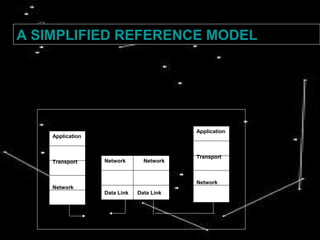
This document discusses mobile computing and its expansion through Eclipse. It defines user and device mobility and examines the constraints of wireless devices and networks compared to traditional computing. Mobile computing aims to make the internet accessible through mobile devices in a compatible, transparent, scalable, and secure way. The document outlines various mobile and wireless applications and concludes that studying mobile computing can provide insights into wireless networks, access control, and security.