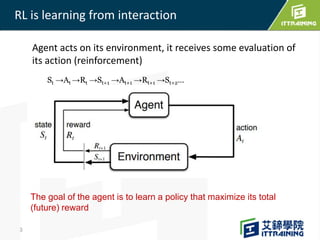
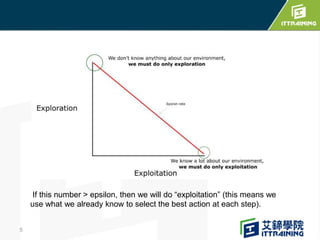
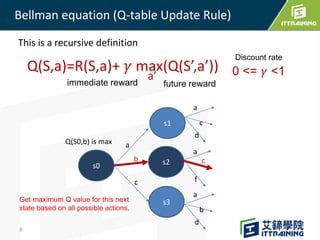
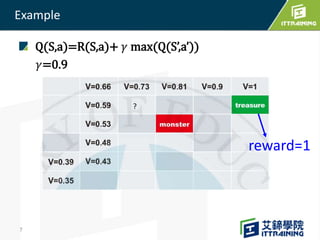
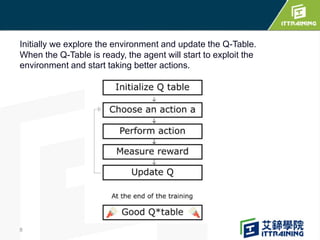
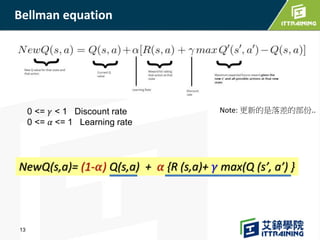
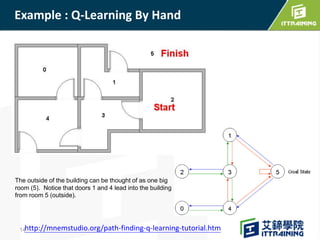
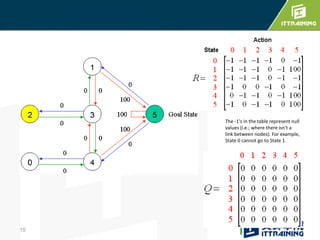
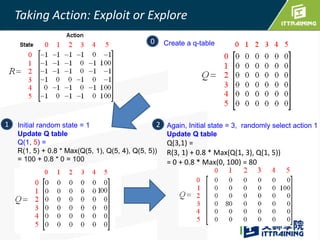
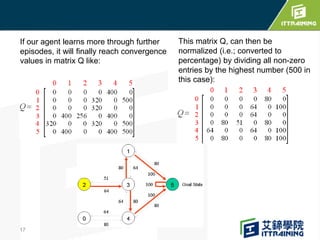
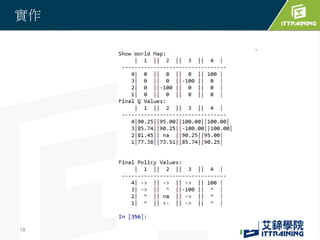
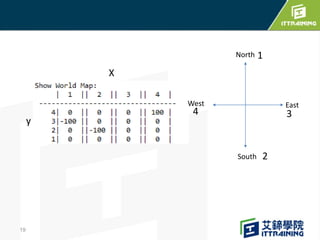
Reinforcement learning allows an agent to learn how to behave through trial-and-error interactions with an environment. The agent takes actions in a state and receives rewards, learning through experience which actions maximize total rewards. The agent learns a policy using a Q-table that represents the estimated utility of taking an action in a given state. Initially the agent explores randomly, but over time exploits what it has learned from the Q-table to select the highest-valued actions. The Q-learning algorithm iteratively updates the Q-table values using the Bellman equation to improve its estimates of the best actions.