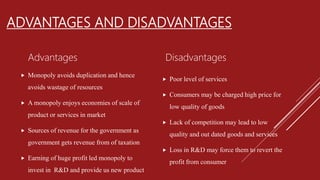
The document explains the concept of monopoly, characterized by a single seller, lack of close substitutes, and barriers to entry. It outlines different types of monopolies, including private, public, absolute, discriminative, legal, natural, and technological monopolies, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Examples, such as the Indian Railways, illustrate the application of monopolies in real markets.