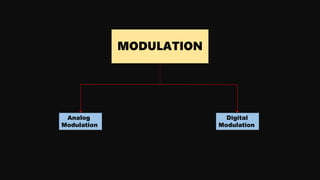
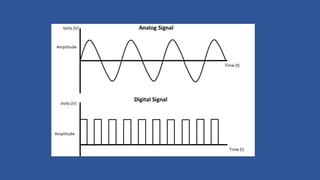
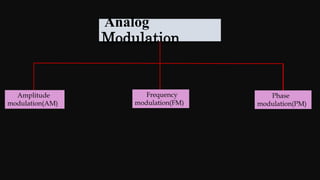
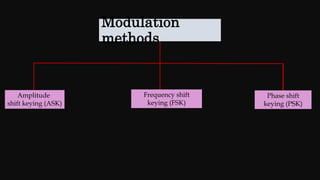
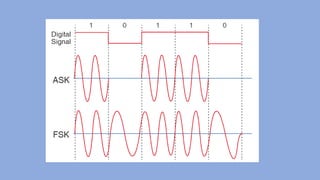
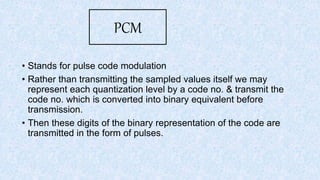
Modulation is the process of altering a carrier signal to transmit information, which is vital for sending audio signals over distances. It can be categorized into analog and digital modulation techniques, with various methods such as amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM), and pulse code modulation (PCM). Digital modulation techniques include amplitude shift keying (ASK), frequency shift keying (FSK), and phase shift keying (PSK), each using distinct approaches to represent data through variations in signals.