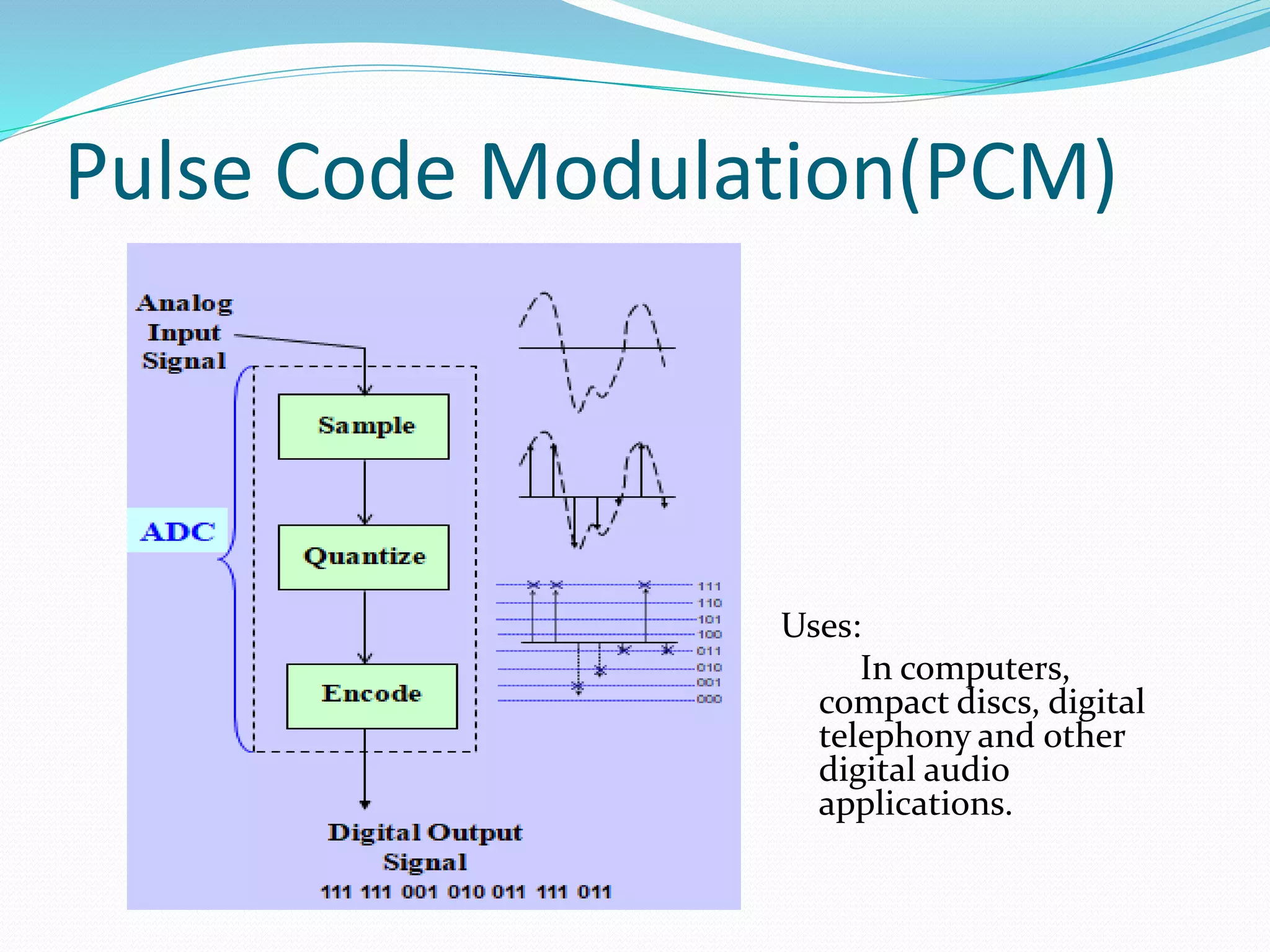
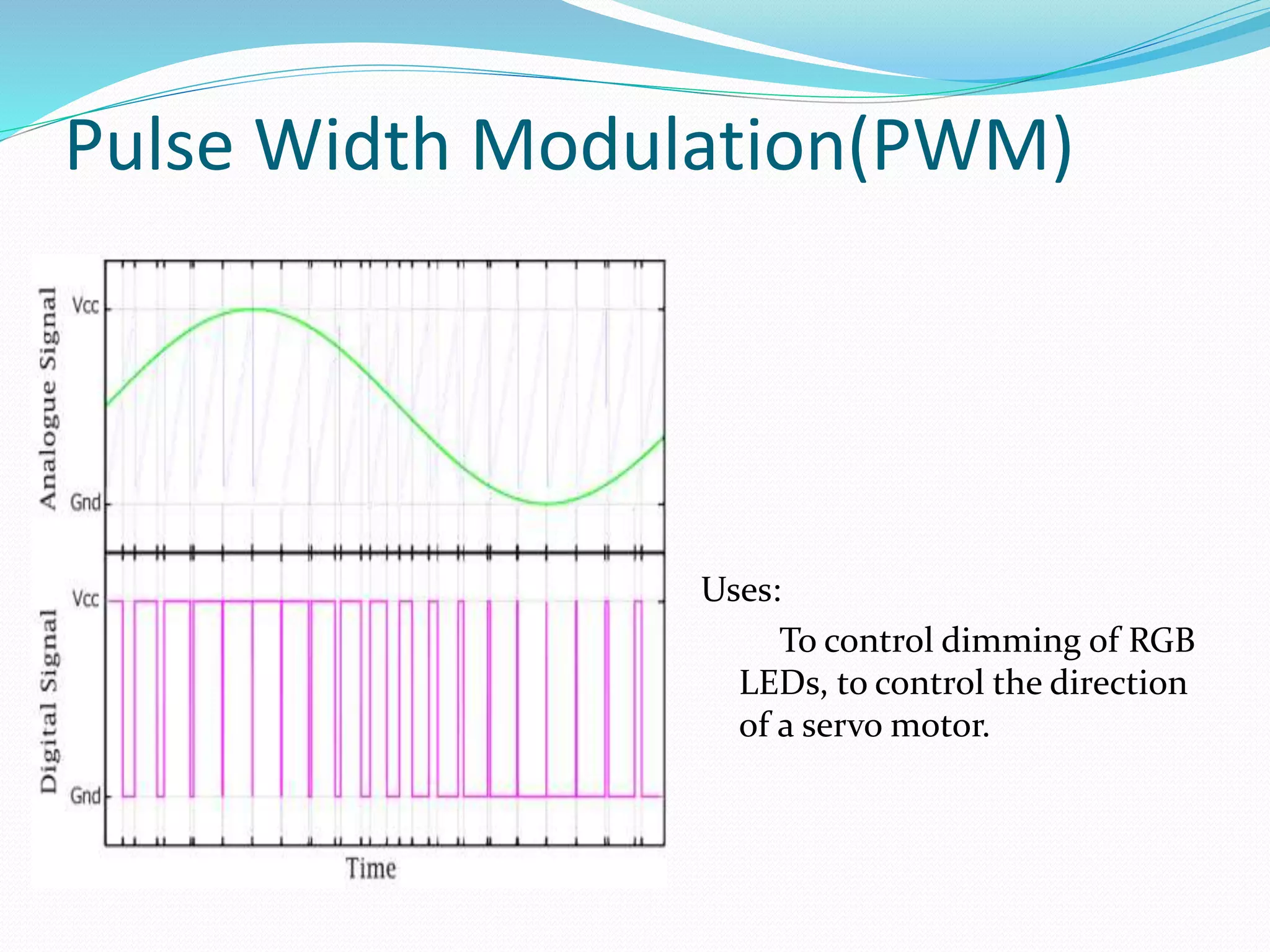
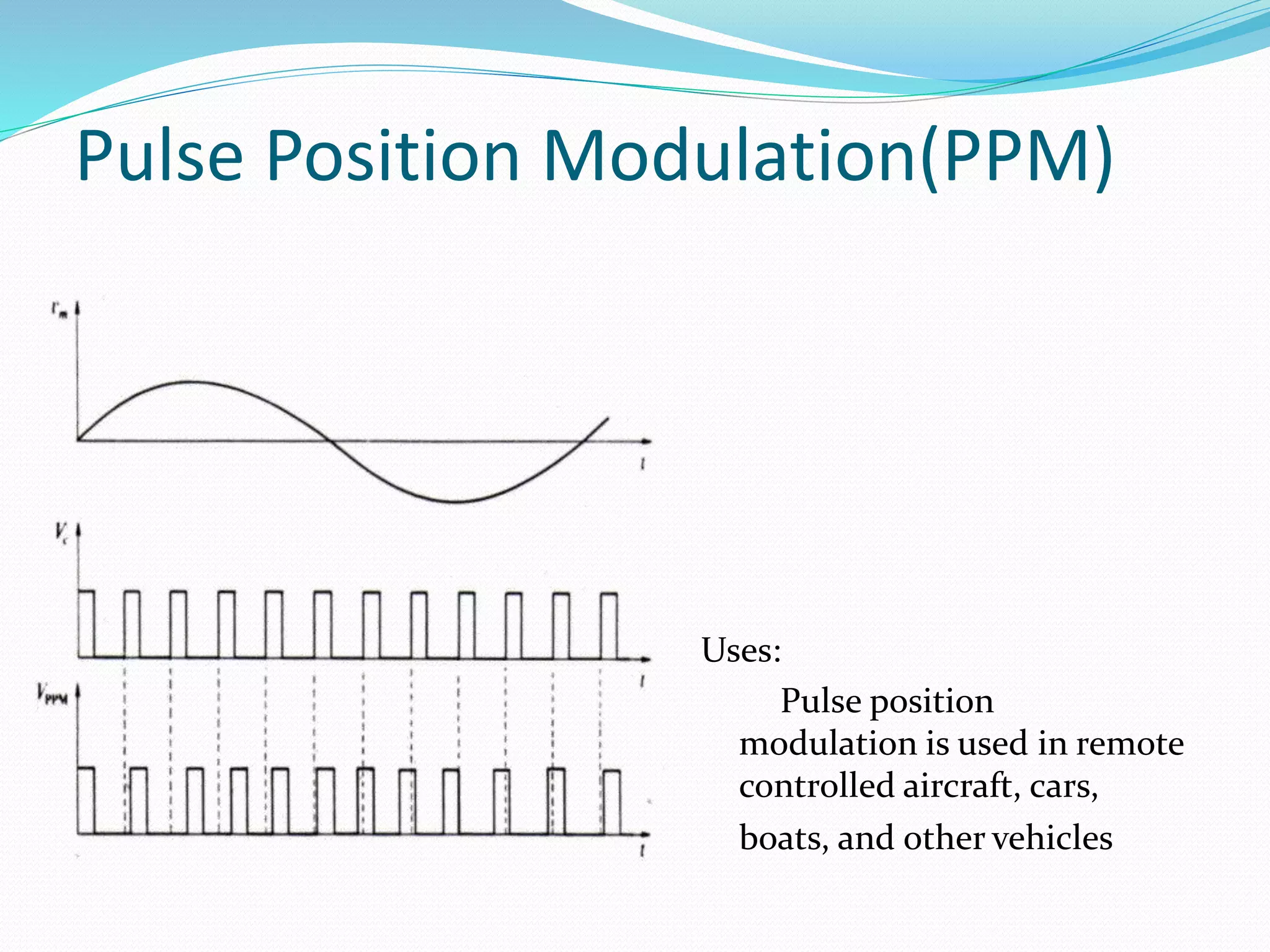
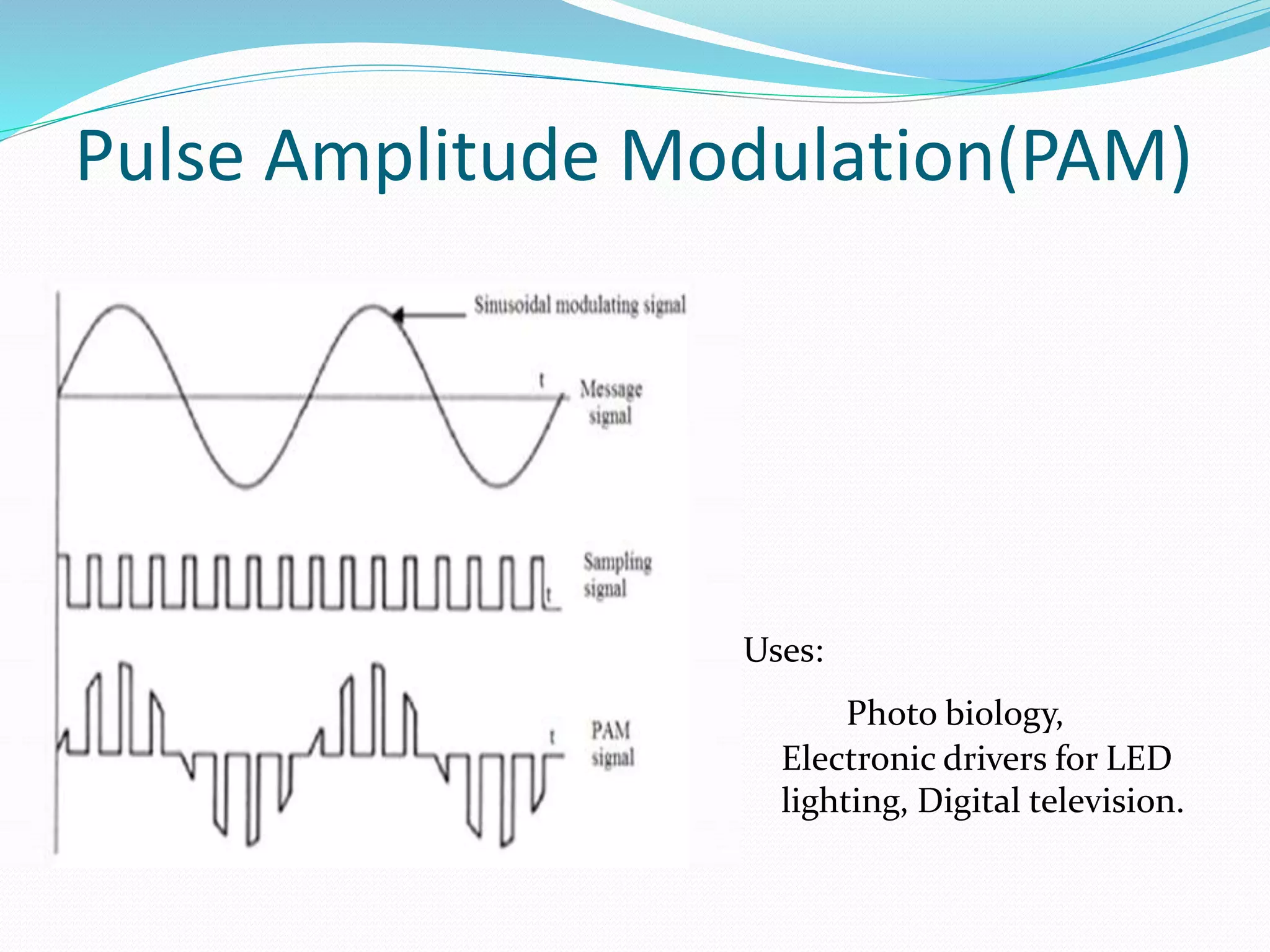
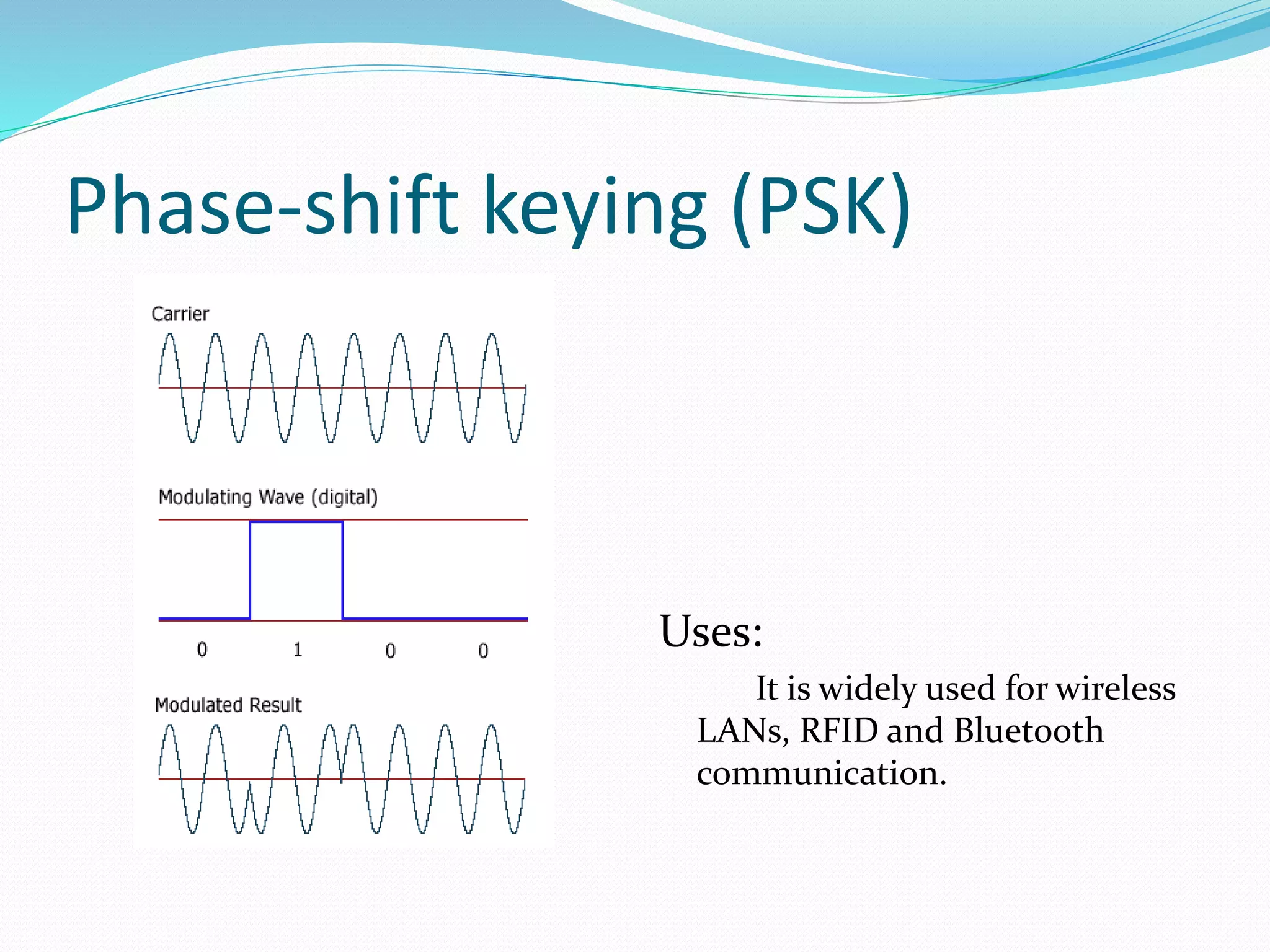
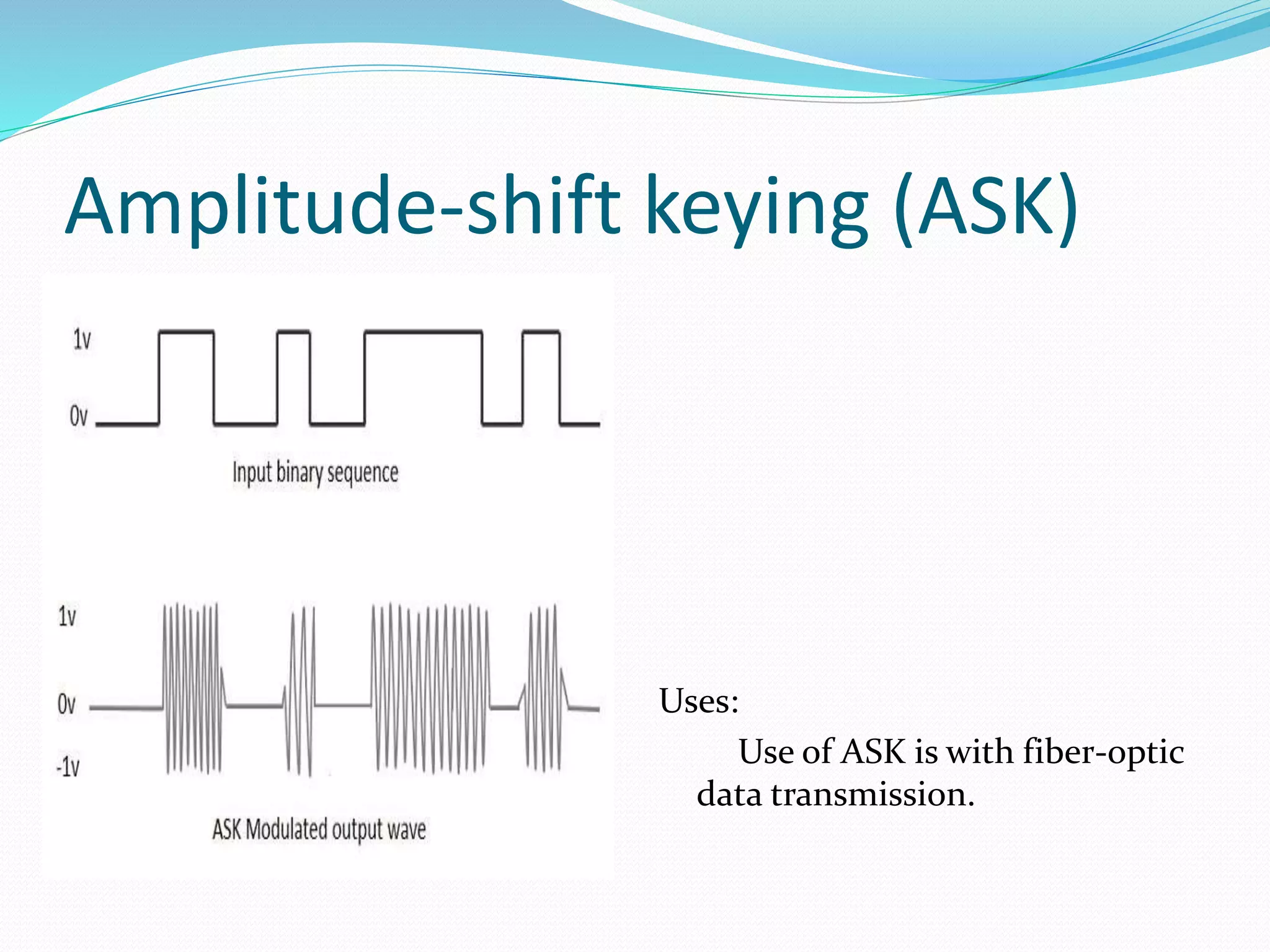
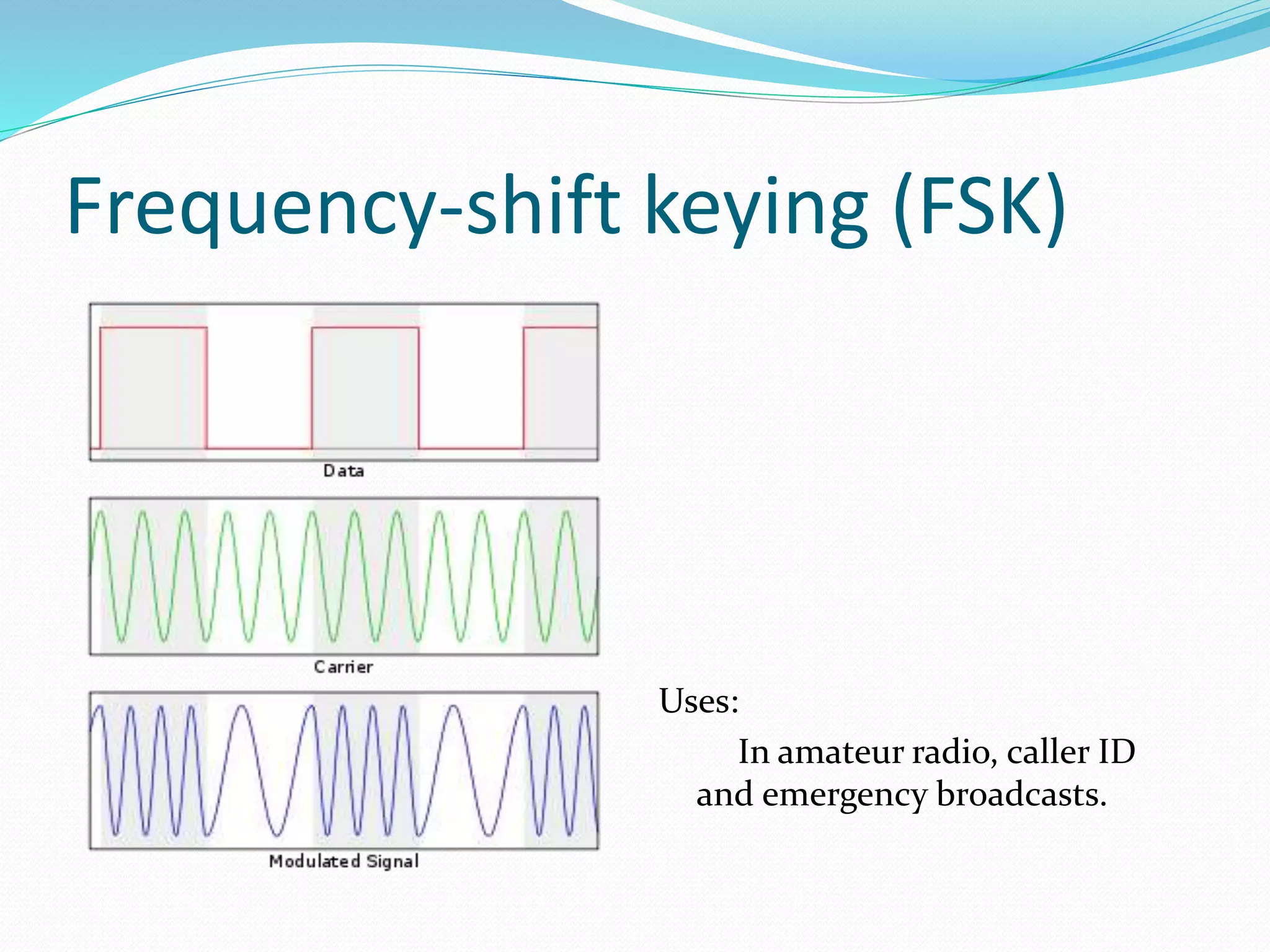
This document discusses various digital modulation techniques. It defines modulation as changing the properties of a high frequency carrier signal based on a low frequency message signal. It then explains several digital modulation methods including Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) used for digital audio, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) used to control LEDs and motors, and Phase-shift Keying (PSK) used for wireless communication. The document provides examples of common uses for each modulation technique.