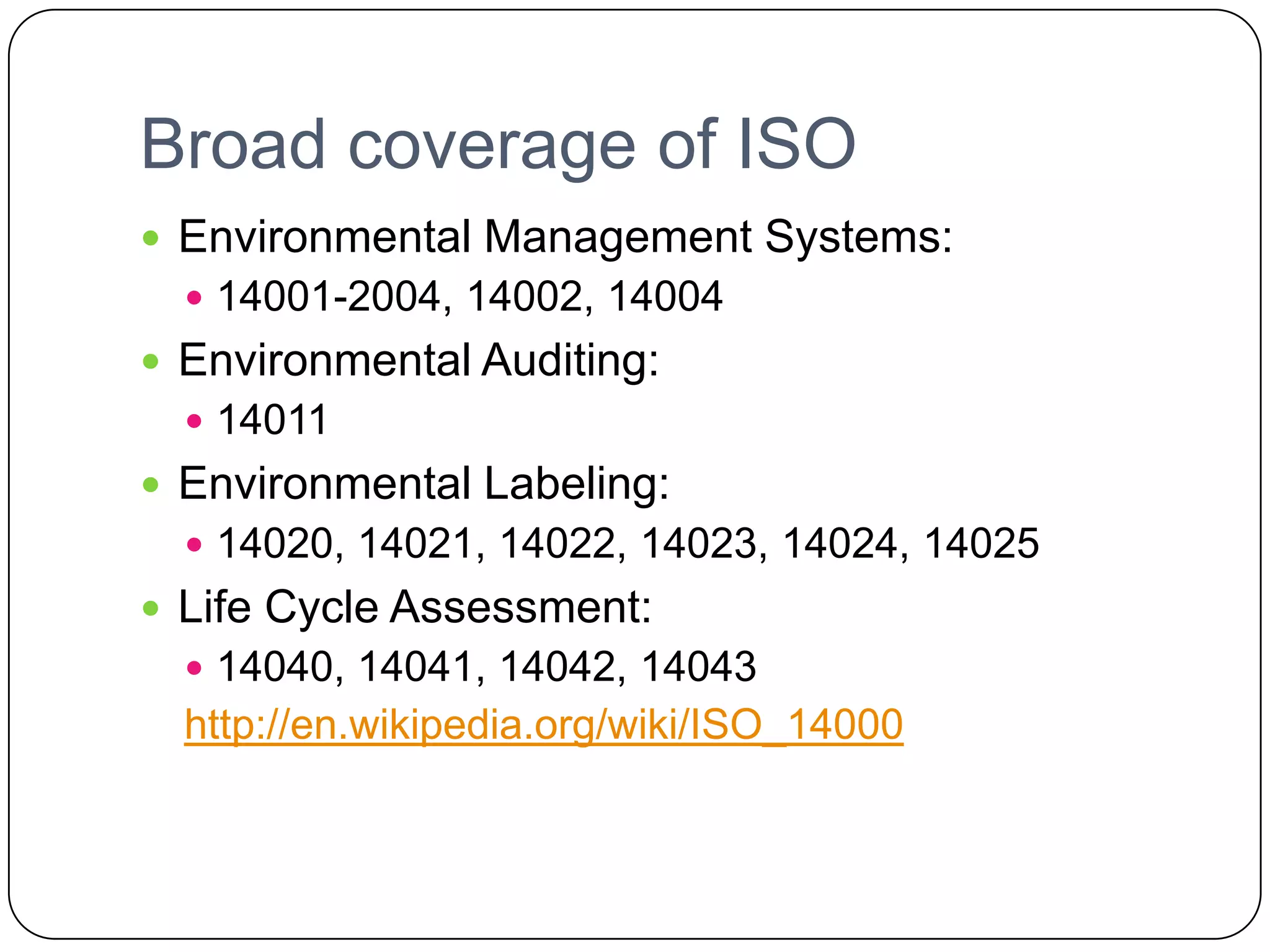
The document discusses environmental management and provides definitions. It defines environmental management as the management of human interaction with and impact on the environment. It also discusses carrying capacity, environmental resources, pollution, and environmental management systems. Specifically, it defines an environmental management system as the management of an organization's environmental programs in a comprehensive and planned manner. It also outlines the 17 requirements of the ISO 14001:2004 standard for environmental management systems.