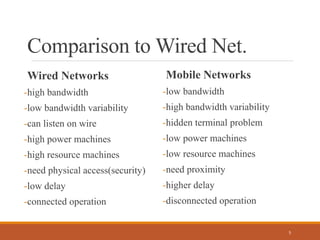
Mobile computing allows users to access network services from anywhere using portable devices. It enables connectivity even without existing infrastructure and brings computing power to more mobile scenarios. Mobile objects are software programs that can carry state between different hosts, communicating with each other through cooperation of the hosts. While mobile computing provides many applications, it also faces challenges of low bandwidth, security risks, and the wide variety of devices with different capabilities. Future advances in areas like artificial intelligence and integrated circuitry may help address current limitations and further the growth of mobile computing.