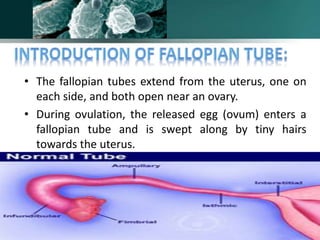
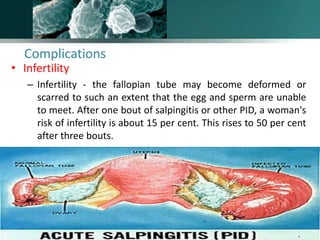
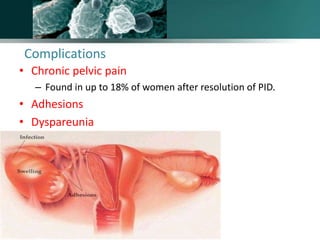
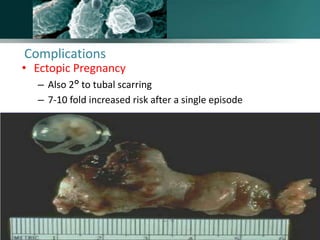
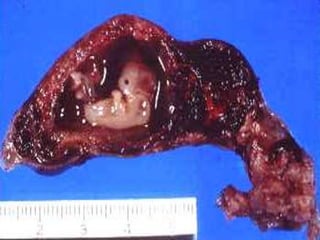
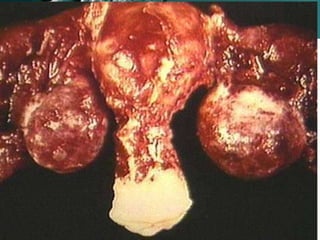
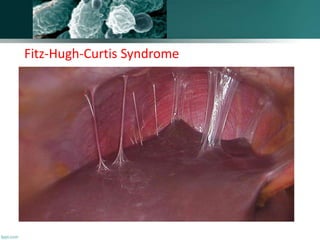
Salpingitis is the inflammation of the fallopian tubes, often caused by bacterial infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea, and is a significant cause of female infertility. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include abnormal discharge and abdominal pain, while complications can lead to chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancies, and infertility. Diagnosis typically involves physical examinations and laboratory tests, and treatment may include antibiotics, hospitalization, and surgery depending on the severity of the condition.