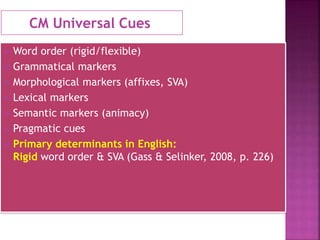
The Competition Model describes how language learners use different cues like word order, grammatical markers, and animacy to interpret sentence meanings. It involves competition among cues, with stronger or more appropriate cues determining the correct interpretation. For native language acquisition, younger children may rely on weaker cues like animacy that are replaced by stronger cues like word order as they age. For second language acquisition, learners must learn the relative importance of cues in the new language, which can interfere with cues from their first language. The model is used to study how modified input helps learners recognize and adopt the appropriate cues of the language being learned.