The document lists various sources that influenced India's constitution:
- The Government of India Act (1935) influenced provisions around federalism, the governor's office, and public service commissions.
- The UK influenced aspects like parliamentary government, citizenship, lawmaking procedures, an independent judiciary, and more.
- The US influenced the preamble, fundamental rights, impeachment procedures, an independent judiciary, and the vice president's role.
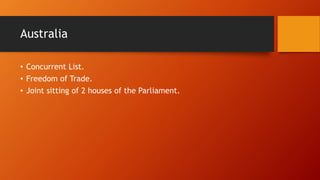
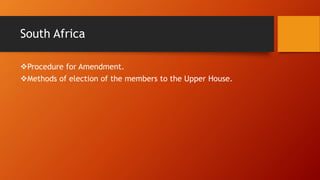
- Other countries like Ireland, Canada, Australia, Germany, South Africa, Russia, Japan, and France also contributed influences around topics like directive principles, legislative procedures, and constitutional ideals.
The constitution drew from different countries to address India's unique conditions at the time of its formation