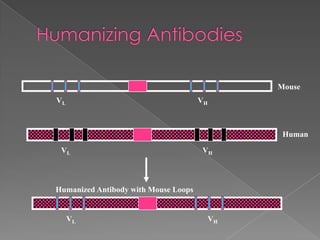
Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins produced by B cells that recognize and bind to foreign substances like viruses and bacteria. There are two main types: polyclonal antibodies which recognize multiple epitopes on an antigen and are produced through serum, and monoclonal antibodies which are derived from a single clone and recognize a single epitope. Monoclonal antibodies are important for research, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Antibody engineering techniques allow modifying antibodies to make them more effective, such as humanizing mouse antibodies to reduce immunogenicity.