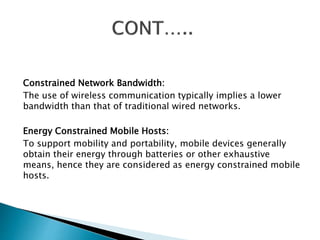
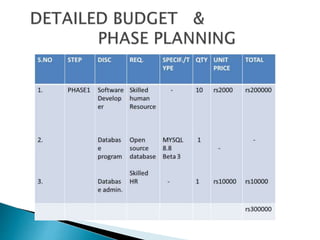
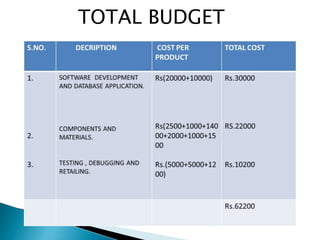
This document outlines a project to improve security and efficiency in mobile computing networks. It discusses issues like limited physical security of wireless networks and constrained bandwidth. The project will use mobile agents to distribute tasks across nodes, reducing unnecessary data transmission loads. Mobile agents can migrate between nodes as needed to complete tasks, without requiring constant client connection. This helps prevent increased workloads from network expansion. The document also lists benefits like increased productivity and flexibility from mobile computing. It proposes a key management and access control method for mobile agents to enhance security and performance efficiency.