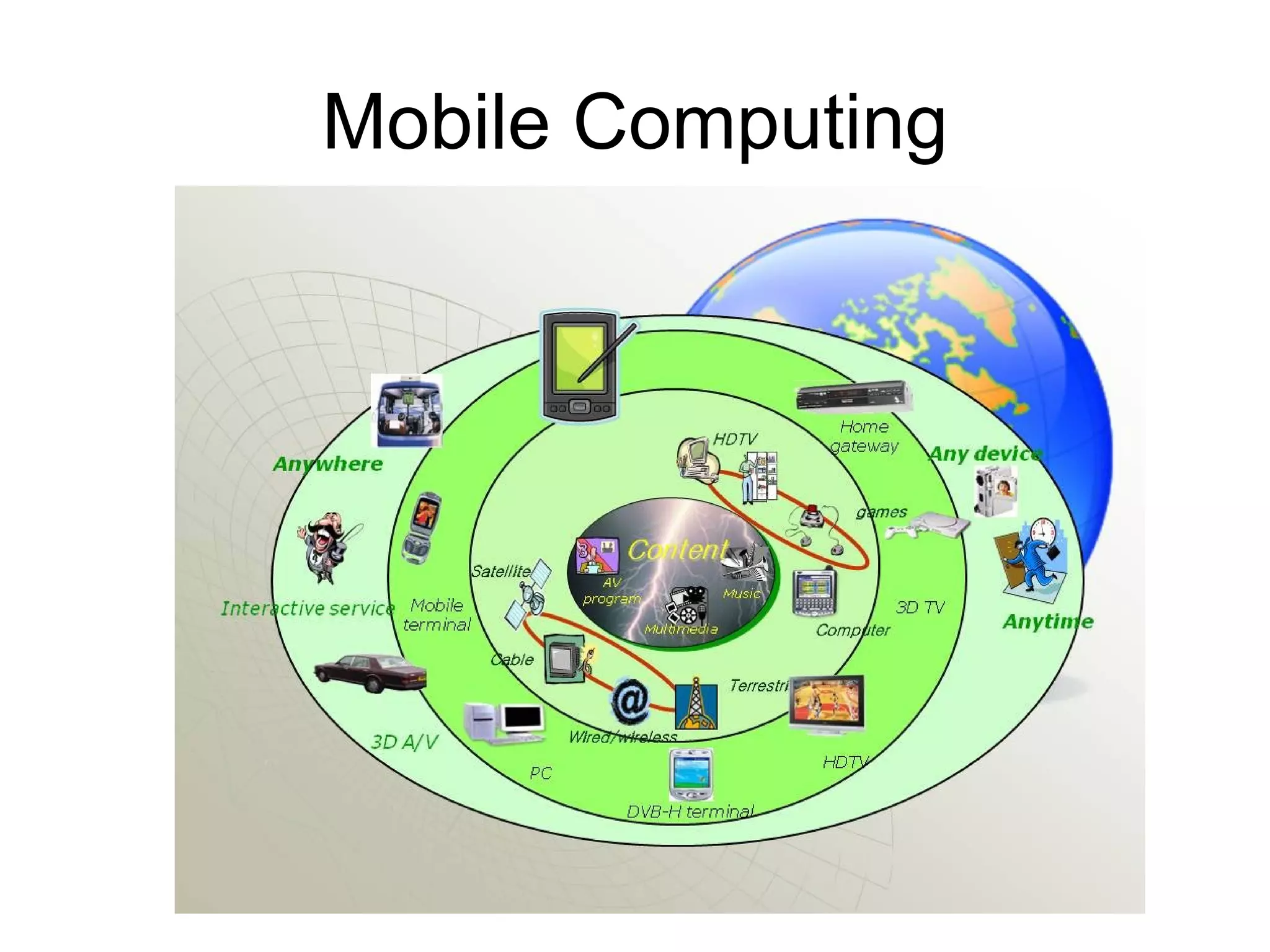
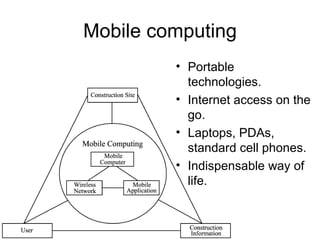
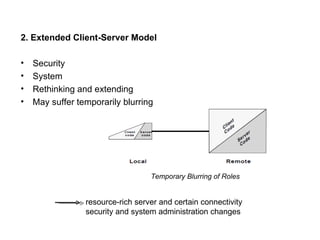
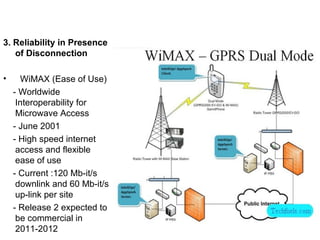
Mobile computing allows transmission of data without a fixed physical connection via a computer. It involves human-computer interaction and transportation of computing during normal usage. It aims to provide useful information to clients anywhere and anytime, altering lifestyles and work methods. Key aspects include mobile communication, mobile hardware, and mobile software running on handheld devices. Mobile computing is now an indispensable part of everyday life via technologies like WiFi, cellular broadband, and cloud computing.