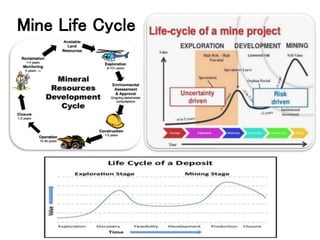
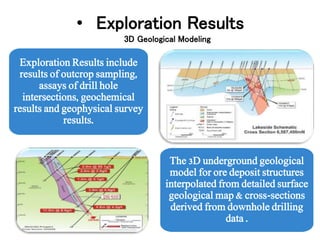
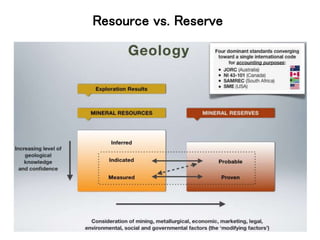
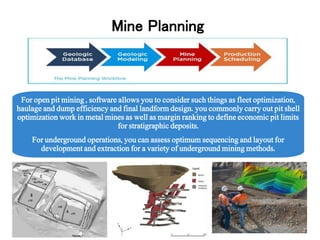
The document discusses the history and modern practices of mining. It covers the earliest records of mining from 3000 BC by Egyptians extracting gold, silver and copper. Modern mining involves prospecting, feasibility studies, extracting desired materials using surface or underground techniques, and reclaiming land after closure. Key aspects covered include exploration methods, resource and reserve estimation, adhering to mining codes, and establishing feasibility studies to evaluate project risk and define scale prior to development and operation.