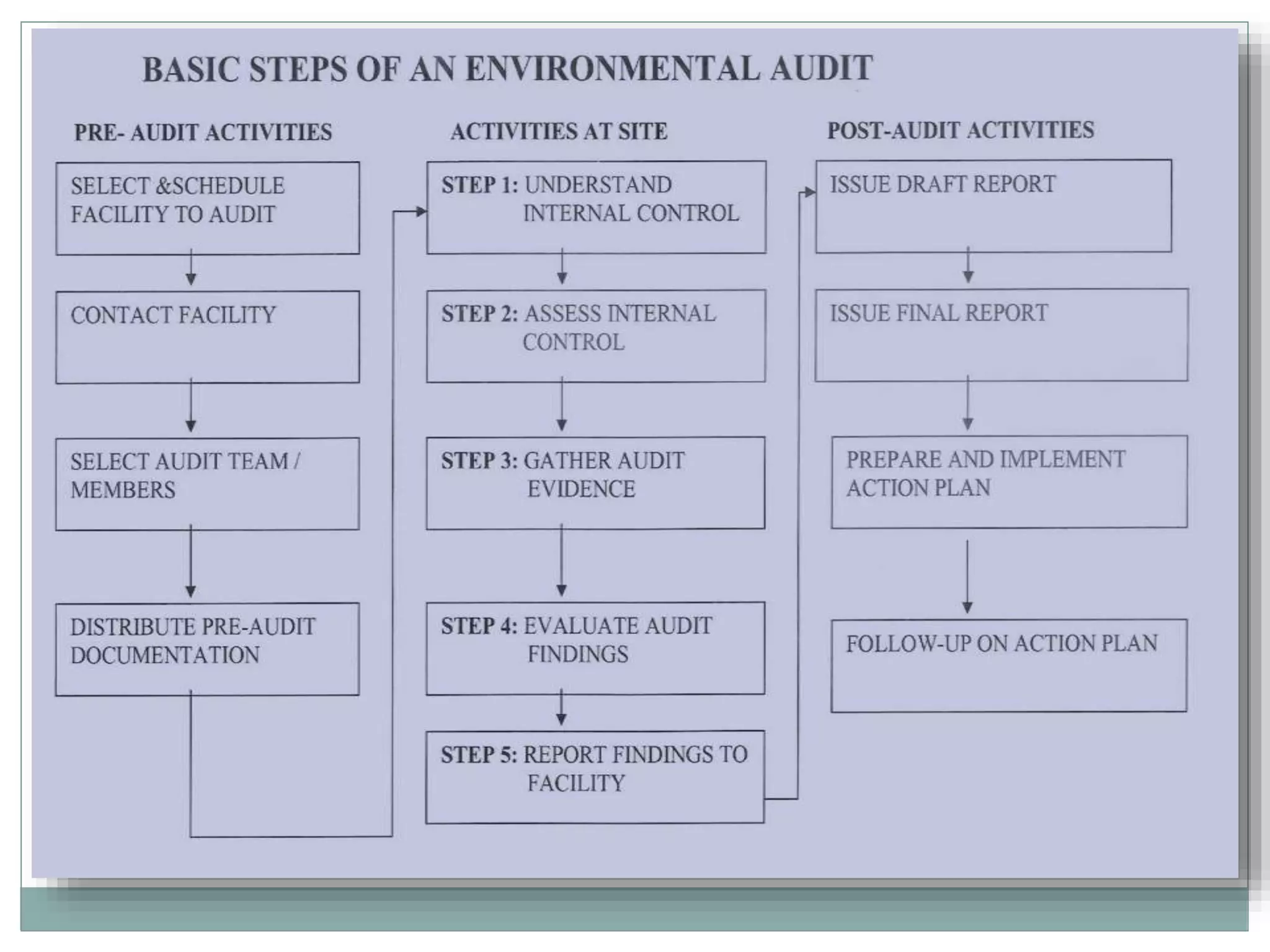
Environmental auditing involves periodically evaluating an organization's environmental performance, policies, and compliance with regulations. It aims to help protect the environment and minimize health risks. The audit scope includes assessing waste management, emissions, environmental protection systems, energy use, emergencies planning, and occupational health and safety compliance. The audit process consists of planning, on-site evaluation of controls, gathering evidence, recording findings, and evaluating results to determine how well environmental management systems are functioning.