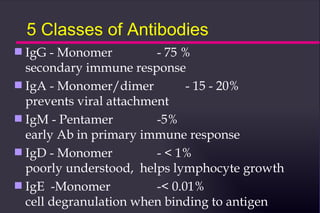
This document summarizes key concepts in immunology, including the three lines of defense against pathogens, primary and secondary immune organs, lymphocytes and immunity types, immunologic disorders, antibodies, and common immunologic problems. It covers cellular and humoral immunity, the immune response process, and immunologic terminology.