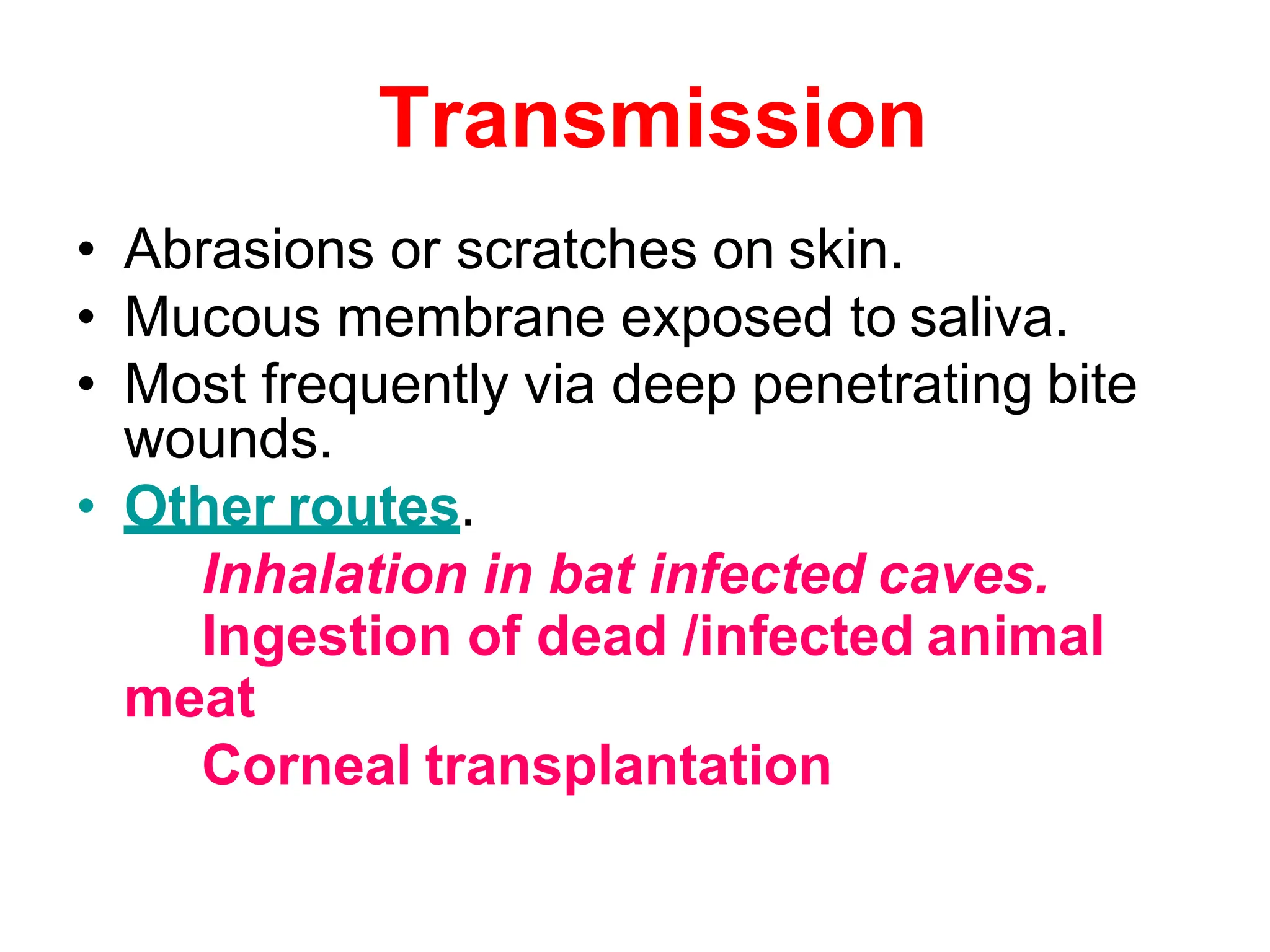
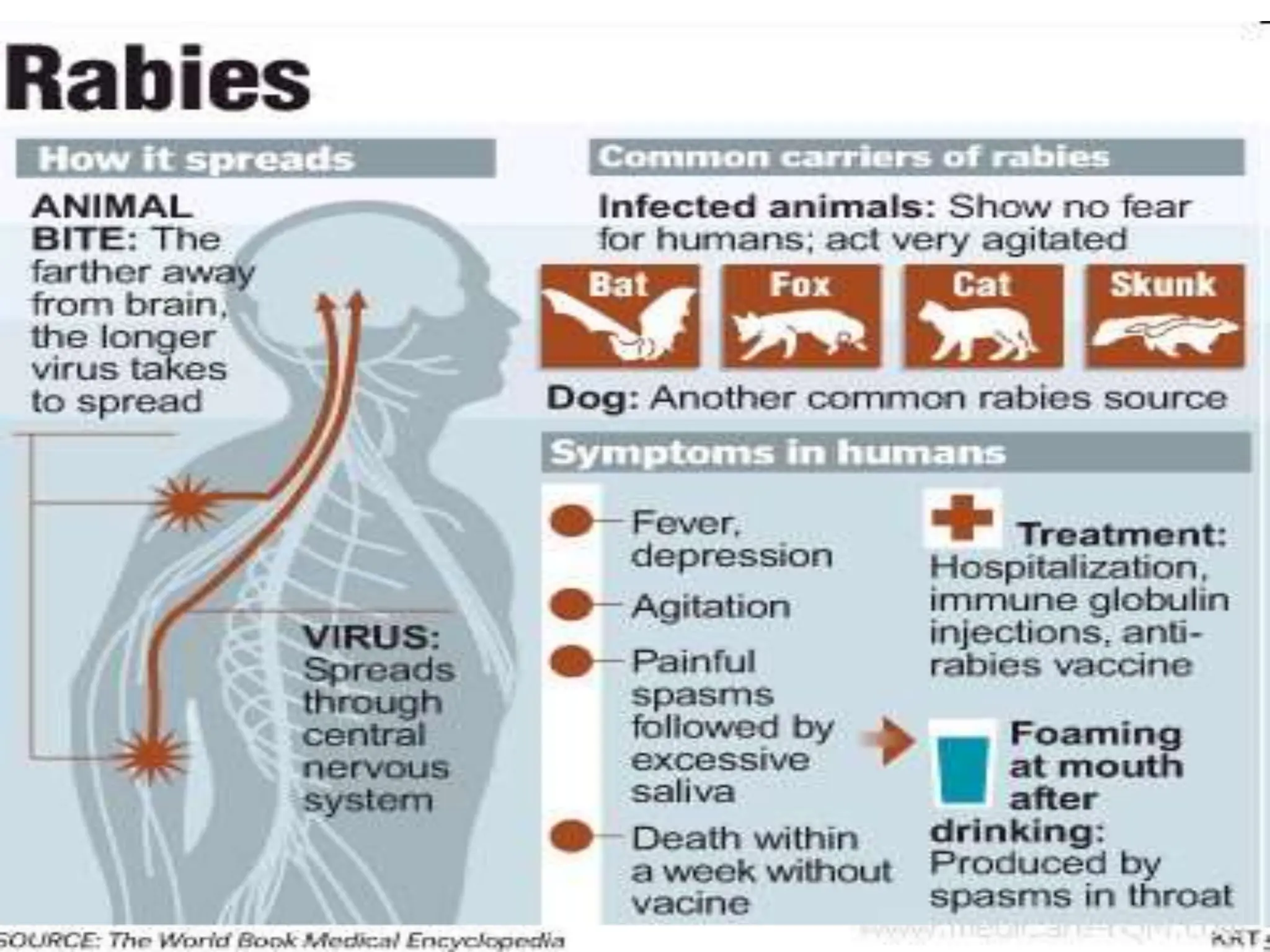
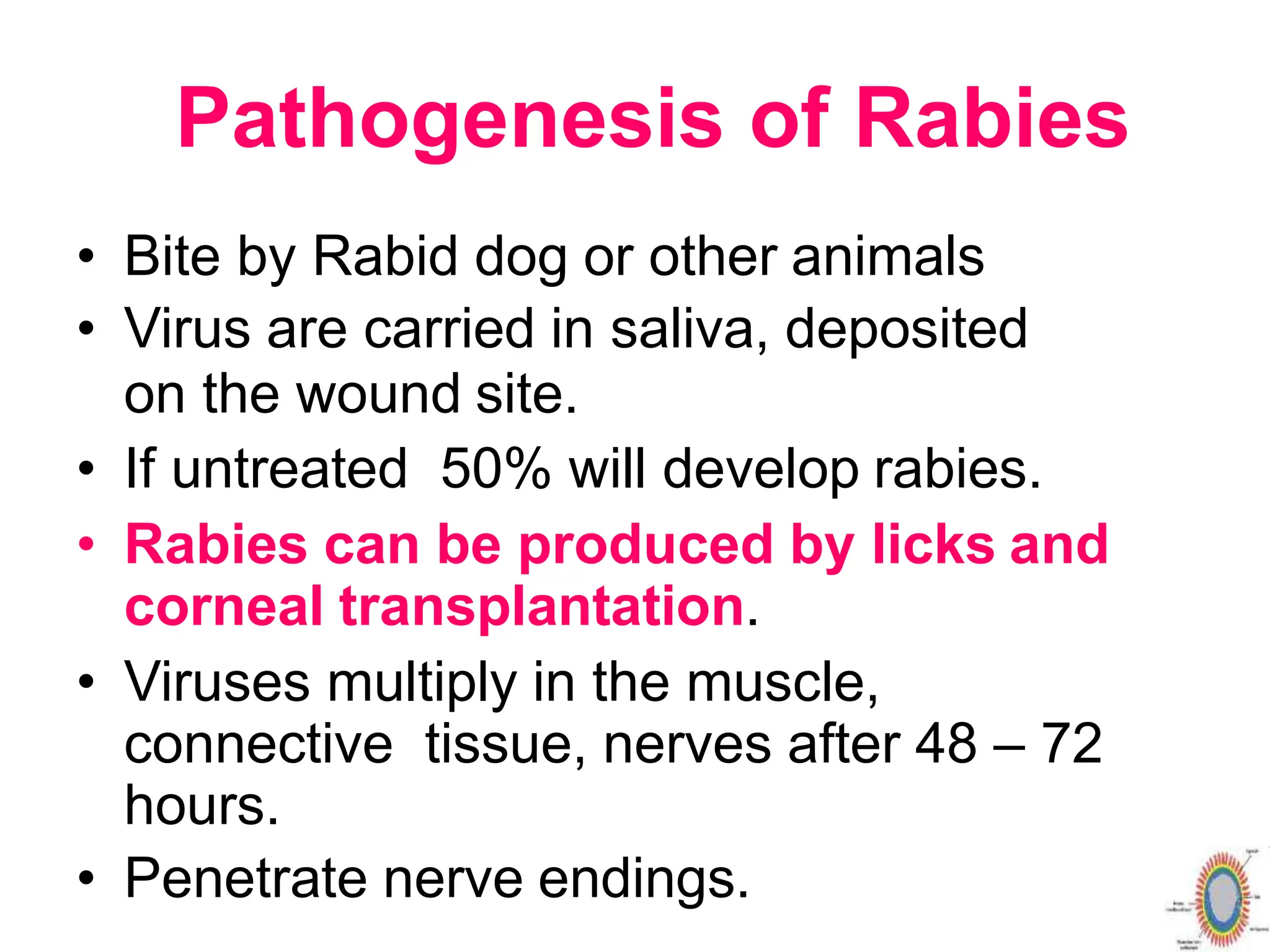
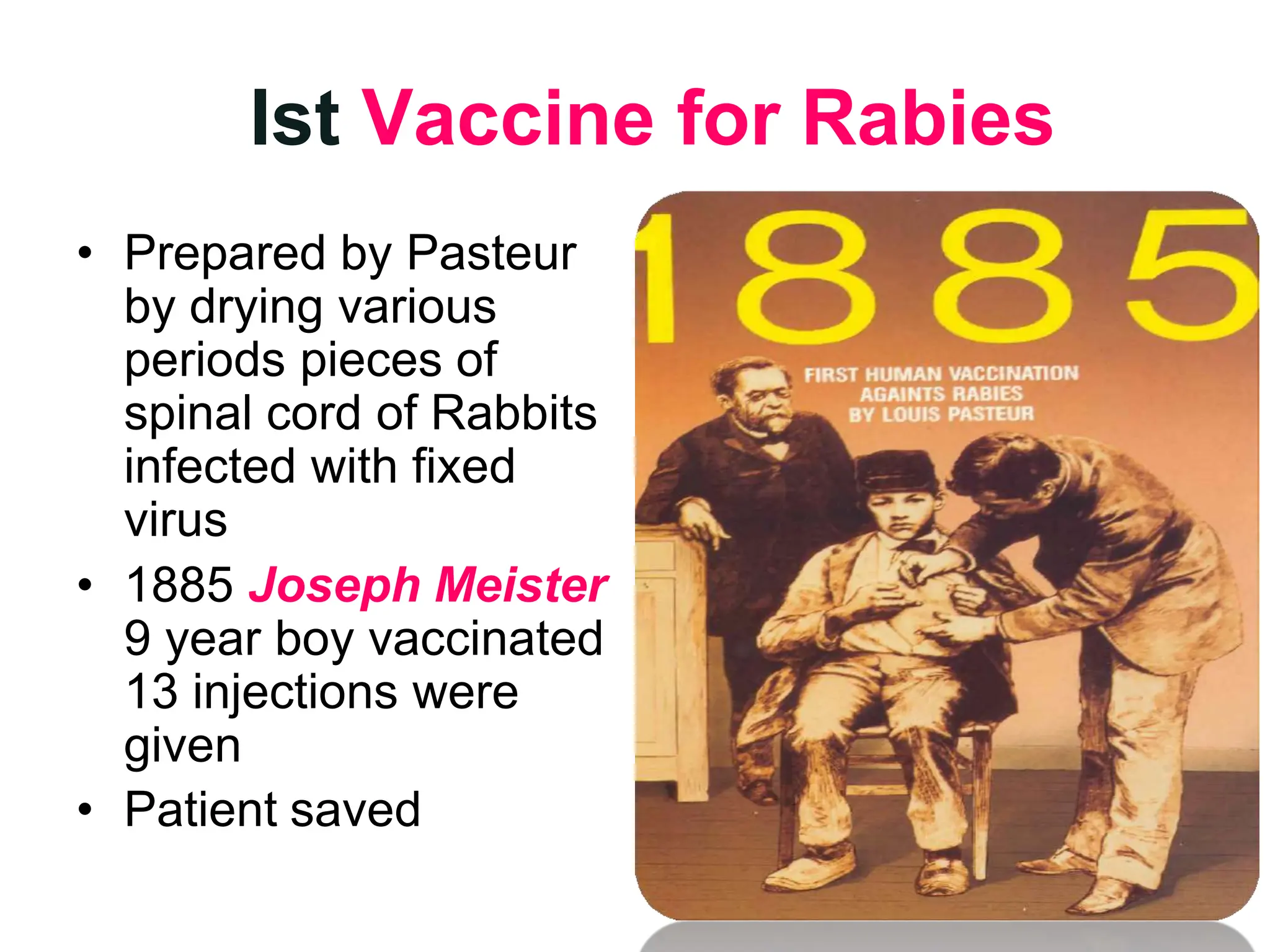
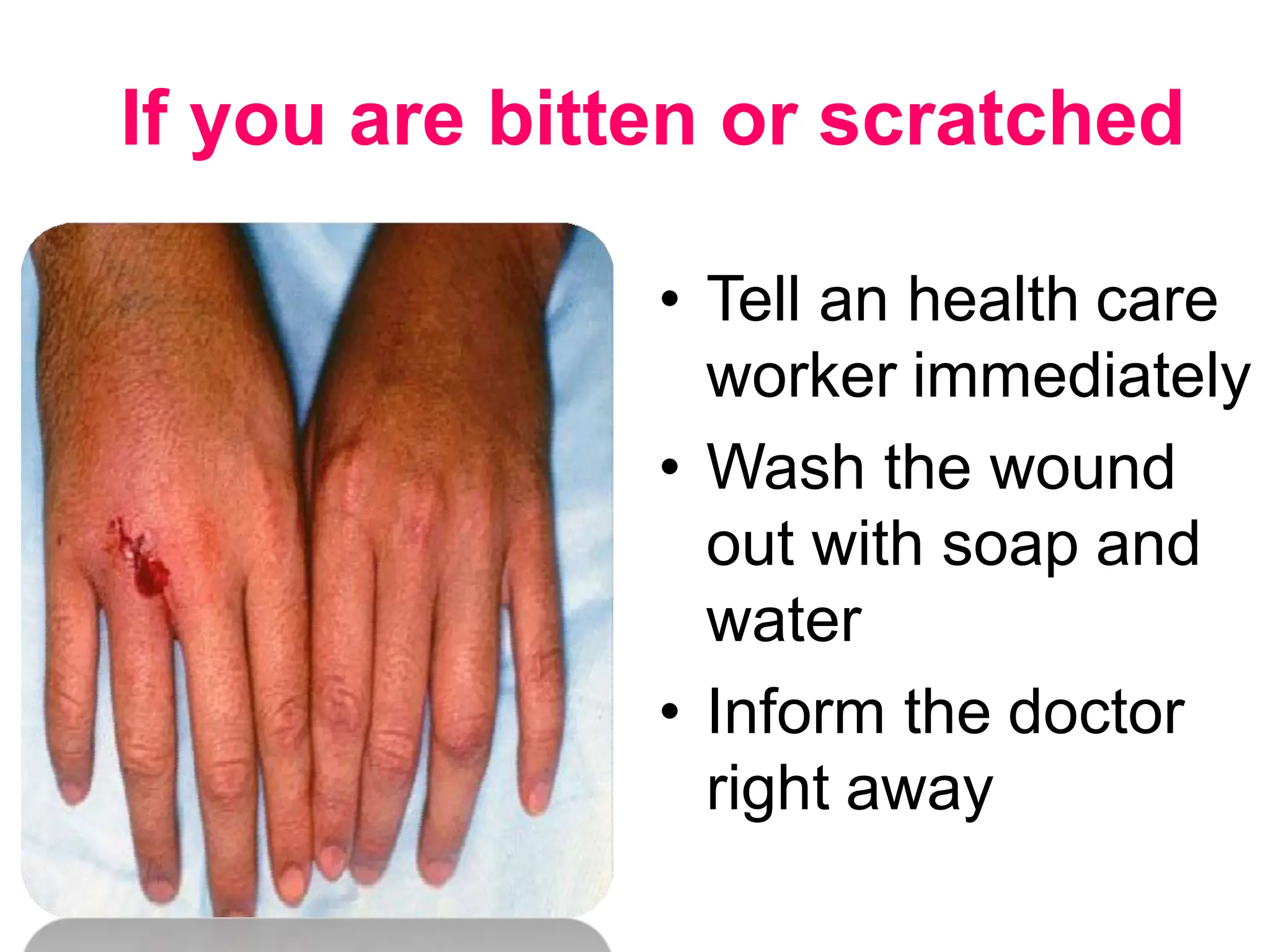
Rabies is a fatal viral disease spread to humans through bites or scratches from infected animals. It is endemic in parts of Asia and Africa, where over 95% of human deaths occur. The rabies virus infects the central nervous system and is usually fatal once symptoms develop. Common symptoms include fear of water, paralysis, and death. Laboratory diagnosis involves detecting the virus or antibodies in samples or observing Negri bodies in brain tissue. Prevention includes pre- and post-exposure vaccination and prompt wound cleansing following exposure.