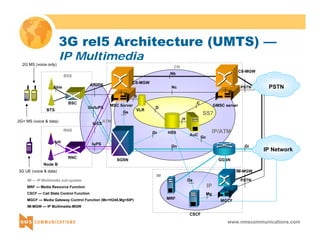
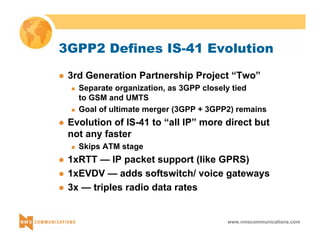
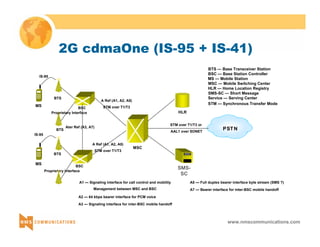
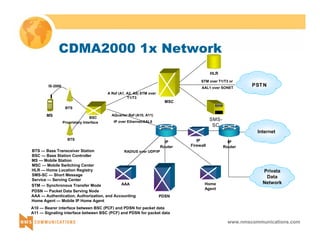
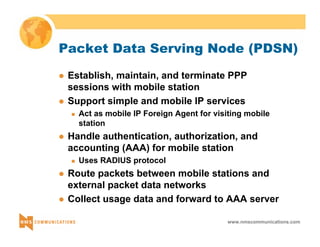
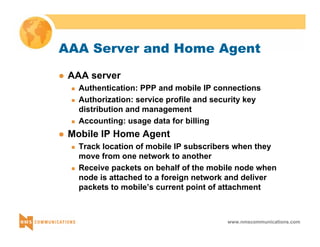
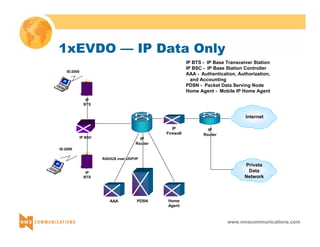
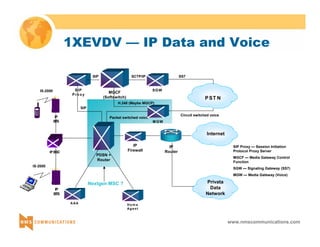
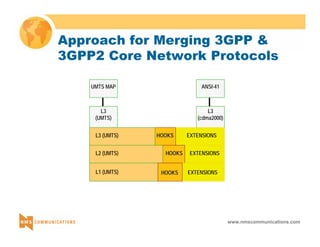
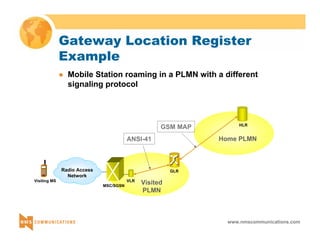
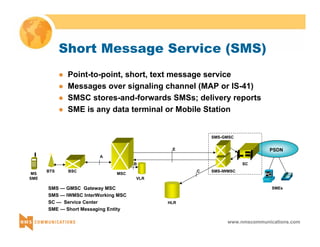
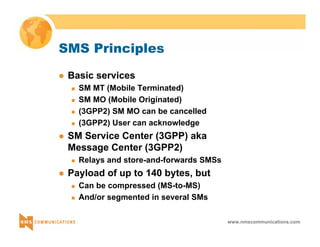
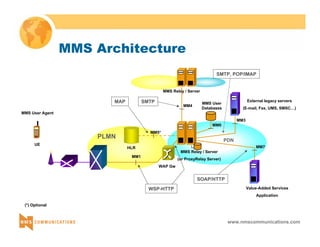
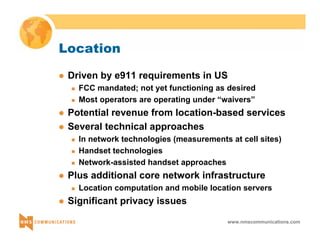
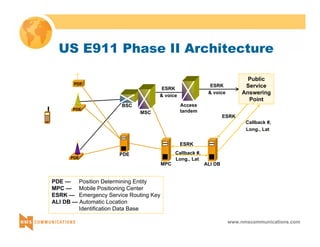
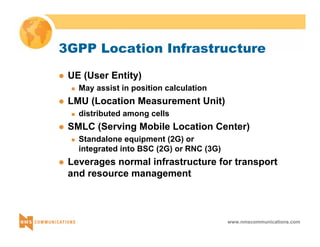
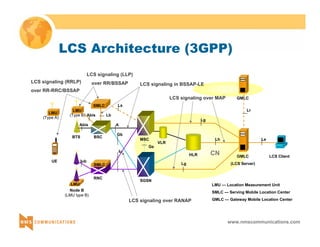
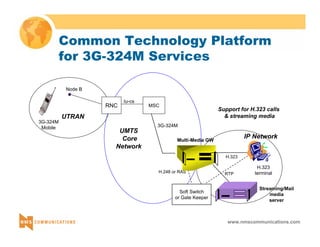
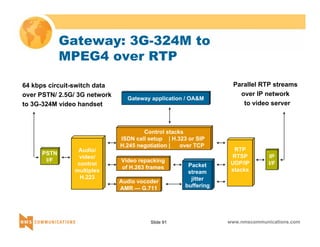
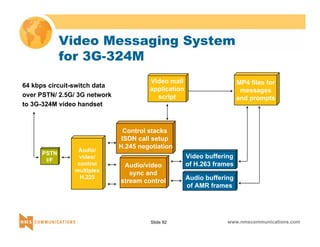
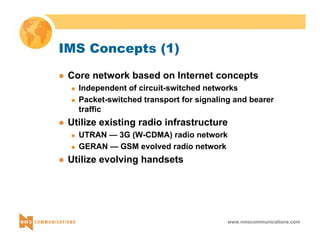
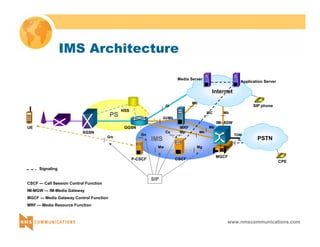
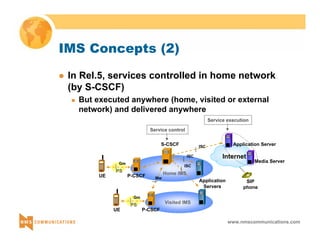
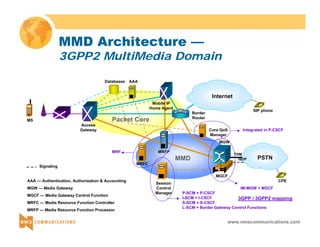
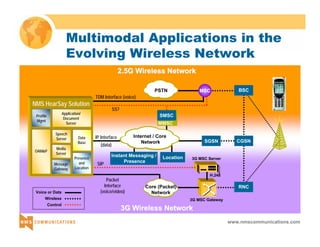
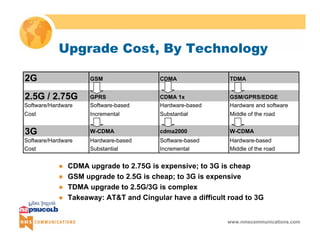
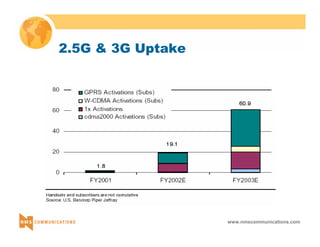
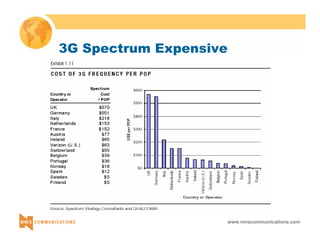
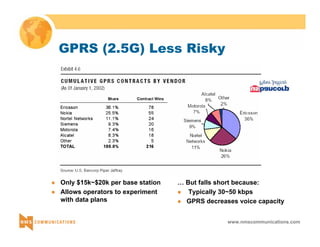
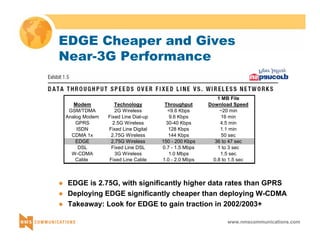
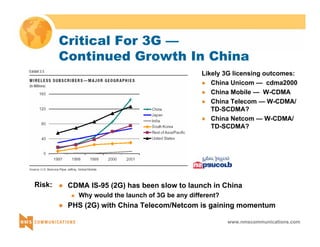
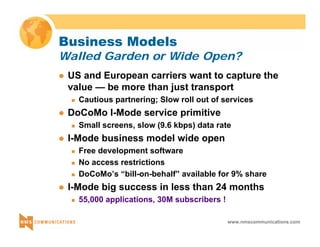
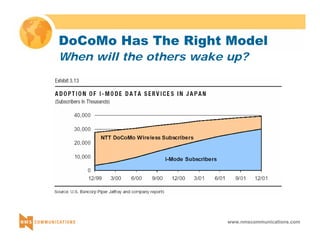
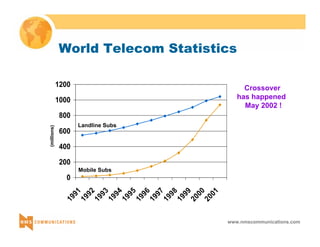
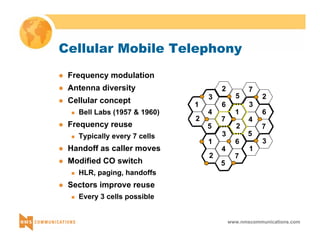
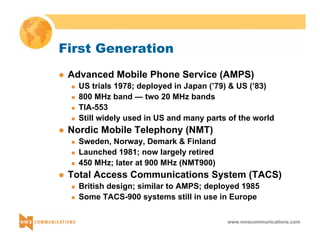
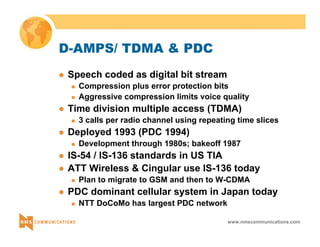
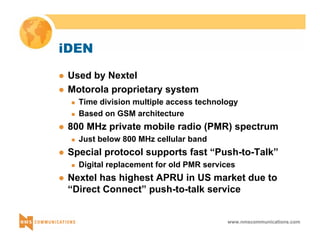
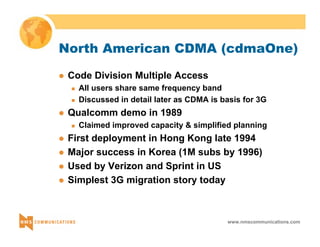
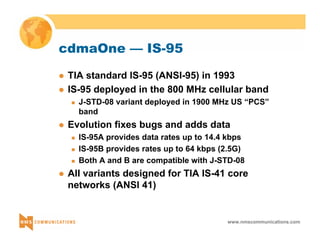
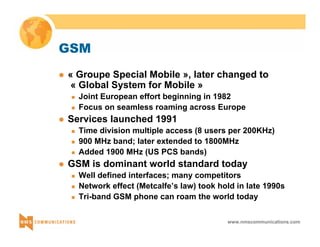
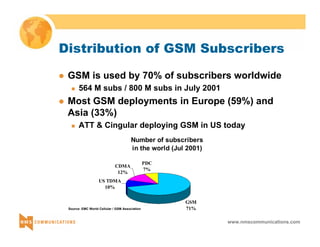
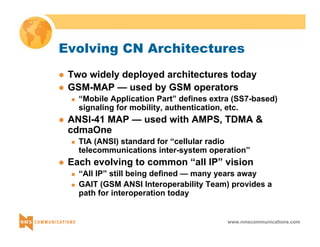
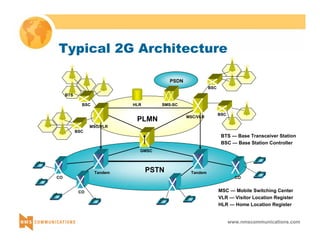
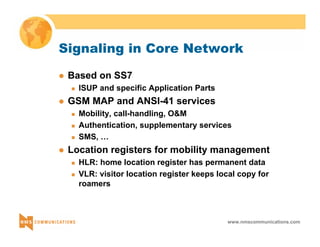
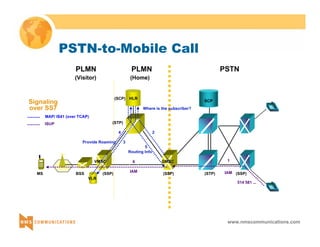
This document provides an overview of 3G mobile radio technology. It begins with a brief history of cellular wireless standards from 1G to 2G, including AMPS, TDMA, CDMA, GSM and their evolution. It then discusses evolving network architectures, focusing on the migration from GSM and ANSI-41 networks to all-IP networks. The document also outlines evolving services, applications and business models for 3G. Key topics covered include 3G standards like UMTS, CDMA2000 and TD-SCDMA, as well as spectrum bands and the challenges of global roaming.

















![TFO – Tandem Free Operation
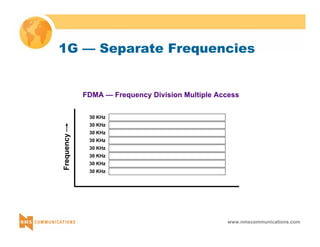
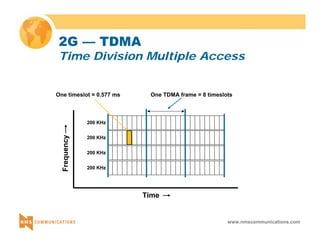
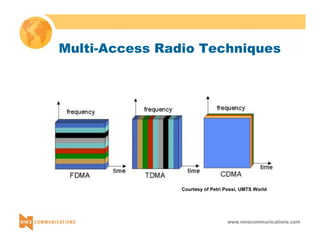
GSM Coding G.711 / 64 kb GSM Coding CD
CD
DC
PSTN*
GSM Coding [GSM Coding + TFO Sig] (2bits) + G.711 (6bits**) / 64 Kb GSM Coding CD
TF
O
www.nmscommunications.com
z No TFO : 2 unneeded transcoders in path
A
DC
z With TFO (established) : no in-path transcoder
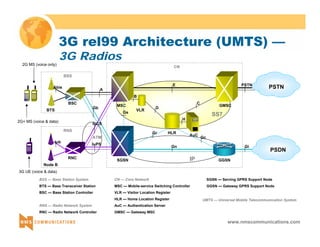
Abis
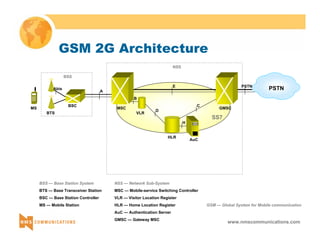
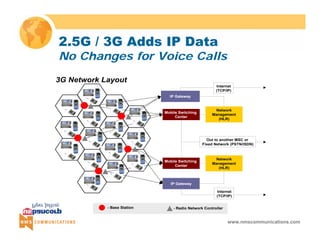
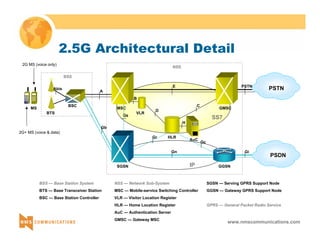
BTS BSC
TRAU
Ater
MSC MSC
TRAU
MS BSC BTS MS
A
Abis
BTS BSC
TF
O
TRAU
Ater
MSC MSC
(**) or 7 bits if Half-Rate coder is used
TRAU
MS BSC BTS MS
DC
PSTN*
(*) or TDM-based core network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3gtutorial-140910050134-phpapp01/85/3g-tutorial-46-320.jpg)



![TRAU
www.nmscommunications.com
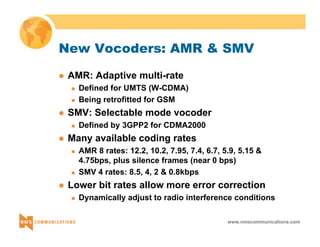
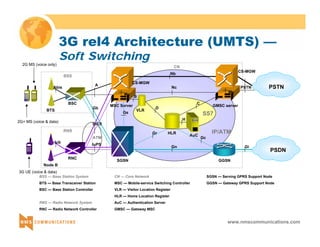
TrFO + TFO Example
z 2G handset to 3G handset: by combining TrFO and
TFO, in-path transcoders can be avoided
3G Packet
Radio Access
Network
CS-MGW
3G UE Core Network
2G PLMN
MSC Server
CS-MGW
GMSC Server
MSC
GSM Coding (TrFO) GSM Coding CD
DC
TF
O
[GSM Coding + TFO Sig] (lsb)
+ G.711 (msb) / 64 Kb TF
O
Radio Access
Network
2G MS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3gtutorial-140910050134-phpapp01/85/3g-tutorial-58-320.jpg)