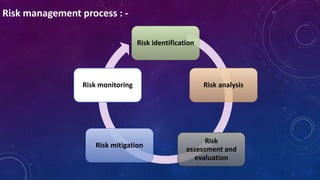
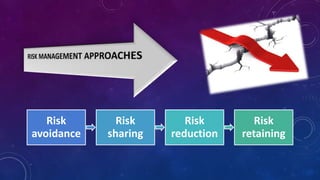
Risk is defined as exposure to danger, and risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and controlling threats to an organization's capital. It is integral for defining future objectives and achieving goals while keeping risks under control, distinguishing between unsystematic and systematic risks. Frameworks such as ISO 31000 provide guidelines for continuous improvement in risk management processes, emphasizing value creation and adaptability.