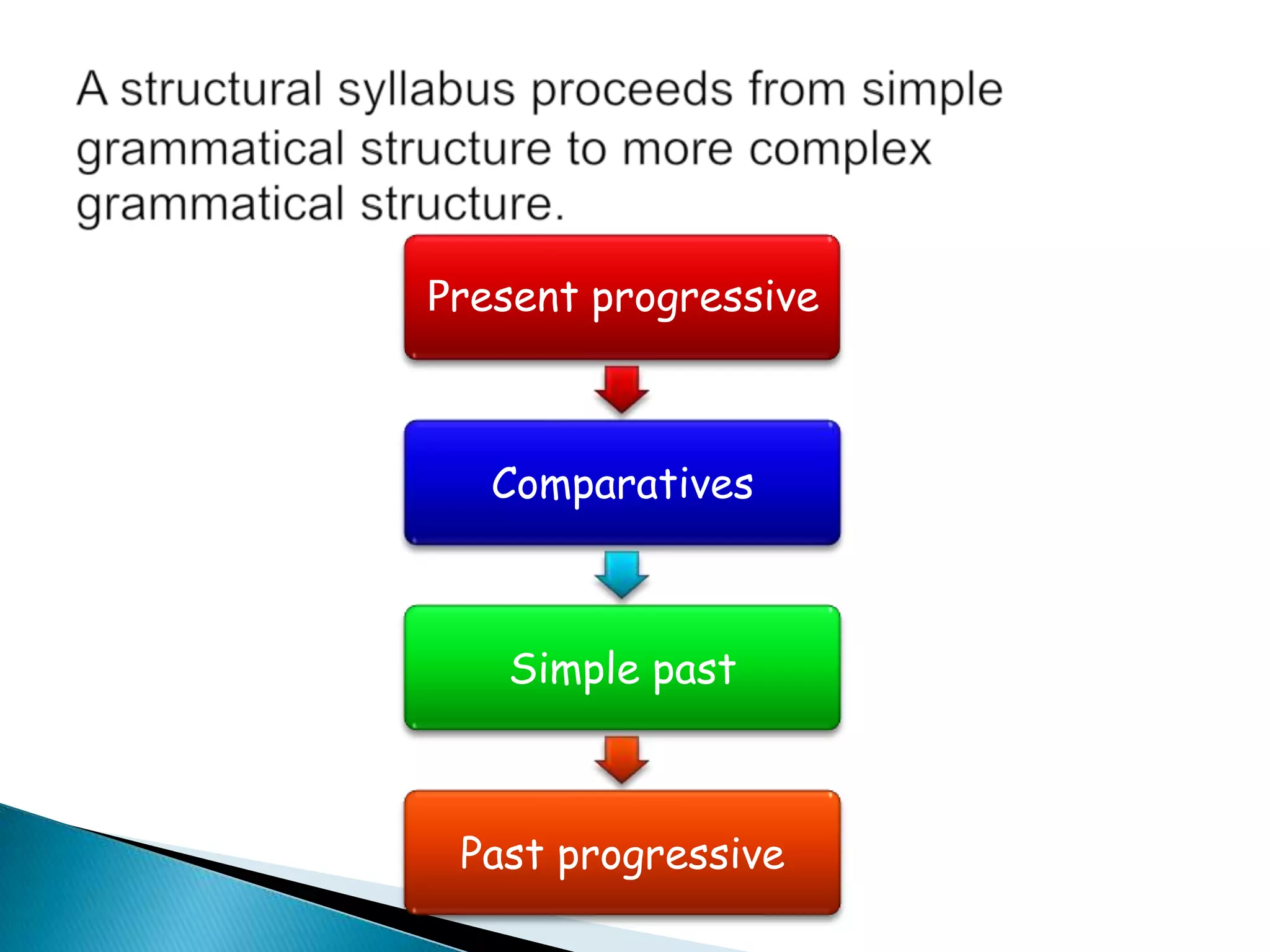
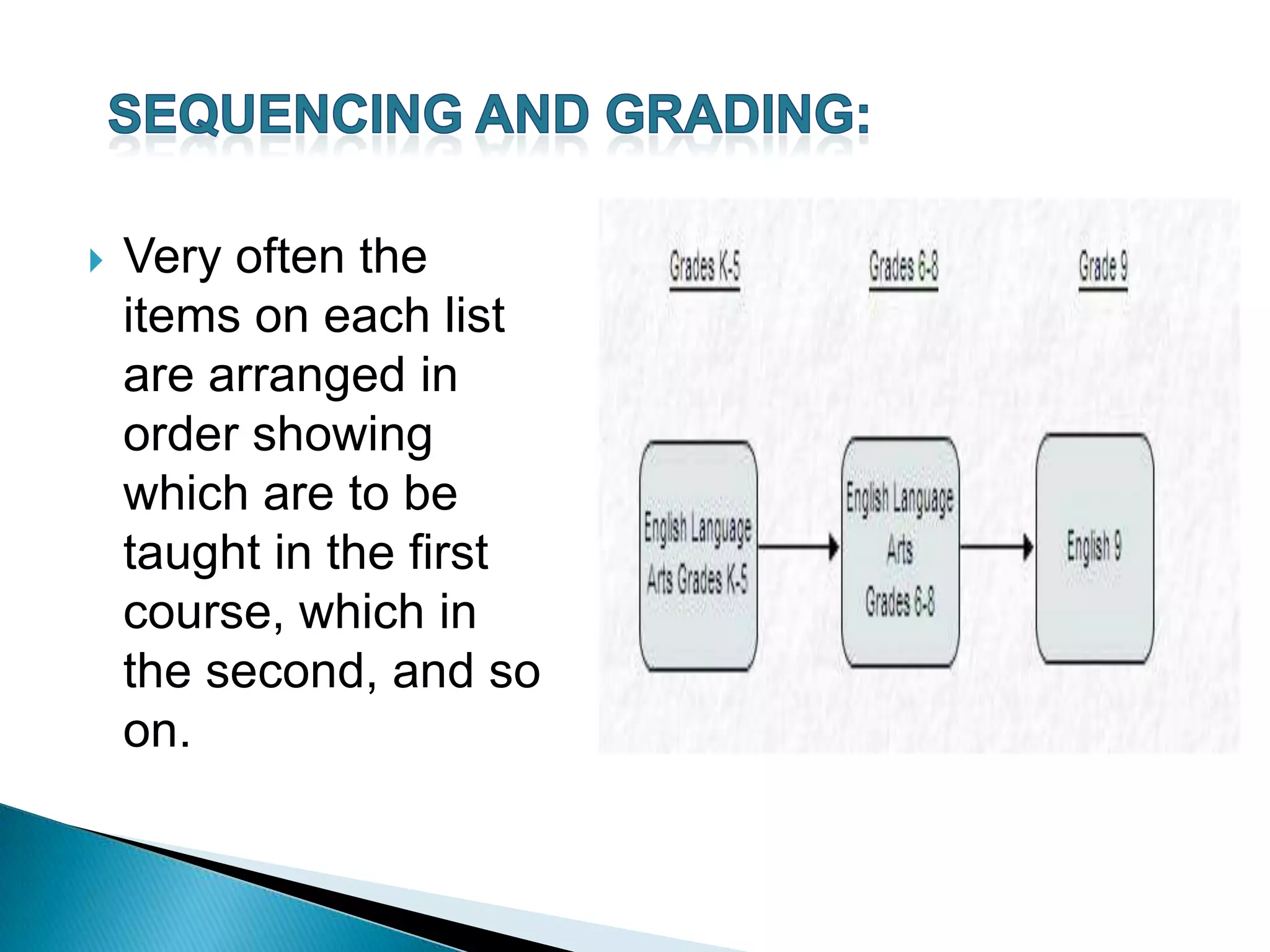
The document discusses the structural or grammatical syllabus, which organizes language learning around the mastery of grammatical structures. It presents the structural syllabus as one that teaches language rules in a step-by-step, systematic fashion, moving from simpler to more complex grammar. Adherents view language as a set of rules and believe learning means mastering these rules. The structural syllabus remains common today for its simplicity, frequency, and learnability.