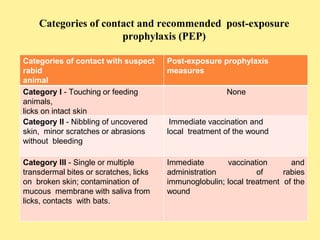
Rabies is a fatal viral disease that causes inflammation of the brain. It is transmitted primarily through bites from infected animals like dogs, bats, and wolves. Notable points in the history of rabies include Louis Pasteur developing the first vaccine in 1890. Rabies virus targets the central nervous system and symptoms include hydrophobia, increased salivation, and death. Dogs are a major reservoir and transmission can occur through bites or contact with their saliva. Post-exposure prophylaxis includes wound cleansing and a vaccine series, while pre-exposure vaccination provides protection for those at high risk of exposure.