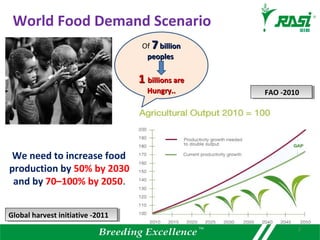
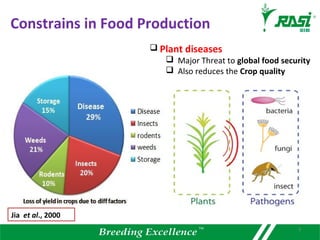
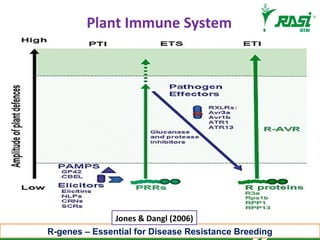
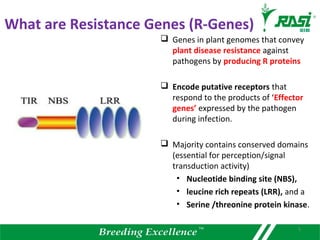
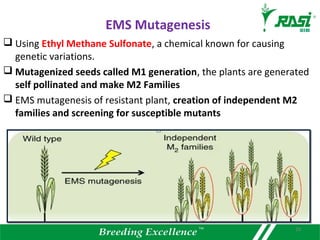
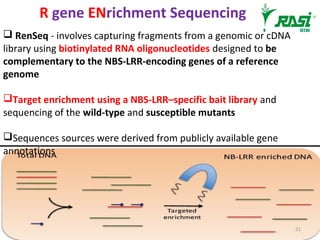
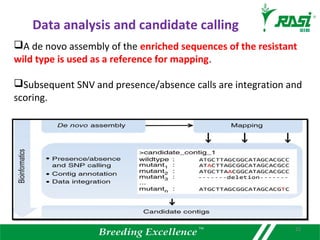
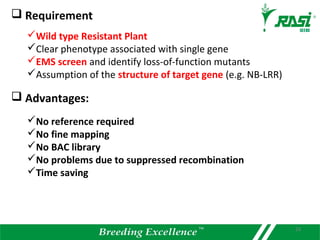
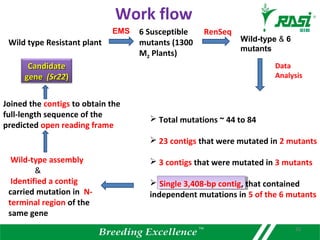
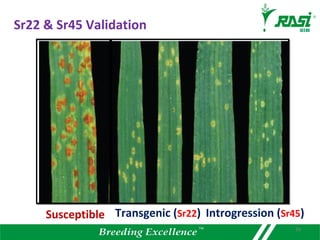
The document discusses plant disease resistance genes (R-genes) and their importance in crop breeding for disease resistance. It contains the following key points:
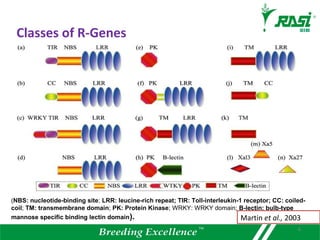
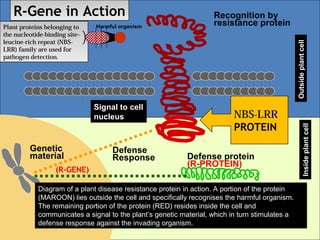
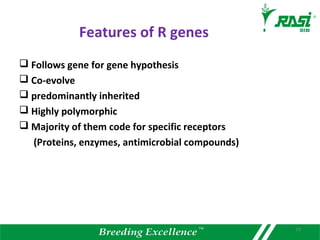
1. R-genes encode receptors that recognize pathogen effector proteins and trigger plant immune responses. Most R-genes contain nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat domains.
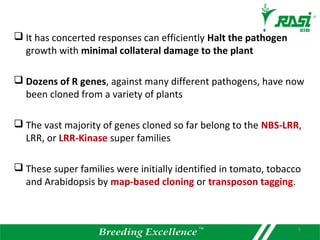
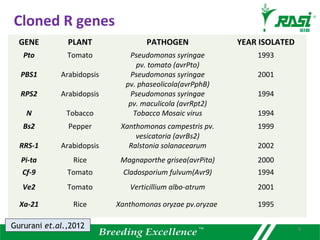
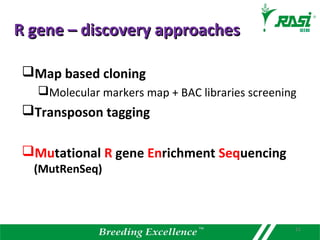
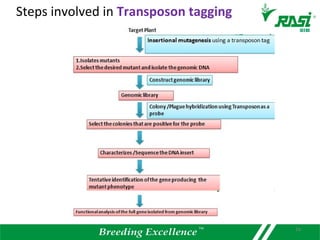
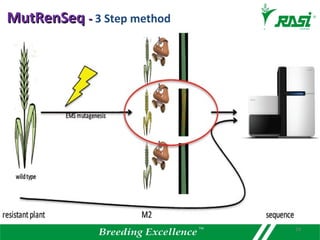
2. Dozens of R-genes have been cloned from various plants using map-based cloning, transposon tagging, or a new method called MutRenSeq that enriches for R-gene sequences.
3. Introducing R-genes from wild crop relatives into domestic crops can provide natural and sustainable resistance to diseases while avoiding pesticide use and potential environmental damage.