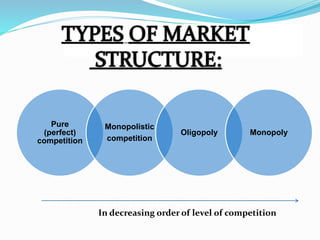
This document discusses oligopoly, which is a market structure dominated by a few large firms. It begins by defining oligopoly and noting its key characteristics, including few sellers, barriers to entry, and mutual dependence between firms.
It then outlines six types of oligopoly: pure, differentiated, collusive, non-collusive, open, and closed. Examples are provided to illustrate each type. Common barriers to entry in oligopolistic markets are also defined.
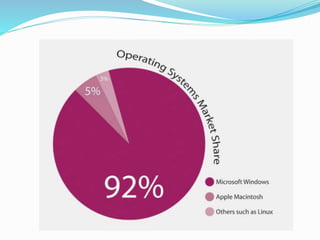
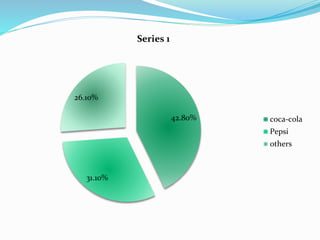
Several real-world examples of oligopolistic industries are explained, such as the smart phone, computer, music, auto, and soft drink industries. Models of oligopoly behavior are briefly introduced, focusing on the kinked demand model and price leadership models