The document summarizes key events of the Cold War era:
1) The Berlin Airlift of 1948-1949 was a response to the Soviet blockade of West Berlin, in which Western allies airlifted supplies to the city to support its residents. Over 200,000 flights delivered enough food and fuel to sustain West Berlin.
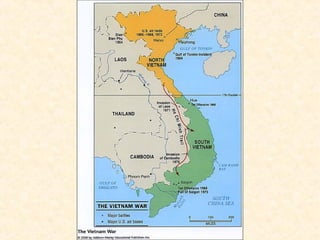
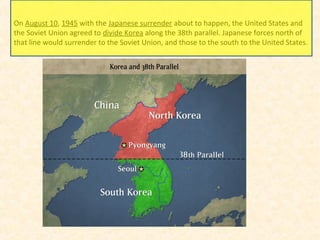
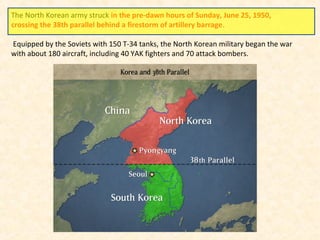
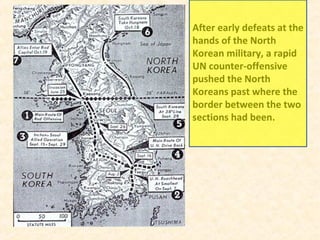
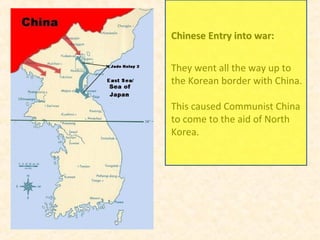
2) The Korean War began in 1950 when North Korea invaded South Korea, supported by the Soviet Union and China. After early successes, UN forces pushed the North Koreans back until China entered the war, leading to a stalemate along the original border.
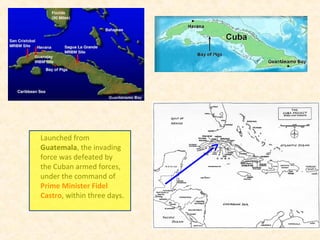
3) The Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962 brought the world closest to nuclear war as the US and Soviet Union confronted each















![August 13, 1961
The Berlin Wall was a concrete barrier built by the German Democratic Republic (GDR, East
Germany) [The idea of their masters - The Soviet Union.] that completely enclosed the city of
West Berlin, separating it from East Germany, including East Berlin.
The Wall included guard towers placed along large concrete walls, which surrounded a wide
area (later known as the "death strip") that contained anti-vehicle trenches and other defenses.
Before the Wall's erection, 3.5 million East Germans escaped Esat Germany by walkingt into
West Berlin, then getting on a plane to West Germany.
The goal of the wall was to stop people escaping from Communist control in East Germany.
During its existence from 1961 to 1989, the Wall stopped almost all escapes from East Germany
After it was put up, around 5,000 people attempted to escape over the wall, with estimates of
the resulting death toll varying between around 100 and 200.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module8-140320103243-phpapp01/85/Module-8-Conflict-22-320.jpg)