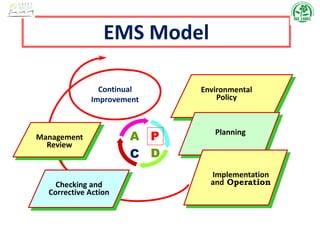
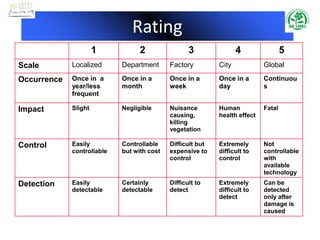
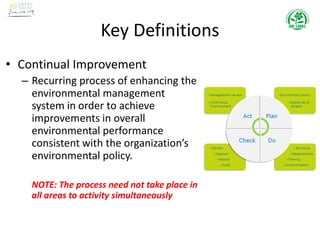
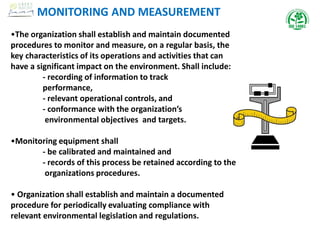
The document outlines the scope, terms, conditions, and objectives of an Environmental Management System (EMS), as well as key definitions related to environmental aspects, impacts, and management practices. It emphasizes the importance of compliance with legislation, pollution prevention, and continual improvement within organizations' environmental policies, objectives, and targets. Additionally, it details procedures for monitoring, measuring, and auditing the EMS to ensure effective implementation and management of environmental performance.