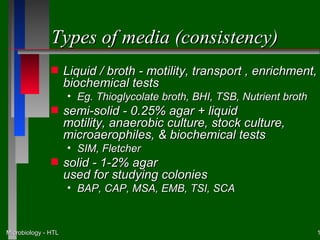
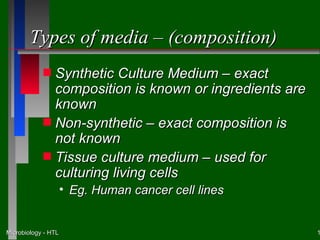
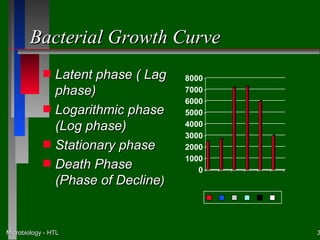
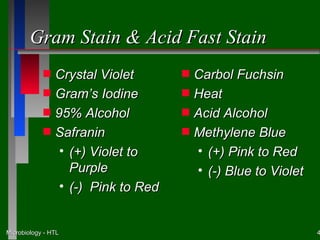
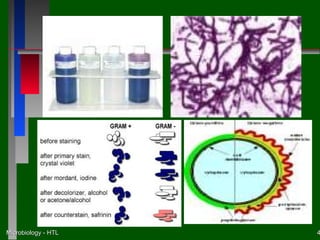
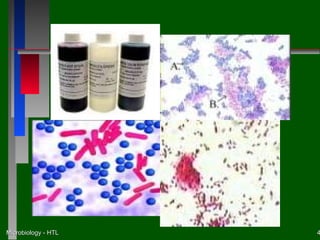
This document discusses the nutritional and environmental requirements for bacterial growth, including the need for carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and other elements. It describes different types of culture media like liquid broth, semi-solid agar, and solid agar plates and how they are used. The document also covers bacterial colony morphology, describing smooth, mucoid, and rough colony types. It discusses factors that provide a suitable growth environment for bacteria, such as oxygen levels, temperature, pH, and osmotic pressure requirements.