The document estimates the natural frequencies of axial vibrations of a uniform bar using consistent and lumped mass matrices with a two element mesh. It provides the element matrix equations for both methods. For the consistent mass matrix, the natural frequencies are found to be 108 and 108. For the lumped mass matrix, the natural frequency is found to be √(108E/pL^2). The exact solution is given as (πi/L)√(E/p) for i=1,2,3,... and the results are compared to this expression.
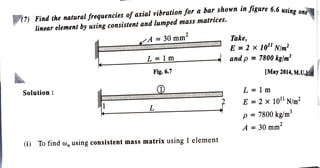
![ff:(; For a uniform cross-section bar as shown in figure 6.6 of length L = I m made up of
Jmaterial having E = 2 x 10
11
N/m
2
and p = 7800 kg/m
3
estimate the natura~ lfo
f
frequencies of axial vibrations of the bar using both consistent and lumped mass
matrices. Use a two element mesh. If the exact solution is given by the relation
CO; = ~~ {¾ ,i =1, J, 5, ••••• oo
compare your answer and give your comments, A = 30 x 10-6
m2
•
1 L 2 3
A
~ Fig. 6.6 [May 2011, Dec. 2012, May 2016, May 2018, Dec. 2018, M.U ,fl
. •v
Solution:
L 2
(i) Natural frequencies roi using Consistent Mass Matrix
The element matrix equation is given by
3
L = 1 m
E = 2 x 1011
N/m2
p = 7800 kg/m3
A = 30 X 10-6
m2
1~[~l -/]{~:} = ro
2
p:h, [~ ~]{~:}
we take two elements of equal length he = 0.5 m
Cancelling A on either side of the equation, we get
2 x0t 1
[ ~
1
-/ ]{ ~:} = 002 780x 0.5 [ ~ ~]{ ~:}
i.e. 108[_: -4
4
]{~:} = 002 [ :.:
5
o/:] {~J
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module6-230226081914-34f1f267/75/Module-6-1-lumped-and-consistent-mass-pdf-1-2048.jpg)
!['o,,.-dd{Jr a ,,,,.iforn• cro.,·s-section bar of length L made up of a material whose Young'iY ·
{Si ~ d 1 ~ a,id ,lc11,,·ity are Kive11 by .E and p. Estimate the natural 'requenc/es oif axial
"'" " ,,.. . J'
ti n of t/ie bar ,,.,.t,,g bot/, con.,·lstent and lumped ma,w; matricet,.
,,/bra o ~-
4
__..______
L
______-'j
l?lg. 6.5 (D~c. 2016, M.V.J
S
olution: Since actual values of£, L and pare not given, we shaJJ consider only a single
element to find the frequency.
(I) Natural frequency using Consistent Mass Matrix
The element matrix equation is given by
~~[}l ~1][~:} = ro
2
p:h, [ ~ ; ](iJ
·: we take one element he = L
Cancelling A on either side of the equation and simplifying, we get
E ro2p L - E - w2p L U1
L 3 L 6 _ O
_ E _ w 2
p L E _ w
2
p L
J L 6 L 3
rnpobe b h t '
o und a ry co nditi o ns i. e . U 1 = 0, write t e equ a wn
E w2p L = 0
L 3
') JE
:. w· = ~
Ill) N pl
lt lu r~1 f
1 rt:qu e n cy Uij lng Lumped Mass Matrix
-ll rnPect ,n . . . . A h r l O I
i:l t,;:,; mu tr1x is g ive n h y p , " " ,
w = fl_ , ff
L VP
-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module6-230226081914-34f1f267/85/Module-6-1-lumped-and-consistent-mass-pdf-2-320.jpg)

![11111
taAM IHI
492
(91 Find rhc natural frequencin of longitudinal vibratio11.~ of tlie constr • d
· Ulnt Sit ·
of arrru A and 2A and of equal lengths (L), a.1t s'1own ;,, figure 6 9 Co PPed Jha/t
· · mpare ti,
nhfo;ned using lumped mass matrix approacl, , e results
ill Lt
A
L
Fig. 6.9 [May 2015 (old), Dec. 2019, M.u.1
Solution : To fi nd natura l frequencies
IA] Lumped mass matri.x approach
(i ) The element matrix equation for this problem is
olpA he
2
(ii ) Now, we bave two elements
:. Element matrix equation for element 1 is
21E [_ ~l][~J = w2AL [~ ~][~J
:. Element matrix equation for element 2 is
A/[_
~
I][~;]'= ro
2
p/L[~ ~] [~:)
(W) Global matrix equation is given by
- 2 0 ]{U
1
)
3 - 1 U2
- 1 1 U3
w
2
pAL [
2
= 2 0
0
Impose global boundary condi tions i.e. U1
= 0, we get
[ p2f, [}]~]]-.,z [~ ~]][~:) = (~)
i.e.
H
}]~l ] 0)2 [ ~ ~ ]] [ ~ : ) = ( ~) where k =
0
3
0
2 E
P Lz
g](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module6-230226081914-34f1f267/85/Module-6-1-lumped-and-consistent-mass-pdf-5-320.jpg)
![i 1 -, rri! 1/;r nn,11rnl f'r·,0
Qno1f'_
' n.f 11 rfol d h rnrimts nf a bor of tat(fr,rm c rn.fls section of
in ,,,m ... n'1d n_f ltnKth , m . 1ala n =-= l >" JO ~ N!mm ;, and () == 8000 kg/m
1
. Take two
[May 2012. Uec. 2015 , M.U .j
~olntinn : n,, 1dc the I hcde <.1l,m:t in of th e problem into two e lements.
.,.
CV
,,_~
~
I Q)
G) gj •
~
ill &
Fig. 6.1
The element matrix equation for the pr9blem is obtained from equation (6.7) viz.
oipA he [2 1] {U1}
6 1 _
2 U2
· · we Lake two elements of equal length he = 0.5 m
Car1celling A on either side of the equation, we get
E [ 1 -IJ{U1) _
he- -1 1 . V2
w
2
phe [2 1] {U1}
6 1 2 U2
2x JO
11
[ 1-lJ{U1]
o.s - 1 1 .u2
(J} 2 8000x0.5 [2 l]fU1}
6 _1 2 lU2
1.c. 1OR [
4
-
4
1
{U1)·
- 4 4 U2
w2 [l.3= 0.671 { U1}
_0.6 7 l.33j U2
:e that.in these proble.ms, units of length are to be taken in m only.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module6-230226081914-34f1f267/85/Module-6-1-lumped-and-consistent-mass-pdf-6-320.jpg)

![6..3 CONShTfNl ANO lUMl'fO tiA'-~ MAHUCf~
M1M1 ~P H)D mm.11 b, w no~lrnr ttlld l11Mr~d l'JMH 1t111trit=I-! :' IJ, rfr~ "'" sam, for linear
,Cr r1(!;mml. lM•1101!, Jaot- 2017. M.U.j
lff., 1 :"W fC tf'.t lU>n f' 4
ml lTI in cqu,1 1,on th.7). we hove conqidcrcd masG of the
f"h:Dh rH at r. f "'. 1h J,,1 nl"Uh'ti I h «"m-: 'h,u t th e c kmc n t A lsn. we have u~cd th e sa rne
!,l Hlfi" luvCU1J,t1 fe r , "'....,,r11tti _ b(~th ma~" iHH.l stiffness rn at riccs. Hence. these mass
mtHrh'. ' tiH ,-.al k d a !- , on~hrent metrftes.
, '-- r.i ai~l."l l F ·· t-iuh' the Cf"mrlctc mc_, s~ of the cle me nt eq u a lly at the two nodes as
1':bJ'-'·n i1n lflE'-' ..C (J:.
ffi
pA h~
2
Fig, 6~
2
r.n1e m3'-'- matni fo rmed in :this v.-ay is ca lled as Lumped mass matrix and is given as
l-fJ =
p A he [ 1
2 0
~] for a bar element
~d, aot.:.gt ~ of L-umped ~fa ss ~fa trices
, J > Tht.> ~umpre: m.::.~~ ma trix is a diago nal matrix.
l I f gcn, ~!uc- p: Gbkm s are so.
lved by iteration methods an d dynamic respunse
:~k..1btwo ~re uftt:n ma de by taking incremental time steps. Hence. computations
...~c :,me ccr1~u~rng. D iagon al ma tr ix fo rm eases :i nd re duces co mputations.
rl I f i nd tlt1: ,.,,, o nowrof fnqut'neies of t rt.UIS )1erse n'hrations of a bram fix~d at ht.1th tlt/U as
~hu • n 1.11 fr,;Urt· 6. J . L :) t C,nn i ~,, W Ma 't' ":. Mal r ix.
I nn it
- - .
---.-.--.._
-
-
_____
--~_··---d
- ·------ ,t
l·I~. td
E l
) ·•
J.. ."1
= I 06
units
_ J0° units
.J
~l](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module6-230226081914-34f1f267/85/Module-6-1-lumped-and-consistent-mass-pdf-8-320.jpg)