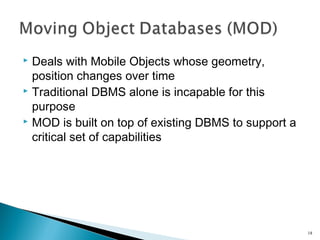
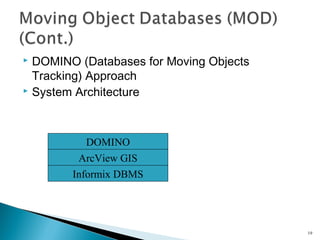
This document discusses mobile computing, including:
- Definitions of mobile computing as using portable computers while moving and accessing network services anywhere, anytime.
- Comparisons between wired and mobile networks in terms of bandwidth, connectivity, and resources.
- Types of wireless devices used for mobile computing like laptops, PDAs, and cell phones.
- Challenges of mobile computing involving disconnection, low bandwidth, and security risks.
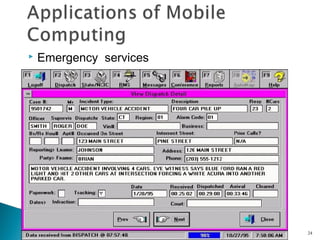
- Potential applications and the future of mobile computing with advances in areas like artificial intelligence and integrated circuitry.