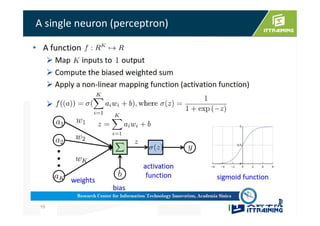
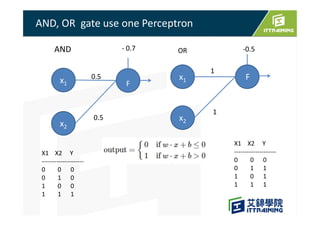
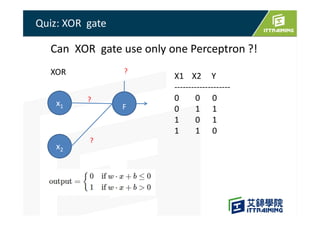
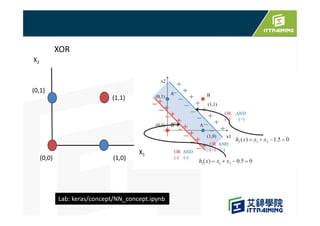
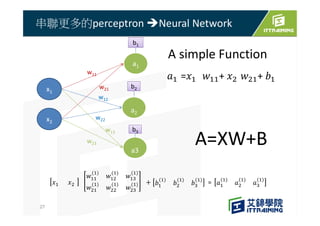
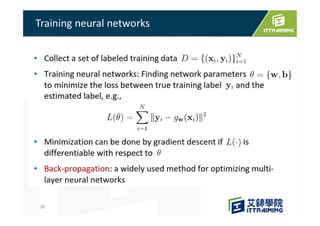
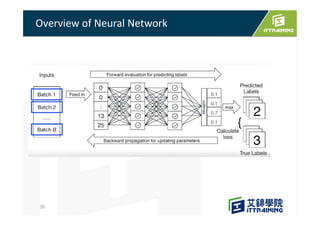
This document discusses the basics of artificial neural networks including multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs). It explains that MLPs use multiple hidden layers between the input and output layers to extract meaningful features from the data. The document also covers topics like training neural networks using backpropagation and stochastic gradient descent, the use of mini-batches to speed up training, and common activation and loss functions.