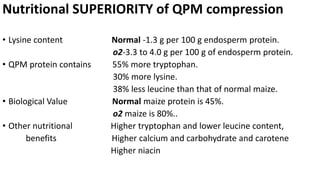
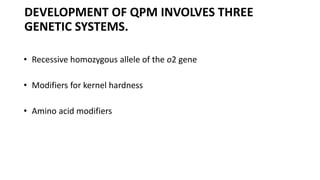
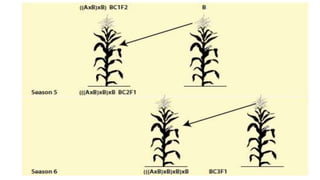
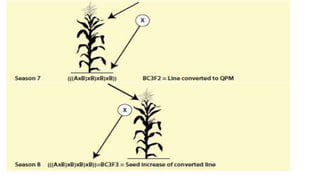
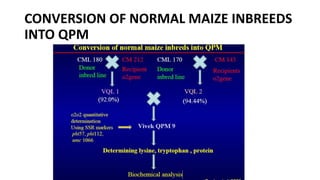
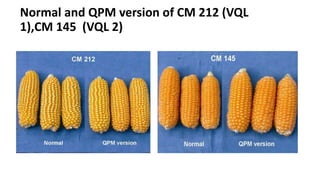
- Quality Protein Maize (QPM) is a variety of maize that contains higher amounts of lysine and tryptophan with lower amounts of leucine in the endosperm compared to normal maize.
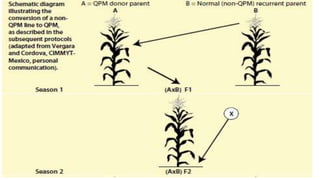
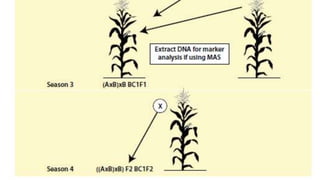
- Two scientists from CIMMYT led the development of QPM over three decades to produce maize with a hard kernel, good taste, and disease/insect resistance.
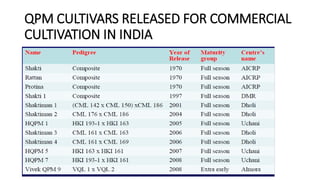
- QPM research and development spread from Mexico to Central/South America, Africa, Europe, and Asia. India released several QPM hybrids using parental lines developed from CIMMYT QPM inbreds.