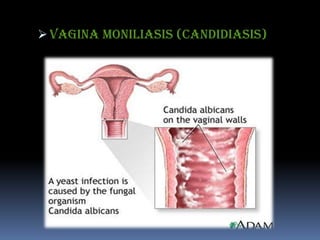
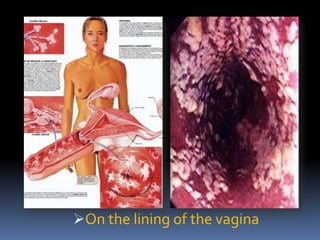
Moniliasis, or candidiasis, is a common fungal infection caused by Candida that usually infects moist areas of the body like the vagina. It is more common in those with diabetes, obesity, pregnancy, or those using antibiotics or hormonal contraceptives. Symptoms include burning, itching, and thick white discharge. Diagnosis involves examination and testing. Treatment consists of antifungal creams or suppositories used for 1-2 weeks. Nursing focuses on pain management, health education to prevent further infections, and monitoring for complications.