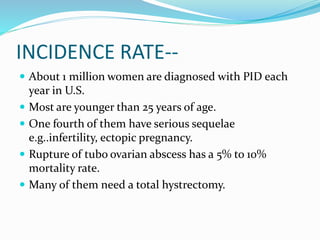
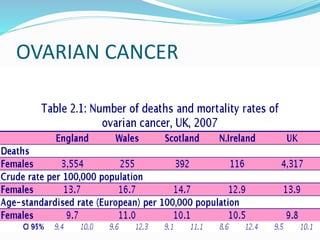
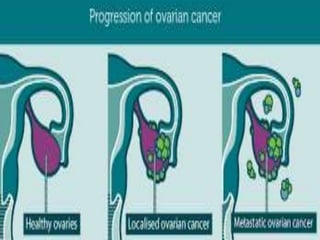
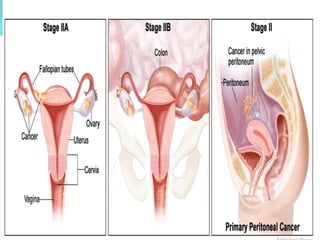
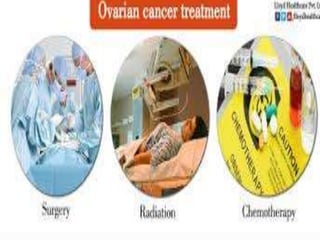
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an inflammatory condition of the pelvic cavity that is usually caused by bacteria, viruses, or other microbes. It commonly affects sexually active young women and can cause long-term complications like infertility or ectopic pregnancy if left untreated. Symptoms include lower abdominal pain and vaginal discharge. Treatment involves antibiotics, bed rest, and care of any sexual partners. Nursing care focuses on monitoring, education, and supporting patients through treatment.